Also
advertisement
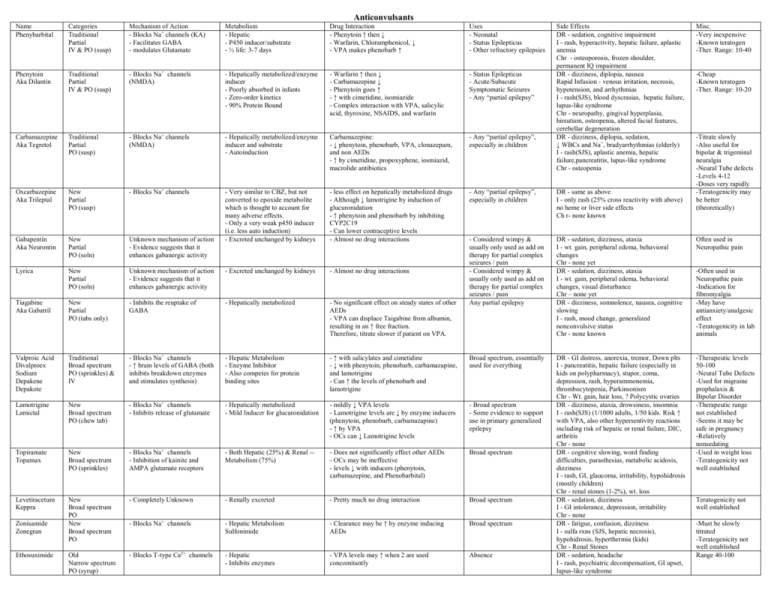
Anticonvulsants Name Phenybarbital Categories Traditional Partial IV & PO (susp) Mechanism of Action - Blocks Na+ channels (KA) - Facilitates GABA - modulates Glutamate Metabolism - Hepatic - P450 inducer/substrate - ½ life: 3-7 days Drug Interaction - Phenytoin ↑ then ↓ - Warfarin, Chloramphenicol, ↓ - VPA makes phenobarb ↑ Uses - Neonatal - Status Epilepticus - Other refractory epilepsies Phenytoin Aka Dilantin Traditional Partial IV & PO (susp) - Blocks Na+ channels (NMDA) - Hepatically metabolized/enzyme inducer - Poorly absorbed in infants - Zero-order kinetics - 90% Protein Bound - Warfarin ↑ then ↓ - Carbamazepine ↓ - Phenytoin goes ↑ - ↑ with cimetidine, isomiazide - Complex interaction with VPA, salicylic acid, thyroxine, NSAIDS, and warfarin - Status Epilepticus - Acute/Subacute Symptomatic Seizures - Any “partial epilepsy” Carbamazepine Aka Tegretol Traditional Partial PO (susp) - Blocks Na+ channels (NMDA) - Hepatically metabolized/enzyme inducer and substrate - Autoinduction Carbamazepine: - ↓ phenytoin, phenobarb, VPA, clonazepam, and non AEDs - ↑ by cimetidine, propoxyphene, iosmiazid, macrolide antibiotics - Any “partial epilepsy”, especially in children Oxcarbazepine Aka Trileptal New Partial PO (susp) - Blocks Na+ channels DR - same as above I - only rash (25% cross reactivity with above) no heme or liver side effects Ch r- none known New Partial PO (soln) Unknown mechanism of action - Evidence suggests that it enhances gabanergic activity - less effect on hepatically metabolized drugs - Although ↓ lamotrigine by induction of glucuronidation - ↑ phenytoin and phenobarb by inhibiting CYP2C19 - Can lower contraceptive levels - Almost no drug interactions - Any “partial epilepsy”, especially in children Gabapentin Aka Neurontin - Very similar to CBZ, but not converted to epoxide metabolite which is thought to account for many adverse effects. - Only a very weak p450 inducer (i.e. less auto induction) - Excreted unchanged by kidneys New Partial PO (soln) Unknown mechanism of action - Evidence suggests that it enhances gabanergic activity - Excreted unchanged by kidneys - Almost no drug interactions Tiagabine Aka Gabatril New Partial PO (tabs only) - Inhibits the reuptake of GABA - Hepatically metabolized - No significant effect on steady states of other AEDs - VPA can displace Taigabine from albumin, resulting in an ↑ free fraction. Therefore, titrate slower if patient on VPA. DR - sedation, dizziness, ataxia I - wt. gain, peripheral edema, behavioral changes Chr - none yet DR - sedation, dizziness, ataxia I - wt. gain, peripheral edema, behavioral changes, visual disturbance Chr – none yet DR - dizziness, somnolence, nausea, cognitive slowing I - rash, mood change, generalized nonconvulsive status Chr - none known Often used in Neuropathic pain Lyrica - Considered wimpy & usually only used as add on therapy for partial complex seizures / pain - Considered wimpy & usually only used as add on therapy for partial complex seizures / pain Any partial epilepsy Valproic Acid Divalproex Sodium Depakene Depakote Traditional Broad spectrum PO (sprinkles) & IV - Blocks Na+ channels - ↑ brain levels of GABA (both inhibits breakdown enzymes and stimulates synthesis) - Hepatic Metabolism - Enzyme Inhibitor - Also competes for protein binding sites - ↑ with salicylates and cimetidine - ↓ with phenytoin, phenobarb, carbamazapine, and lamotrigine - Can ↑ the levels of phenobarb and lamotrigine Broad spectrum, essentially used for everything Lamotrigine Lamictal New Broad spectrum PO (chew tab) - Blocks Na+ channels - Inhibits release of glutamate - Hepatically metabolized - Mild Inducer for glucuronidation - mildly ↓ VPA levels - Lamotrigine levels are ↓ by enzyme inducers (phenytoin, phenobarb, carbamazapine) - ↑ by VPA - OCs can ↓ Lamotrigine levels - Broad spectrum - Some evidence to support use in primary generalized epilepsy Topiramate Topamax New Broad spectrum PO (sprinkles) - Blocks Na+ channels - Inhibition of kainite and AMPA glutamate receptors - Both Hepatic (25%) & Renal -Metabolism (75%) - Does not significantly effect other AEDs - OCs may be ineffective - levels ↓ with inducers (phenytoin, carbamazepine, and Phenobarbital) Broad spectrum -Therapeutic levels 50-100 -Neural Tube Defects -Used for migraine prophalaxis & Bipolar Disorder -Therapeutic range not established -Seems it may be safe in pregnancy -Relatively nonsedating -Used in weight loss -Teratogenicity not well established Levetiracetum Keppra New Broad spectrum PO New Broad spectrum PO - Completely Unknown - Renally excreted - Pretty much no drug interaction Broad spectrum - Blocks Na+ channels - Hepatic Metabolism Sulfonimide - Clearance may be ↑ by enzyme inducing AEDs Broad spectrum Old Narrow spectrum PO (syrup) - Blocks T-type Ca2+ channels - Hepatic - Inhibits enzymes - VPA levels may ↑ when 2 are used concomitantly Absence DR - GI distress, anorexia, tremor, Down plts I - pancreatitis, hepatic failure (especially in kids on polypharmacy), stupor, coma, depression, rash, hyperammonemia, thrombocytopenia, Parkinsonism Chr - Wt. gain, hair loss, ? Polycystic ovaries DR - dizziness, ataxia, drowsiness, insomnia I - rash(SJS) (1/1000 adults, 1/50 kids. Risk ↑ with VPA, also other hypersentivity reactions including risk of hepatic or renal failure, DIC, arthritis Chr - none DR - cognitive slowing, word finding difficulties, parasthesias, metabolic acidosis, dizziness I - rash, GI, glaucoma, irritability, hypohidrosis (mostly children) Chr - renal stones (1-2%), wt. loss DR - sedation, dizziness I - GI intolerance, depression, irritability Chr - none DR - fatigue, confusion, dizziness I - sulfa rxns (SJS, hepatic necrosis), hypohidrosis, hyperthermia (kids) Chr - Renal Stones DR - sedation, headache I - rash, psychiatric decompensation, GI upset, lupus-like syndrome Zonisamide Zonegran Ethosuximide Side Effects DR - sedation, cognitive impairment I - rash, hyperactivity, hepatic failure, aplastic anemia Chr - osteoporosis, frozen shoulder, permanent IQ impairment DR - dizziness, diplopia, nausea Rapid Infusion - venous irritation, necrosis, hypotension, and arrhythmias I - rash(SJS), blood dyscrasias, hepatic failure, lupus-like syndrome Chr - neuropathy, gingival hyperplasia, hirsutism, osteopenia, altered facial features, cerebellar degeneration DR - dizziness, diplopia, sedation, ↓ WBCs and Na+, bradyarrhythmias (elderly) I - rash(SJS), aplastic anemia, hepatic failure,pancreatitis, lupus-like syndrome Chr - osteopenia Misc. -Very inexpensive -Known teratogen -Ther. Range: 10-40 -Cheap -Known teratogen -Ther. Range: 10-20 -Titrate slowly -Also useful for bipolar & trigeminal neuralgia -Neural Tube defects -Levels 4-12 -Doses very rapidly -Teratogenicity may be better (theoretically) -Often used in Neuropathic pain -Indication for fibromyalgia -May have antianxiety/analgesic effect -Teratogenicity in lab animals Teratogenicity not well established -Must be slowly titrated -Teratogenicity not well established Range 40-100








