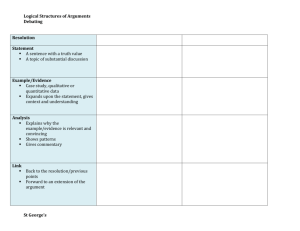
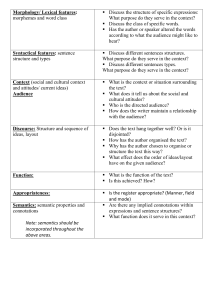
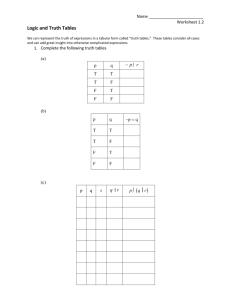
The following are the basic thinking and debating skills to be
advertisement

Useful Expressions and Thinking Skills for the Elective Modules on Social Issues and Debating The following are the basic thinking and debating skills and useful expressions for analysing social issues and presenting debating speeches. English teachers should exercise their discretion as to what to cover based on students’ language abilities and needs. Thinking skills for writing and debating 1. Identify and Related language features for different purposes group Use of connectives, sequence similar or different words and cohesive devices to ideas under meaningful show how ideas are organized categories Grouping different ideas Examples: Pros Vs cons Positive side Useful expressions Vs negative side Advantages Vs disadvantages Facilitating and hindering factors Evidence (e.g. facts and figures) Examples (e.g. experience, people, events and precedents Language Learning Support Section Useful expressions and thinking skills for elective modules on social issues and debating Firstly, secondly, then, finally… Showing the contrast of ideas However, but, yet, conversely, in contrast with, on the other hand, on the contrary… Grouping similar ideas Similarly, in a similar way, the same goes for, in like manner … Giving evidence According to, based on, the figures show that… Giving examples For example, for instance, such as… Giving analogies ...is like…,…can be compared to… 1 Workshop on Inter-school Collaborative Planning of NonLanguage Arts Electives in the NSS English Language Curriculum 25 January 2008 for explaining an idea) 2. Identify causal relationships in ideas Examples: Action and Use of verbs, nouns, adverbs, adverb clauses / phrases of result and reason, prepositional phrases and conditional sentences consequences Causes and consequences Causes and impacts Giving causes Showing effects and impacts Expressions for describing causes …stems from .. … is caused by … … is resulting from … …can be attributed to … … can be accounted for by … …the most likely causes of …are … is an important factor … ..one of the main causes is … …a contributing factor is that … …the root of ... is … …may cause … Expressions for describing effects and consequences … can lead to … …can result in … …can give rise to… …can bring about … …the most likely effects of … are… … is a result / consequence of … …can have a serious effect / impact / influence on …. …as a result of … Consequently As a result / consequence… Language Learning Support Section Useful expressions and thinking skills for elective modules on social issues and debating 2 Workshop on Inter-school Collaborative Planning of NonLanguage Arts Electives in the NSS English Language Curriculum 25 January 2008 …so that… the first and second conditional sentences (e.g. if we eat poisonous food, we may Expressing reasons for causes and consequences get sick.) Expressions for giving reasons as elaboration Owing to… Due to… …because of …because / as / since… The reason why … is that … It explains why… 3. Distinguish between Use of formulaic expressions facts and opinions and and reporting verbs with between facts and myths different connotations Examples: A fact - a thing that is known to be true or can be proved A myth - something that many people believe but that does not exist or is false An opinion - your feelings or thoughts about somebody or Language Learning Support Section Useful expressions and thinking skills for elective modules on social issues and debating Expressing facts It is a fact that… It is true to say that… Expressing statistical data It shows an increase / decrease of…,…analysed by sex / age,…the percentage of...was/is..., the percentage of …has dropped slightly / drastically,…compared with …, …display similar / different patterns… Expressing myths It is only a myth that…, many people believe that… Expressing opinions Reporting verbs to show the extent of agreement - Neutral connotations (e.g. say, show, announce, report, state, describe, etc.) 3 Workshop on Inter-school Collaborative Planning of NonLanguage Arts Electives in the NSS English Language Curriculum 25 January 2008 something A fantasy imagination - Positive connotations (e.g. agree, recommend, assert, etc.) - one’s - Negative connotations (e.g. disagree, argue, object, complain, etc.) Pointing out invalid statements / claims 4. Use perspectives to express opinions It is incorrect / ridiculous / wrong / invalid / unjustified / fallacious to say… different Use of formulaic expressions and phrases ideas and Examples: Different parties - Parents, teachers, principals, students, the government, etc. Different aspects resources (e.g. time, money, human resources, etc.) and views (e.g. historical, economic, political aspects, etc.) Language Learning Support Section Useful expressions and thinking skills for elective modules on social issues and debating Expressing personal points of view In my opinion…, I think…, I consider…, I believe…, on a personal level… Expressing different parties’ points of view From parents’ / the Government’s / citizens’ point of view… They think / believe… They hold the view that…. A different view is held by… Expressing perspectives different …in terms of human / financial resources… …looking at…in monetary terms …if we view the issue from a historical / political / social / economic perspective… …at a micro / macro level… 4 Workshop on Inter-school Collaborative Planning of NonLanguage Arts Electives in the NSS English Language Curriculum 25 January 2008