Supplemental Material - Springer Static Content Server
advertisement

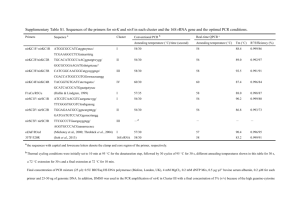
1 Supplementary Material 2 The bacterial 16S rRNA gene and the fungal ITS1 region were amplified from the total DNA using FAM 3 (6-carboxyfluorescein)-labeled polymerase chain reaction (PCR) forward primer and an unlabeled 4 reverse primer. The primers used for the 16S rRNA gene and the ITS1 region were B27-FAM (5'- 5 AGAGTTTGATCCTGGCTCAG) (Lane 1991), 1401-R (5'- CGGTGTGTACAAGACCC) (Nübel et al. 1996), ITS1F- 6 FAM 7 TCCTCCGCTTATTGATATGC) (White et al. 1990), respectively. For the 16S rRNA gene, the 50 µl reaction 8 mixture contained 5 µl of 10x PCR buffer, 2.5 µl MgCl2 50 mM, 5 µl dNTPs 2 mM, 1 µl of each primer, 9 1.25 µl DMSO, 1 µl BSA 3%, 500 U Taq-Polymerase, 30.75 µl H2O (DEPC), and 2 µl DNA from each 10 sample. Amplification of the 16S rRNA gene was performed in the T3 Thermocycler (Biometra, Germany) 11 using the following program: a 5 min hot start at 94ºC, followed by 35 cycles consisting of denaturation 12 (1 min at 94ºC), annealing (1 min at 57ºC), extension (1 min at 72ºC), and a final extension step for 10 13 min at 72ºC. For amplifying the fungal ITS1 region, the 100 µl reaction mixture contained 10 µl of 10x 14 PCR buffer, 10 µl of 10x Corralload, 5 µl MgCl2 25 mM, 10 µl 5x Q-Solution, 0.5 µl Top Taq DNA 15 polymerase (Top Taq DNA Polymerase, Qiagen, Germany), 10 µl dNTPs 2 mM, 48.5 µl H2O (DEPC), 2 µl of 16 each primer, and 2 µl DNA of each sample. Amplification of the ITS1 region was performed on the T3 17 Thermocycler (Biometra, Germany) with the following program: a 5 min hot start at 94ºC, followed by 35 18 cycles consisting of denaturation (1 min at 94ºC), annealing (1 min at 50ºC), extension (1 min and 30s at 19 72ºC), and a final extension step at 72ºC for 10 min. (5’- CTTGGTCATTTAGAGGAAGTAA) (Gardes and Bruns 1993), and ITS4 (5’- 20 21 T-RFLP analysis 22 Diversity analysis by terminal restriction fragment length polymorphism (t-RFLP) was also performed 23 targeting the bacterial 16S rRNA gene and the fungal ITS 1 region. For amplification, primer pairs and 24 PCR profiles were performed, as described for PCR. Purification of the PCR products was performed with 25 the NucleoSpin Gel and PCR clean-up kit (Macherey-Nagel, Germany), and digestion was performed 26 using the restriction enzyme MSP1 (New England Biolabs, Germany) (Sakamoto et al. 2004) for the 16S 27 rRNA gene, and Hinf1 (Fermentas, Lithuania) (Koide et al. 2007) for the ITS1 region. For digestion with 28 MSP1, one microliter of the enzyme, 5 µl of 10x buffer, 10 µl H2O (DEPC), and 200 ng of the amplicon 29 were used by using following program on the thermocycler: 4 h at 37ºC and 20 min at 80ºC. For 30 digestion with Hinf1, 0.5 µl of the enzyme, 2.5 µl buffer, 12 µl H2O (DEPC), and 200 ng of the amplicon 31 were used by using the following program on the thermocycler: 3 h at 37ºC and 20 min at 65ºC. The 32 digested amplicons (50 ng) were desalted and purified with the Gel and PCR clean-up kit (Macherey- 33 Nagel). One microliter was then mixed with 13 μl of Hi-Di formamide (Applied Biosystems, Germany) 34 containing a 400-fold dilution of a 6-carboxy-X-rhodamine-labeled MapMarker 1000 ladder (Bio- 35 Ventures, USA), denatured (5 min at 95ºC), cooled on ice, and size-separated on a 3730 DNA analyzer 36 (Applied Biosystems). Electrophoresis was performed with POP-7 polymer in a 50-cm capillary array 37 under the following conditions: 10 s injection time, 2 kV injection voltage, 7 kV run voltage, 66ºC run 38 temperature, and 63 min analysis time. Electropherograms were analyzed using the GeneMapper 3.5 39 software package (Applied Biosystems). 40