Amino Acid Sequences Evolution
advertisement

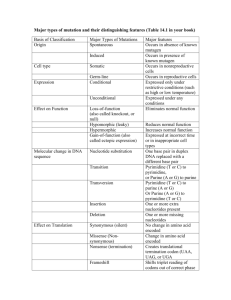
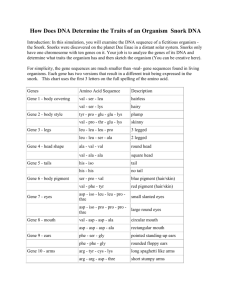
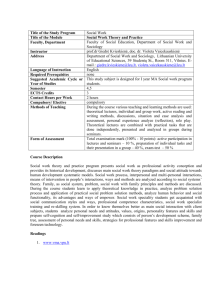
NAME:________________________________________ Amino Acid Sequences: Evidence of Evolution Scientists have gathered a variety of evidence to support the theory of evolution: fossil record, radioactive dating, coevolution, embryonic similarities, structural similarities, and biochemical similarities. Similarities in structure and biochemistry provide support for Darwin’s conclusion: living organisms evolved through gradual modification of earlier forms, that is, decent from a common ancestor. One biochemical similarity that can be studied is the similarity in amino acid sequences in homologous proteins of different organisms. The greater the similarity in amino acid sequences of homologous proteins the closer the evolutionary relationship; the greater the differences the more distant the relationship. You will study two proteins in vertebrates: hemoglobin and cytochrome c. Hemoglobin is the oxygen carrying molecules founds in red blood cells; it is composed of several long chains. The sequence used in this lab is a portion of a chain consisting of 146 amino acids. Cytochrome c is a respiratory enzyme found in mitochondria consisting of 104 amino acids. Part I: Examine Figure I, which compares portions of hemoglobin molecules in humans and five other vertebrae animals. Hemoglobin, a protein composed of several long chains of amino acids, is the oxygen carrying molecule in red blood cells. Only a portion of the chain is shown in Figure I. 1) Highlight the differences between humans and each of the other organisms; remember to compare humans versus the other species; do not compare adjacent rows Figure I 87 Human THR Chimp THR Gorilla THR Rhesus GLN Horse ALA Kangaroo LYS Human Chimp Gorilla Rhesus Horse Kangaroo 88 LEU LEU LEU LEU LEU LEU 89 SER SER SER SER SER SER 90 GLU GLU GLU GLU GLU GLU 91 LEU LEU LEU LEU LEU LEU 92 HIS HIS HIS HIS HIS HIS 93 CYS CYS CYS CYS CYS CYS 94 ASP ASP ASP ASP ASP ASP 95 LYS LYS LYS LYS LYS LYS 96 LEU LEU LEU LEU LEU LEU 97 HIS HIS HIS HIS HIS HIS 98 VAL VAL VAL VAL VAL VAL 99 ASP ASP ASP ASP ASP ASP 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 ASN ASN ASN ASN ASN ASN PHE PHE PHE PHE PHE PHE ARG ARG LYS LYS ARG LYS LEU LEU LEU LEU LEU LEU LEU LEU LEU LEU LEU LEU GLY GLY GLY GLY GLY GLY ASN ASN ASN ASN ASN ASN VAL VAL VAL VAL VAL ILE LEU LEU LEU LEU LEU ILE VAL VAL VAL VAL ALA VAL CYS CYS CYS CYS LEU ILE VAL VAL VAL VAL VAL CYS LEU LEU LEU LEU VAL LEU ALA ALA ALA ALA ALA ALA HIS HIS HIS HIS ARG GLU 2) Compile these amino acid differences in Table below. Table I: amino acid difference between humans/species pairs Organisms Number of Amino Acid Differences Human/ chimpanzee 0 Human/ gorilla 1 Human/ rhesus monkey Human/ horse Human/ kangaroo Number Positions in which they vary 104 100 PRO PRO PRO PRO PRO PRO 101 GLU GLU GLU GLU GLU GLU NAME:________________________________________ Questions: 1) If the amino acid sequences in homologous proteins of two organisms are similar, what can you conclude about the DNA of the two organisms? 2) In the human and gorillas there is a difference of only one amino acid in one chain of hemoglobin. Give a possible explanation for this. 3) Using the hemoglobin data you collected, which organisms appear most closely related to humans? Which appear to be least related? Explain you answers. Most Closely: How do you know? Least Closely: How do you know? Part II: Another commonly studied protein is cytochrome c. This protein, consisting of 104 amino acids, is located in the mitochondria of cells, where it functions as a respiratory enzyme. Examine Table 2. Using cytochrome c as a standard, the amino acid differences between humans and other organisms are shown. Table 2 Species Pairings Human-chimpanzee Human-fruit fly Human-horse Human-pigeon Human-rattlesnake Human-red bread mold Human-rhesus monkey Human-screwworm fly Human-snapping turtle Human-tuna Human-wheat Number of Difference 0 29 12 12 14 48 1 27 15 21 43 NAME:________________________________________ Questions: 1) Using the data in Table 2 construct a bar graph below to illustrate amino acid differences between humans and other organisms. 2) Name the pair of organisms that appear to be equally related to humans on the basis of cytochrome c similarity. ___________________________________________________________________________ Part III: Now we will be examining and comparing the cytochrome c in fruit flies. Below, in Table 3, the fruit fly is used as the standard in comparing the amino acid differences in several organisms. Use the data to construct a bar graph to illustrate the amino acid differences between fruit flies and other organisms: Table 3 Species Pairing Fruit fly- dogfish shark Fruit fly-pigeon Fruit fly-screwworm fly Fruit fly-silkworm moth Fruit fly-tobacco hornworm mother Fruit fly-wheat Number of Differences 26 25 2 15 14 47 NAME:________________________________________ Questions: 1) Use the data to construct a bar graph belpw to illustrate the amino acid differences between fruit flies and other organisms. 2) Agree or disagree with the following statement and give reasons to support your answer. “Fruit Flies appear to be more closely related to silkworm moths than they are screwworm flies” 3) It is generally accepted that the fewer differences found in the amino acid sequences of homologous proteins the less time since the species diverged from the common ancestor. Biologists believe that humans, chimpanzees and gorillas diverged from common ancestor only a few million years ago (a short time in evolutionary history). Use your data to explain this statement. 4) If the amino acid sequences in the proteins of two organisms are similar, why will their DNA also be similar?