WHAP Teacher Copy Post Classical Trade Routes
advertisement

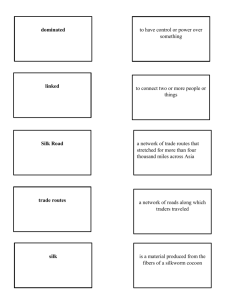
Post-Classical Trade Routes WHAP/Napp Cues: Objective: To compare and contrast the impact of significant trade routes in the post-classical world Do Now: List facts about the Silk Roads. ___________________________________________ _______ Notes: I. The Silk Roads A. Land-based trade routes that linked pastoral and agricultural peoples B. Linked large civilizations on Eurasia’s outer rim C. More of a “relay trade” in which goods were passed down the line D. Outer Eurasia 1. Relatively warm, well-watered, and suitable for agriculture 2. Civilizations of China, India, the Middle East, and the Mediterranean E. Inner Eurasia 1. Eastern Russia and Central Asiaharsher and drier climate 2. Not conducive to agriculture 3. Inhabited by pastoral peoples herding animals from horseback 4. Products of the forest and semi-arid northern grasslands known as the steppes included hides, furs, livestock, wool, and amber 5. Movement of pastoral peoples diffuse Indo-European languages, bronze metallurgy, horse-based technologies across Eurasia F. Silk Road trading networks prospered most when large and powerful states provided security for merchants and travelers 1. Trade flourished during the classical era - Roman and Chinese empires 2. Flourishedseventh and eighth centuries CE the Byzantine Empire, the Muslim Abbasid dynasty, and the Tang Dynasty in China 3. Flourished Thirteenth and fourteenth centuries, during the Pax Mongolia of the Mongol Empire G. Most of the goodsluxury products for an elite/wealthy market rather than staple goods: Of course, silk came to symbolize this exchange system 1. Chinese originally held a monopoly on silk-making, by the sixth century C.E., knowledge and technology for producing raw silk had spread 2. Byzantines, Koreans, Japanese, Indians, and Persians learned 3. Silk was used as currency in Central Asia 4. Symbol of high status – gift to monasteries (symbol of high honor) H. Conduit of Culture 1. Buddhism spread on Silk Roads – owing much to merchants 2. Buddhism had appealed to merchants its universal message 3. But Persian Zoroastrianism blocked spread of Buddhism to west, except oasis cities of Central Asia: Merv, Samarkand, Khotan, and Dunhuang 4. Buddhism changed on the Silk Roads a) More devotional Mahayana form of Buddhism flourished on Silk Roads rather than more austere psychological teachings of Buddha b) In northwest India, statues of the Buddha revealed distinctly Greek influences from the invasions of Alexander the Great Summaries: Cues: 5. Diseases a) Diseases traveled the trade routes of Eurasia too b) Smallpox and measles devastated populations of both the Roman Empire and Han dynasty, contributing to their political collapse 1. Yet these diseases may have strengthened the appeal of Christianity in Europe and Buddhism in China c) Bubonic plague ravaged the coastal areas of the Mediterranean Sea between 534 and 750 CE 1. Preventing Byzantium from reintegrating Italy into its version of a renewed Roman Empire 2. Repeated recurrence weakened the ability of Christendom to resist the Muslim armies pouring in seventh century CE 3. Most well-known dissemination of diseaseMongol Empire during the thirteenth and fourteenth centuriesBlack Death from China to EuropeBetween 1346 and 1350, about one-third of the population of Europe perished from the plague II. Indian Ocean Trade A. Until the creation of a genuinely oceanic system of trade after 1500represented the largest sea-based system B. Transportation costs were lower on the SeaShips could accommodate larger and heavier cargoes than camels C. Monsoons with their alternative wind currents that blew predictably eastward during the summer months and westward during winter D. Operated across an “archipelago of towns”Dates back to First CivilizationsIn Classical Era, learned to use monsoon winds E. The fulcrum of this growing commerce lay in India itself F. Oceanic commerce had a significant impact on Southeast Asia and East Africa, especially the introduction of Hindu, Buddhist, or Islamic beliefs G. Malay sailors opened an all-sea route between India and China through the Straits of Malacca around 350 CE 1. Malay kingdom of Srivijaya dominated choke point from 670 to 1025 H. Sailendra kingdom in central Java, an agriculturally rich region between the eighth and tenth centuries featuring Hindu temples/Buddhist monuments (most famousBorobudur: largest Buddhist monument-world) I. In East Africa, a civilization known as Swahili (also a language) emerged in the eighth century CE, stretching from present-day Somalia to Mozambique 1. With rise of Islam, increased commerce on western Indian Ocean 2. Language: grammatically African within Bantu family but Arabic script III. West Africa A. Trans-African trade connected North Africa and West Africa, part of sub-Saharan AfricaSalt for GoldCamel introduced 300 to 400 CE B. Islam entered along trade routesAlso Kingdoms of Ghana, Mali, and SonghaiUrban and commercial centers – such as Koumbi-Saleh, Jenne, Timbuktu, Gao, Gobir, and Kano IV. Americasgeographic obstacles to tradeNorth/South Orientation Summaries: Strayer Question: What lay behind the emergence of Silk Road commerce and what kept it going? What made silk such a highly desired commodity across Eurasia? List major economic, social, and cultural consequences of Silk Road commerce. What accounted for the spread of Buddhism along the Silk Road? What was the impact of disease along the Silk Road? How did Indian Ocean trading network differ from that of the Silk Roads? What lay behind the flourishing of Indian Ocean commerce in postclassical era? What is the relationship between the rise of Srivijaya and Indian Ocean commerce? What was the role of Swahili civilization in the world of Indian Ocean commerce? What changes did trans-Saharan trade bring to West Africa? In what ways did trade in Western Hemisphere differ from Eastern Hemisphere? 1. Why were trade routes particularly 4. Where were there no slave markets prior extensive in Eurasia? to 1000 C.E.? (A) Because a wide variety of (A) Antarctica communities, from Europe to (B) Africa East Asia, were linked by trade. (C) China (B) Eurasia was where most goods (D) the Far East were produced. (E) the Mediterranean region (C) Europeans did not yet know how to build roads. 5. The truths that the Buddha claimed (D) Russian tsars built all these either draw on or depart from the routes using forced labor. fundamental principles of which belief (E) Trade routes were not well system? developed at all in Eurasia. (A) Christianity (B) Hinduism 2. What is diffusion? (C) Islam (A) The assimilation of a minority (D) Judaism ethnic group into the population (E) Hellenism (B) The splitting of the atom (C) The conquering of one civilization 6. The Indian Ocean by a more powerful one I. Is the world’s second-largest ocean (D) The spread of foods, trade goods, II. Is the site of thousands of years of concepts, norms, practices, and travel and economic exchange inventions among different III. Can be reached from the Atlantic peoples and the Pacific Oceans (E) None of the above IV. Extends only as far south as the eastern coast of Africa 3. Leading up to 1000 C.E., what was the Which are correct? most vital overland trade route? (A) I, III, and IV (A) The Silk Road (B) I, II, and IV (B) The Sahara Desert (C) II, III, and IV (C) The Sahel (D) II and III (D) The Trans-Siberian (E) All of the above (E) Indian Ocean Trade Excerpt from saudiaramcoworld.com “…On the western shore, in the second century B.C.E., at around the time that Hippalos discovered the secret of the monsoon, the caravan city of Gerrha flourished in what is now the Eastern Province of Saudi Arabia. Strabo, quoting a source named Artemidorus, says: ‘From their trafficking both the Sabaeans and the Gerrhaeans have become richest of all; and they have a vast equipment of both gold and silver articles, such as couches and tripods and bowls, together with drinking vessels and very costly houses; for doors and walls and ceilings are variegated with ivory and gold and silver set with precious stones.’ …To the southwest of the Arabian Peninsula, across the Red Sea, lay the Ethiopian Christian kingdom of Aksum, with its port of Adulis. Aksum exported gems, spices— including cassia—incense and gold to Byzantium, India, Sri Lanka and Persia. The gold came from the African interior and the incense was grown in Aksumite territory, but the cassia and other spices almost certainly came from India and what is now the Indonesian archipelago. The Ethiopic liturgical language, Ge’ez, was derived from one of the non-Arabic Semitic languages of South Arabia. Its alphabet is the only Semitic alphabet to indicate vowels, and the system by which it does this is elsewhere found only in the various writing systems of India—further evidence of the extent to which ideas as well as spices were trafficked across the Indian Ocean. …The discovery of the sea route between the Arabian Gulf and China was an event equal in importance to the discovery by the Portuguese of the sea route to India. It was one thing to cross the Indian Ocean with the monsoon to Gujarat or the Malabar coast, or even to sail south of Sri Lanka and turn north to the Bay of Bengal or east to Malaya—but it was quite another to make the far longer voyage to Canton through a lesser-known sea with its own pattern of winds, to say nothing of the perpetual danger of piracy and the typhoons of the South China Sea. Yet in early Islamic times, direct sailing to Canton via the Gulf seems to have been common practice. The bahr al-hind, the “Sea of India,” or the bahr al-sin, the “Sea of China,” as the Indian Ocean was often called, was not a single entity. Those who sailed it said it was made up of seven different seas, each with its own characteristics—the traditional division from which we derive our expression for far-ranging travel, “to sail the seven seas.” …The names of these seven seas derive from the languages of the peoples who lived on their shores. The names preserve, as if in amber, the varied linguistic and cultural backgrounds of the seafarers who first explored these waters, and they sounded just as exotic to Arabic-speakers in the ninth and 10th centuries…” Thesis Statement: Continuity and Change Over Time: Silk Roads or Indian Ocean Trade ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________