b. matching
advertisement

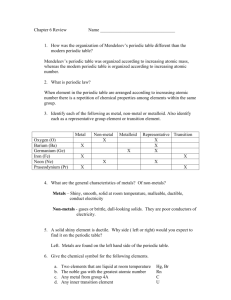
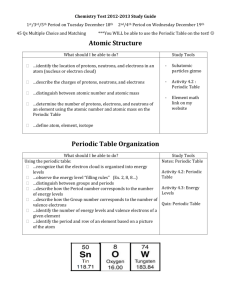
CHEMISTRY-CP, PERIOD 6 CHAPTERS 6—PERIODIC TRENDS DAILY PLANNER DAY CLASSWORK 1 Tues, Feb. 21 2 Periodic Table Basics Review (10 Points) 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 Tent. March 14 HOMEWORK Vocabulary Definitions Notes: Electron Configurations, Highest Energy Levels, Valence Electrons, Lewis Dot Diagrams, Oxidation Numbers Daily Quiz Notes: Atomic Size/Ionic Size Density Lab (25 Points) Vocabulary Quiz (20 Points) Ionization Energy/Electronegativity Handout (5 Points) Daily Quiz Notes: Ionization Energy/Electron Affinity/Electronegativity Lab: Chemical Reactivity (15 Points) Daily Quiz Notes: Chemical Reactivity The Elements and Periodic Trends Project (Part 1) Element Key (40 Points) The Elements and Periodic Trends Project (Part 2) Class Jigsaw for Group and Period Trends (20 Points) Finish Part 2 of Project The Elements and Periodic Trends Project (Part 3) Designing a Power Point (50 Points) Finish Power Point Design Group Presentations: Hydrogen/Alkali Metals/Alkaline Earth Metals Group Presentations: Transition Metals/Boron Group/Carbon Group Group Presentations: Nitrogen Group/Oxygen Group/Halogens HW1: Worksheet A Group Presentations: Noble Gases/Lanthanides/Actinides Homework & Extra Credit Due (50 Points) Review Puzzle Review for Test Test Chapters 5 & 6 (100 Points) HW8: Worksheet H HW2: Worksheet B Finish all of today’s work for homework HW3: Worksheet C HW4: Worksheet D Finish Element Key Complete Today’s Handout Complete Lab HW5: Worksheet E HW6: Worksheet F HW7: Worksheet G Top Groups Chapter 5 Haley Warner & Brooke Vanim Total Possible Points This Chapter: 345 Points + 24 Extra Credit Points Homework Grades A: 50/50 B: 45/50 C: 40/50 D: 35/50 E: 32/50 F: 30/50 0/50 8/8 Complete 7.5/8 Complete 7/8 Complete 6/8 Complete 5/8 Complete 4/8 Complete Less than 4/8 Complete Extra Credit: 4 Points: Worksheet I 3 Points: Worksheet J 7 Points: Worksheet K 5 Points: Determine which element is responsible for the following paint colors and create a poster to display your information. Red, Orange, Yellow, White, Green, Blue, Violet 6 Points: Complete the “Quick Lab” on Text p. 175 WORKSHEET A ELECTRON CONFIGURATIONS Write electron configurations for atoms that have the following atomic numbers a) 9 __________________________________________ b) 17 __________________________________________ c) 35 __________________________________________ . What do these electron configurations have in common? TABLE IDENTIFICATION Complete the table by describing the characteristics of each numbered element in the periodic table below 1 3 4 2 Number in Above Periodic Table 1 Group Period State Electron Configuration # of Valence Electrons Highest Energy Level Lewis Dot Diagram 2 3 4 What ion is formed when a) a sulfur atom gains two electrons ____________________ b) an aluminum atom loses 3 electrons?____________________ c) an iodine atom gains 1 electron ____________________ d) a magnesium atom loses 2 electrons?____________________ Complete the following table. Symbol # of Protons # of Electrons # of Valence Electrons Oxidation # Mn4+ 13 10 35 -1 46 +1 WORKSHEET B FILL-IN Atomic radii generally _____________________________________ as you move from left to right in a period. Atomic size generally _______________________________ within a given group because there are more ___________________________ occupied and an increased shielding effect, despite an increase in nuclear ___________________________________. TRUE/FALSE _____ 1. The radius of an atom cannot be measured directly. _____ 2. Removing one electron from an atom results in the formation of a positive ion with a 1+ charge. _____ 3. The relative radii of atoms are estimated as being half the distance between the nuclei in diatomic molecules. PROBLEMS 1. Arrange these elements in order of decreasing atomic size: Sulfur, Chlorine, Aluminum & Sodium ______________________________________________________________ 2. Indicate which element in each pair has the greater atomic radius: a) chlorine or fluorine ___________________________ b) calcium or arsenic ___________________________ c) oxygen or fluorine ___________________________ d) tungsten or selenium ___________________________ e) fluorine or sulfur ___________________________ 3. Using the periodic table as a guide, list the following atoms in order of increasing atomic radius. Ba, In, S, Cs, F, As ________________________________________________________________________ 4. For the following pairs of atoms, tell which one has the largest ionic radius. a) Al or B ______________________________ b) S or O ______________________________ c) Br or Cl ______________________________ d) Na or Al ______________________________ 5. Which ion in each pair has the smaller radius? a) K+ or O2- ______________________________ Ba2+ ______________________________ b) or I- c) Al3+ or P3- ______________________________ d) K+ or Cs+ ______________________________ e) Fe2+ or Fe3+ ______________________________ 6. Which of the substances in each of the following pairs is larger? a) Fe or Fe+2 b) Cl or Cl- c) Mg or d) Cu+ Mg+2 or Cu e) O-2 or O ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ 7. Explain why a magnesium atom is smaller than atoms of both sodium and calcium. 8. Would you expect a Cl- ion to be larger or smaller than a Mg2+ ion? Explain. 9. Why do atoms get smaller as you move across a period? WORKSHEET C A. FILL-IN The energy required to remove an electron from an atom is known as the ____________________ energy. This quantity generally _________________________ as you move left to right across a period. The size of an ion depends on whether the atom from which it formed gained or lost an _______________________. The ionic radius of anions and cations increases as you move __________________. B. MATCHING _____ 1. Ionization Energy a) half the distance between the nuclei of two atoms _____ 2. Electronegativity b) When the elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, there is a periodic pattern in their physical and chemical properties. _____ 3. Atomic Radius c) the energy required to overcome the attraction of the nuclear charge and remove an electron from a gaseous atom _____ 4. Cation d) positively charged ion _____ 5. Periodic Law e) the tendency for the atoms of an element to attract electrons when they are chemically combined with another element PROBLEMS 1. Indicate which element of the following pairs has the greater electronegativity. a) calcium, gallium ___________________________ c) chlorine, sulfur ___________________________ b) lithium, oxygen ___________________________ d) bromine, arsenic ___________________________ 2. Which atom or ion in each pair has the larger ionization energy? a) Na or O ________________________ d) Cu or Ra ________________________ b) Be or Ba ________________________ e) I or Ne ________________________ c) Ar or F ________________________ f) W or Se ________________________ 3. Describe the periodic trends for the following: a) Atomic Radius: b) Ionic Size: c) Ionization Energy: d) Electronegativity: e) Electron Affinity: MULTIPLE CHOICE _____ 1. The elements with the highest ionization energies are the a. noble gases b. alkali metals c. halogens d. transition metals _____ 2. The fluorine ion is larger than the fluorine atom because a. F- has a stronger positive charge on its nucleus than F. b. F- has more electron-electron repulsions than F c. F- has one fewer electron d. F- now has an empty valence shell _____ 3. The statement that atoms tend to gain, lose, or share electrons in order to acquire a full set of valence electrons is called the a. octet rule b. triad rule c. rule of octaves d. orbital principle WORKSHEET D A. Among the following pairs of atoms, identify the larger of the two, the one with the greater first ionization energy, the one with the lower electronegativity and the one that is the most reactive. Atoms Larger Li or K C or F Mg or Ca O or S Greater Ionization Lower Most Reactive Energy Electronegativity MULTIPLE CHOICE _____ 1. In the periodic table, there is a periodic pattern in the physical and chemical properties of elements when they are arranged in order of a) increasing atomic mass b) increasing electronegativity c) increasing atomic radius d) increasing atomic number _____ 2. Which sublevel corresponds to the transition metals in the periodic table? a) s b) p c) d d) f 2+ _____ 3. When a strontium atom loses two electrons to form an Sr ion, the electrons are lost from the a) 5s orbital b) 5p orbital c) 3d orbital d) 4f orbital c) period 4 halogen d) period 5 transition metal _____ 4. The element iodine, I, is a a) period 5 alkali metal b) period 5 halogen _____ 5. The subatomic particle that plays the greatest role in determining the physical and chemical properties of an element is the a) proton b) electron c) neutron d) photon _____ 6. Which of the following atoms would you expect to have the largest atomic radius? a) I b) Ca c) K d) Rb _____ 7. From left to right across the second period of the periodic table a) first ionization energy increases b) electronegativity decreases c) atomic radii increase d) atomic mass decreases _____ 8. Among the groups of elements listed below, which have the same number of electrons in their highest occupied energy levels? a) Li, B, C, F b) Na, Mg, Al, S c) K, Ca, Rb, Sr d) N, P, As, Sb _____ 9. As the number of electrons added to the same principal energy level increases, atomic size generally a) increases b) decreases c) remains the same d) varies randomly _____ 10. Which of the following is the most reactive metal on the periodic table? a) hydrogen b) lithium c) francium d) uranium _____ 11. Which of the following is the most reactive nonmetal on the periodic table? a) hydrogen b) fluorine c) helium d) radon WORKSHEET E MATCHING Identify each of the following as either a metal, nonmetal or metalloid. Write the letter of the correct answer on the line. _____ 1. Nickel A. Metal _____ 2. Tellurium B. Nonmetal _____ 3. Sulfur D. Metalloid _____ 4. Radon _____ 5. Potassium Identify the element that is in each group. Write the letter of the correct element on the line. _____ 6. Alkaline Earth Metal A. Bismuth _____ 7. Boron Group B. Iron _____ 8. Halogen C. Sodium _____ 9. Transition Metal D. Aluminum _____ 10. Alkali Metal E. Krypton _____ 11. Carbon Group F. Chlorine _____ 12. Noble Gas G. Strontium _____ 13. Oxygen Group H. Silicon _____ 14. Nitrogen Group I. Oxygen Match element with an element that has the most similar properties. _____ 15. arsenic A. boron _____ 16. bromine B. cesium _____ 17. cadmium C. nitrogen _____ 18. neon D. zinc _____ 19. osmium E. iodine _____ 20. sodium F. xenon D. MULTIPLE CHOICE _____ 21. The transition elements would be located in which block of the modern periodic table? a. s b. p c. d d. f _____ 2. The number of the row of elements is the same as the number of a. the energy level of the valence electrons b. electrons in an atom of that element c. protons and neutrons in an atom of that element d. elements in that particular row of the table _____ 23. Elements that have similar properties have a. nearly the same atomic mass b. the same number of protons c. the same number of valence electrons d. the same number of total electrons _____ 24. The most chemically reactive of all the elements is a. sodium b. carbon _____ 25. Silicon and carbon share some similar properties. a. True b. False c. fluorine d. bromein WORKSHEET F A. From the following list of chemical families, select the one that best fits each description below. Alkali metal Alkaline Earth Metal Transition Metal Inner Transition Metal 1. Cerium, Europium, Uranium _____________________________________ 2. An element found in Group 1 of the Periodic Table _____________________________________ 3. Has an oxidation number of +2 _____________________________________ 4. Sodium or cesium _____________________________________ 5. Has multiple oxidation numbers _____________________________________ 6. An element in Group 5 _____________________________________ 7. Magnesium or barium _____________________________________ 8. Has an oxidation number of +1 _____________________________________ 9. Is denser and harder than its alkali neighbor _____________________________________ 10. Contains a liquid metal _____________________________________ B. Identify the Element by completing the blanks. 1. An alkali metal used in antidepressant medicines. ___ ___ ___ H ___ ___ ___ 2. An alkaline earth metal used in red fireworks and flares. ___ T ___ ___ N ___ ___ ___ ___ 3. This metal will ignite upon contact with water. S ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ 4. This alkaline earth metal is used in the treatment of cancer. ___ A ___ ___ ___ ___ 5. This transition metal is the best electrical conductor. ___ ___ ___ V ___ ___ 6. This element is a liquid metal used in dentistry. ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ 7. This inner transition metal is a fuel in nuclear power plants. ___ ___ A ___ ___ ___ M 8. This alkali metal is used as a replacement in low-sodium diets. ___ ___ T ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ 9. This transition metal is the main component of steel alloys. ___ ___ O ___ 10. An alkaline earth metal found in emeralds. B ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ 11. A patient can drink a compound of this element so that ___ ___ R ___ ___ ___ A doctor can view the patient’s digestive tract 12. The most malleable metal ___ O ___ ___ C. Fill-In 1. Copper is useful as a wire in a lamp because it conducts electricity and it is _______________________________________. 2. Aluminum can be made into foil and cans because it is ____________________________________. 3. Because francium breaks down and gives off particles and energy , it is ________________________________________. 4. The elements iron, cobalt and nickel are sometimes called the iron _______________________________. 5. Cobalt, iron and nickel are the only elements that are _______________________________________. WORKSHEET G BORON GROUP 1) The Boron Group is Group #_____________ on the periodic table. 2) The common e- configuration for the boron group is__________________. 3) The elements in the boron group have _______ valence electrons and an oxidation # of ___________. 4) The elements in the boron group are __________ as reactive as Groups 1 & 2 but are _____________ conductors of heat and electricity. 5) What do the elements in the boron group look like?___________________________________________________________ 6) __________________________________ is found in contact solution, eye wash, laundry detergent and glass. 7) __________________________________ is a strong yet lightweight metal used to make alloys used for many things; such as bikes & airplanes. 8) _________________________________ is used to make mirrors. CARBON GROUP 9) The Carbon Group is Group #_____________ on the periodic table. 10) The common e- configuration for the carbon group is__________________. 11) The elements in the carbon group have _______ valence electrons. 12) The metals in the carbon group have an oxidation # of ___________________. 13) The nonmetals in the carbon group have an oxidation # of ________________. 14) Organic chemistry is the study of compounds containing the element _____________________________________. 15) Elemental __________________________ makes up graphite, charcoal and diamonds. 16) All life on Earth is based on the element _________________________________. 17) ________________________________ is the 2nd most abundant element in the Earth’s crust and is found in glass and sand. 18) _________________________________ is used to shield x-rays. 19) NITROGEN GROUP 20) The Nitrogen Group is Group #_____________ on the periodic table. 21) The common e- configuration for the nitrogen group is__________________. 22) The elements in the nitrogen group have _______ valence electrons and an oxidation # of ________________________> 23) ____________________________________ is the most abundant element in our atmosphere, making up almost 80% of the atmosphere. It is also found in DNA and ammonia. 24) ____________________________________ is used to make smoke bombs, pyrotechnics and matches. OXYGEN GROUP 25) The Oxygen Group is Group #_____________ on the periodic table. 26) The common e- configuration for the nitrogen group is__________________. 27) The elements in the nitrogen group have _______ valence electrons and an oxidation # of ________________________> 28) ____________________________________ is the most abundant element in our atmosphere, making up almost 80% of the atmosphere. It is also found in DNA and ammonia. 29) ____________________________________ is used to make smoke bombs, pyrotechnics and matches. WORKSHEET H A. IDENTIFY THE ELEMENT (Unscramble the letters to determine the element described) 1. This halogen, when combined with hydrogen, forms a very strong acid that is used to etch glass. U R O L E I F N=_____________________ 2. This halogen is added to salt to ensure that it is present in a preson’s diet. D I O N E I = ________________________ 3. This noble gas is used in light bulbs. R G N A O = ________________________ 4. A halogen that acts as a bleaching agent. L R I N E C O H = ____________________ 5. A radioactive noble gas. N D O A R = ________________________ B. Circle the correct response from the choices given in parentheses. 1. The halogens are found in Group (17 or 18). 2. The halogens form (anions or cations) with a (1+ or 1-) charge. 3. The first four halogens are (metals, metalloids or nonmetals). 4. All of the elements in the halogens are nonmetals except (astatine or iodine). 5. (Fluorine or astatine) is a radioactive product of uranium decay. HALOGENS 1) The Halogens are Group #_____________ on the periodic table. 2) The common e- configuration for the halogen group is__________________. 3) The elements in the halogen group have _______ valence electrons and an oxidation # of ___________. 4) The ___________________________________are the most reactive group of nonmetals with ______________________________ being the most reactive element on the periodic table. They are so reactive that they are toxic in elemental form. 5) _________________________________ prevents tooth decay and is found in non-stick pans and refrigerants. 6) _________________________________ is a disinfectant used to kill bacteria and is found in bleach and PVC pipes. 7) __________________________________ is used in photography and is used as a sedative. NOBLE GASES 8) The Noble Gases are Group #_____________ on the periodic table. 9) The common e- configuration for the noble gases is__________________. 10) The elements in the noble gas group have _______ valence electrons and have an oxidation # of 0. a. Due to their number of valence electrons the noble gases are ___________________________ elements. 11) How reactive are the noble gases?_______________________________________________________________________________ a. Because of this they are also known as __________________________________ gases. 12) ___________________________________ is the 2nd most abundant element in the universe. 13) Lasers typically use the noble gases _____________________________________ and ____________________________________. 14) Fluorescent lightbulbs use a mixture of the noble gases ______________________________ and ____________________________. 15) ____________________________________ can be used to displace oxygen to preserve the life of wine and pharmaceutical drugs. WORKSHEET I—EXTRA CREDIT A. Match each element with its use. _____ 1. Most abundant element in Earth’s crust. A. Lead _____ 2. Sand, glass, cement B. Aluminum _____ 3. Toxic substance previously used in paint & gasoline C. Nitrogen _____ 4. Most abundant element in Earth’s atmosphere D. Fluorine _____ 5. Most reactive element E. Silicon _____ 6. Diamonds & graphite F. Phosphorus _____ 7. Tips of matches G. Carbon B. Aliens living on a distant planet discovered and named the six elements described below: Bobble (Bo) is a noble gas but does not have 8 valence electrons. Wobble (Wo) is also an inert gas but has a greater atomic mass. Doggone (D) has the electron configuration 1s22s22p63s23p1 Kratt (Kr) is a halogen in the same period as Doggone Nuute (N) forms a crystalline solid with Kratt that is found in seawater. Quakzil (Q) is in the same period as Wobble and contains only one valence electron. 1. Scientists have determined that his alien planet is composed of the same elements as Earth. Based on this observation, place the above elements in their correct positions on this periodic table. Group 1 Group 2 Group 13 Group 14 Group 15 Group 16 Group 17 Group 18 2. Use what you know about electron configurations to explain why an atom of Nuute is smaller than an atom of Quakzil. 3. Which would you expect to be larger, an atom of Bobble or an atom of Wobble? 4. Nuute is the largest atom in its period and Kratt is one of the smallest. Predict the relative size of an atom of Doggone. 5. How can you explain the change in atomic size as you move from left to right across a period? WORKSHEET J—EXTRA CREDIT Name each element based on the clues provided. 1. This element: a. Has only one energy level b. Is part of an essential liquid. c. Is the lightest element. This element is _____________________________________________ 2. This element: a. Has a smaller atomic radius than oxygen b. Is one electron short of a full octet c. Has the largest electronegativity This element is ____________________________________________ 3. This element: a. Has less ionization energy than sodium b. Has a smaller atomic radius than rubidium c. Has a single letter symbol based on a Latin name This element is ___________________________________________ 4. This element: a. Has electrons in the d sublevel b. Is the heaviest named element in its group c. Is a shiny metal used for jewelry This element is __________________________________________ 5. This element: a. Loses electrons easier than magnesium b. Has a larger atomic radius than any of the actinides c. Emits radiation This element is ________________________________________ 6. This element: a. Is a nonmetal b. Is the only gas in its family c. Is used in dynamite and fertilizers This element is ________________________________________ 7. This element: a. Has an electronegativity greater than indium b. Has an atomic radius larger than carbon c. Has a first ionization energy greater than lead d. Is used to make cans This element is_______________________________________ 8. This element: a. Has a first ionization energy greater than chromium b. Has an atomic radius larger than cobalt c. Has an electronegativity greater than manganese d. Is used to make steel and can be magnetized This element is ______________________________________ 9. This element a. Is lighter than hafnium b. Has a greater electronegativity than zirconium c. Has a smaller atomic radius than scandium d. Is used in aircraft manufacturing This element is ____________________________________ EXTRA CREDIT WORKSHEET K Fill in the appropriate answer Group Name Alkali Metals Alkaline Earth Metals Transition Metals Metals in Groups 13-15 Metalloids Nonmetals in Groups 14-16 Halogens Noble Gases Inner Transition Metals (Rare Earth) # of Valence Electrons Oxidation # Appearance Check all boxes that apply Chemically Reactive Found Freely in Nature Malleable Ductile Conduct Electricity & Heat SemiConductors Brittle Typically Solids Do not form compounds readily Contain many Synthetic Elements