Ch 7
advertisement

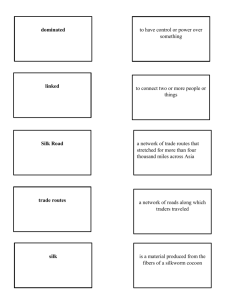
World History: The Earth and its Peoples Chapter 7 Networks of Communication And Exchange, 300 B.C.E. - 1100 C.E. Objectives • Identify the locations and describe the participants of the Silk Road, the Indian Ocean, and the trans-Saharan trade routes.. • Define the term “Africanity” and explain the development of “Africanity” in terms of Bantu migrations.. • Analyze the relationship between environment, transportation technology,and trade along the Silk Road, Indian Ocean, and trans-Saharan trade routes.. • Discuss the causes and patterns of the spread of Buddhism and Christianity.. Silk Road Map Overview Remember to give Students their quizzes Back Trade Routes • agricultural goods • manufactured goods • ideas • social system Did more for cultural inclusion than any emperor or king. The Silk Road Silk Road – connects Middle East to China – 1st Period: 150 BCE - 907 CE – 2nd Period: 13th-17th cen. CE • Origins – nomadic traders – Chinese demand for western products – Mesopotamian markets • Parthians • hybrid camels – existed solely for trade route The Silk Road Zhang Jian – Ferghana horses – alfalfa and domestic grapes • Chinese Exports – silk, pottery, paper Impact of Trade – settling of Iranian nomads – import of Turkic peoples • yurts – interest in foreign religions – military • chariot, bowmen • stirrup • Prosperity from trade = peace Silk Road Map The Indian Ocean Indian Ocean Maritime System – Indian Ocean / South China Sea – multilingual / multiethnic seafarers – E. Africa, Arabia, India, China, and SE Asia • monsoons – lateen sails; long reaches – sail further from shore • colonies – economic, not political – warfare rare The Indian Ocean Origins of Contact and Trade • Africa – SE Asian settling of Madagascar • 2000 years ago • cultures of homeland – Mozambique Channel • 1500 years ago Impact – The Periplus of the Erythraean Sea - 7th century CE • extensive written record of trade • ports of call from E to W – bilingual and bicultural families • cosmopolitan in nature Routes Across the Sahara Sahara – 2500 BCE - 300 BCE • shift in cultural patterns south – Mediterranean - S. Africa barrier – source of European exploration • trans-Saharan caravan routes Culture – cave paintings • cliffs and caves – southern animals • hunters, cattle breeders, horse herders, camel riders • Trans Saharan Trade Routes – camel domestication Camel Domestication Camels in Africa – 1st century BCE – to Egypt from Arabia; S to N • saddle purposes Trade – South • salt for forest products • Sahel - ‘coast’ – Saharan southern border – North • food for Roman Empire – Roman N. African farms • wild animals for Coliseum • post-Roman shift to Middle East • Berber: trade for gold dust Sub-Saharan Africa Ghana - 600 - 1076 CE – “land of gold” – 1st documentable W. Africa – African with Muslim traders • religious toleration Sub-Saharan Africa – most important cultural exchange – geographical obstacles Sub-Saharan Africa Geography – Sahara, Atlantic, Indian, Red Sea – limited navigation of rivers • steppes – treeless plains; coarse grass • savanna – long grasses; scattered forests • tropical rain forest • Cultural traditions as a result of long period of isolation Sub-Saharan Culture Cultural Unity... – “great traditions” • written language, legal system, ethical codes, intellectual traditions – “small traditions” • • • • local customs and beliefs less-population density distance between tribes lack of accessibility to interior – Common Elements • • • • concept of kingship - isolation fixed social categories common agricultural cultivation common music rituals … emanates from Sub-Sahara Bantu Migrations “Africanity” – common African quality Bantu – family of 300 sub-Saharan languages – proto-Bantu as fishermen and agriculturalists – iron-smelting • language distribution • spread of agriculture • use of iron tools The Spread of Ideas Where do ideas and beliefs start? – Iron-smelting and pork Religion – royal sponsorship – monks, missionaries, and pilgrims • Silk Road and Indian Ocean – Buddhism • Ethiopian Christianity – Constantine’s missionaries – Patriarch of Alexandria – writing system • Armenian Christianity