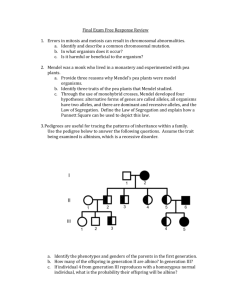
The probability of recombination depends on what
advertisement

JEOPARDY! Questions—4/2 MENDELIAN GENETICS 100: Mendel cross-pollinated the parental generation, creating the (F2/P/F1) generation and then self-pollinated those to create the (F2/P/F1) generation. 200: A red flower and a white flower are cross-pollinated. Their offspring are all pink; they are self-pollinated to produce red, white and pink offspring. This is an example of what? 300: Describe the Law of Segregation as it applies to the alleles for purple flowers (P) and white flowers (p). 400: Describe the Law of Independent Assortment as it applies to the alleles for purple flowers (P) and white flowers (p). 500: Mendel started with the parental or (F2/P/F1) generation using what type of plants? GENETICS AFTER MENDEL 100: What does the Chromosomal Theory of Heredity state? 200: The probability of recombination depends on what? 300: Blonde people usually have pale skin. This suggests what about these two traits? 400: Mendel discovered linked genes. What does it mean, they are linked? What test result in flies having to do with body color and wing shape helped him discover this? 500: A mom carries one recessive allele for color-blindness, which is a sex-linked trait. What does that mean? To which of her children can she pass it on to? BONUS: Can any of her children get color-blindness, even if the dad doesn’t have it? EVOLUTION 100: What is NOT included in Darwin’s theory of evolution? 200: Describe Darwin’s theory of descent with modification. 300: How is the use of anti-bacterial soap creating “super-bacteria”? 400: What was the key difference between Darwin’s theory of evolution and Lamarck’s theory of evolution? (Hint: acquired vs. heritable characters…) 500: For natural selection to occur, what conditions must be true? (More than 1 generation; genetic variation causing phenotypic variation; greater fitness in some; resource competition.) POPULATION GENETICS 100: Natural selection acts on the ________, while evolution acts on the ________. 200: What are the 4 causes of microevolution? Which one allows species to adapt to its environment? Are they random? 300: What is genetic drift? Is genetic drift random? On what type of populations does it have the greatest effect? 400: What does the equation p2 + 2pq + q2 = 1 represent? What does 2pq specifically represent? 500: What does it mean, a population is in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium? What are the 5 requirements a population must follow in order to be under Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium?