Sec 9.4
advertisement

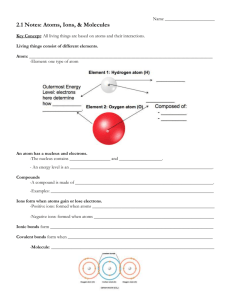
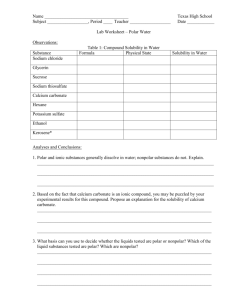
Unit 9 – Solution Chemistry Chem 11 Sec 9.4 Polar and Nonpolar Solvents Copy the table, pg 205 #17 Look at the common solvents on pg 204 and label them as either polar or nonpolar Solvent Polar or nonpolar Water Methanol Ethanol Benzene Solvent Polar or nonpolar Ethoxyethane Acetone Acetic acid Chloroform Solvent Polar or nonpolar Carbon tetrachloride Heptane Liquid ammonia After completing many experiments concerned with MIXING polar and nonpolar solvents with polar and nonpolar solutes points to the following conclusion Polar or Ionic solutes dissolves in polar solvents Nonpolar solutes dissolves in nonpolar solvents LIKE DISSOLVES LIKE Here is the “short” reason why… Polar and ionic solutes have strong bonds holding the solid together. Nonpolar solvents have weak London forces and can not exert enough energy to over come the strong bonds. Only polar solvents have sufficient attraction to the solute to be able to “pull” the solute out of the crystal and into the solution. Therefore polar solvents can dissolve polar solutes Nonpolar species do not possess positive and negative ends. Therefore there is no attraction to polar or ionic species. Only nonpolar solvents can attract nonpolar solutes, because they both have weak London forces. Therefore nonpolar solvents can dissolve nonpolar solutes http://www.chem.iastate.edu/group/Greenbowe/sections/projectfolder/flashfiles/thermochem/solutionS alt.html Unit 9 – Solution Chemistry Chem 11 Sec 9.4 Polar and Nonpolar Solvents Look at the common solvents on pg. 204 and label them as either polar or nonpolar Solvent Polar or nonpolar Solvent Polar or nonpolar Solvent Water Ethoxyethane Carbon tetrachloride Methanol Ethanol Benzene Acetone Acetic acid Chloroform Heptane Liquid ammonia Polar or nonpolar After completing many experiments concerned with MIXING polar and nonpolar solvents with polar and nonpolar solutes points to the following conclusion ________ or ________ solutes dissolves in ________________ ____________ solutes dissolves in ________________________ Here is the “short” reason why… ________ and ________solutes have ________ bonds holding the solid together. ____________ solvents have _______________________and cannot exert enough energy to over come the strong bonds. Only ________ solvents have ____________ attraction to the solute to be able to “pull” the solute out of the crystal and into the solution. Therefore ________________can dissolve ________________. Nonpolar species ____ ____ possess ________and ________ ends. Therefore there is ____ __________to polar or ionic species. Only ________ solvents can attract ________ solutes, because they ________have _______ ____________ _____________. Therefore ________________can dissolve ________________. Unit 9 – Solution Chemistry Chem 11 Sec 9.4 How to distinguish the MOST IMPORTANT BONDS or FORCES in a substance 1. IONIC bond – is there a metal and a non-metal 2. COVALENT bond – 2 non metals 3. HYDROGEN bonds – look for an H bonded to an O, F or N 4. DIPOLE – DIPOLE force – asymmetric molecule; there will be a electronegativity difference 5. LONDON force – present in all substances Read page 204-206 HW pg 207 # 18-22, 23-27