Content Practice A & B Mendel with answers
advertisement

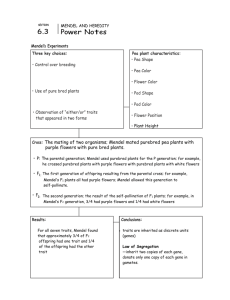
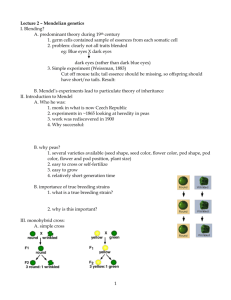
Name Date Content Practice A Class LESSON 1 Mendel and His Peas Directions: On the line before each statement, write T if the statement is true or F if the statement is false. T 1. Genetics is the study of how traits are passed from parents to offspring. F 2. Gregor Mendel studied pea plants because they reproduce slowly and have easily observable traits. F 3. Pollination in pea plants can occur in three ways. T 4. Mendel began his experiments with pea plants that stayed the same from one generation to the next. F 5. He then crossed those plants to create true-breeding plants. T 6. In Mendel’s studies of the colors of purple pea flowers, none of the first-generation crosses had white flowers. F 7. In those same experiments, about three-fourths of the second-generation crosses had white flowers. F 8. From those results, Mendel concluded that white flowers on pea plants are a dominant trait. T 9. In other studies, a trait that showed up in the same proportion of second-generation crosses as white flowers did was yellow pods. T 10. Genetics One trait that Mendel did not study in pea plants was the shape of the plants’ leaves. 13 Name Date Content Practice B Class LESSON 1 Mendel and His Peas Directions: Answer each question or respond to each statement on the lines provided. 1. What is genetics? The study of how traits are passed from parents to offspring. 2. State three reasons why Gregor Mendel chose pea plants for his experiments. Pea Plants reproduce quickly, they have easily observable traits, he could control which pairs of plants reproduced. 3. What did Mendel produce when he cross-bred different true-breeding plants? Hybrids 4. When Mendel crossed plants that had always produced only purple flowers with ones that had always produced only white flowers, what was the outcome of the first-generation cross? All the plants had purple flowers. 5. What happened when he crossed those plants to produce a second-generation cross? About 25% of the plants had white flowers and about 75% had purple flowers. 6. What conclusions did Mendel draw from these results and from experiments with other pea-plant traits? Describe genetic factors and the principle of dominant/recessive. He concluded that the color of pea-plant flowers and other traits of the plants are determined by two factors-one from the sperm cell and one from the egg cell. Each factor is dominant or recessive. A dominant factor blocks a recessive factor, so only by the inheritance of two recessive factors can the trait produced by the factor be expressed in the plant. 14 Genetics






![Biology Chapter 3 Study Guide Heredity [12/10/2015]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/006638861_1-0d9e410b8030ad1b7ef4ddd4e479e8f1-300x300.png)


