Lesson Plans
advertisement

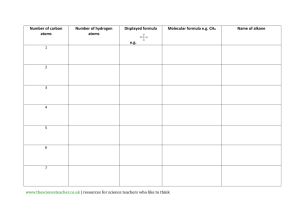
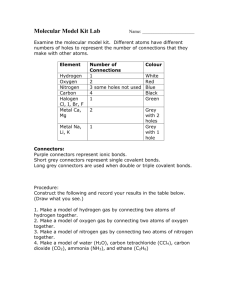
Lesson Plan To engage the students in learning about Villin we have designed an activity whereby the students need to compute the molar mass of Villin. There is a teacher’s version of the activity and there is a student’s version. In summary, the activity requests that the students compute the molar mass of villin. Students will have to add the molar mass of each amino acid forming the villin polymer and subtract for the water molecules that leave the polymer as a result of peptide bonds being formed. This activity will be introduced after the students have built the snack model, so as to be more familiar with the various amino acids and the villin protein. Page 1 Claudia Winkler Molar Mass of Villin: Teacher’s edition Subject: High School Chemistry California State Standard addressed as part of this activity Conservation of Matter and Stoichiometry 3. The conservation of atoms in chemical reactions leads to the principle of conservation of matter and the ability to calculate the mass of products and reactants. As a basis for understanding this concept: d. Students know how to determine the molar mass of a molecule from its chemical formula and a table of atomic masses and how to convert the mass of a molecular substance to moles, number of particles, or volume of gas at standard temperature and pressure. Organic Chemistry and Biochemistry 10. The bonding characteristics of carbon allow the formation of many different organic molecules of varied sizes, shapes, and chemical properties and provide the biochemical basis of life. As a basis for understanding this concept: a. Students know large molecules (polymers), such as proteins, nucleic acids, and starch, are formed by repetitive combinations of simple subunits. b. Students know the bonding characteristics of carbon that result in the formation of a large variety of structures ranging from simple hydrocarbons to complex polymers and biological molecules. c. Students know amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. f.* Students know the R-group structure of amino acids and know how they combine to form the polypeptide backbone structure of proteins. Page 2 Claudia Winkler Introduction In this activity students will be asked to compute the molar mass of Villin. To complete the activity student will have to know how to compute the molar mass of a chemical compound and to compute percentage by mass and by number of the various amino acids that make up villin. Students will also have to know how to account for the condensation bonds that occur between contiguous amino acids and to subtract the molar mass of the molecules of water that are formed in the peptide bonds. Required time to complete activity: 2 hours Planning time: 1 hour to make copies of students’ worksheet and a couple of overhead transparencies Material needed: paper, pen, calculator, periodic table Objective: • Knowing that villin is made of the following sequence of amino acids DEDFKAVFGMTRSAFANLPLWKQQNLKKEKGLFMLS 1. Compute the molar mass of villin. 2. Compute the percentage by number of each atom component. 3. Compute the percentage by mass of each atom component. Step 1: Identify the components of each amino-acid and the number of times that each amino acid appears in the Villin protein D * 2 = 2 * (4*O + 4*C + 6*H+N) = 8O + 8C + 12H + 2N E * 2 = 2* (5*C+8*H+4*O+N) = 10C + 16 H +8O + 2N F * 4 = 4 * (9*C+11*H+N+2*O) = 36C + 44H +4N + 8O K * 5= 5 * (6*C+14*H +2*N +2*O) = 30C + 70H +10N + 10O A * 3 = 3 * (3 *C + 7*H+ N+ 2*O) = 9C + 21H +3N + 6O V * 1 = 1* (5*C + 11*H + N+ 2*O) = 5C + 11H + N +2O G * 2 = 2* (5*C + 11*H + N + 2*O) = 10C + 22H + 2N + 4O M * 2 = 2 * (5*C+ 11*H+ N+ 2*O + S) = 10C + 22H +2N +4O + 2S T * 1 = 1* (4 *C+ 9*H + N+ 3*O) = 4C + 9H + N + 3O Page 3 Claudia Winkler R * 1 = 1 * (6*C+ 14* H + 4*N + 2*O) = 6C + 14H + 4N + 2O S * 2 = 2 * (3*C + 7*H + N + 3 *O) = 6C + 14H + 2N + 6O N * 2 = 2 * (4*C + 8*H + 2*N + 3* O) =8C + 16H + 4N + 6O L * 5 = 5 * (6 * C + 3 * H + N + 2 * O) = 30C + 15H + 5N +10O P * 1 = 1 * ( 5 *C + 9 * H + N + 2 * O) = 5C + 9H + N + 2O W * 1 = 1 * ( 11 * C + 12 * H + 2 * N + 2 * O ) = 11C + 12H + 2N + 2O Q * 2 = 2 * ( 5 * C + 10 * H + 2 * N + 3 * O) = 10C + 20H + 4N +6 O Step 2: Add all carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen, sulfur atoms. This will lead to: 79 Oxygen atoms 198 Carbon atoms 327 Hydrogen atoms 49 Nitrogen atoms 2 Sulfur atoms Step 3: Account for peptide bonds that occur between amino-acids. These bonds cause water molecules to be condensed away from the amino acid chain. A peptide bond occurs between two adjacent pairs. There are 36 amino acids linked by 35 peptide bonds. Each bond releases one molecule of water. A total of 35 * H2O molecules of water needs to be subtracted from the above numbers Total number of Hydrogen atoms = 327 – 35*2 = 257 Hydrogen atoms Total number of Oxygen atoms = 79 – 35 = 44 Oxygen atoms Page 4 Claudia Winkler Step 4: Compute molar mass of Villin knowing that: Molar mass of C = 12g/mol Molar mass of O = 16g/mol Molar mass of H = 1g/mol Molar mass of Nitrogen = 14g/mol Molar mass of Sulfur = 32 g/mol Each molecule of Villin contains: 44 Oxygen atoms 198 Carbon atoms 257 Hydrogen atoms 49 Nitrogen atoms 2 Sulfur atoms Each mole of Villin will contain the above number of moles of the respective atoms. We can now compute the molar mass of one mole of Villin: 44 mol O* 16g/mol O + 198 mol C * 12 g/mol C + 257 mol H * 1g/mol H + 49 mol N * 14 g/ mol N + 2 mol S *32 g/mol = 4087 g/mol Step 5 Compute the percentage by number of each atom component. The total number of atoms that make up a Villin molecule can be easily obtained adding the number of the respective Oxygen Hydrogen Carbon, Nitrogen and Sulfur atoms: 44 + 198 + 257 + 49 + 2 = 550 atoms. Page 5 Claudia Winkler Percentage Hydrogen / Total atoms = 257/550 * 100 = 46.72% Percentage Oxygen / Total atoms = 44/550 *100 = 8% Percentage Carbon / Total atoms = 198/550 *100 = 36% Percentage Nitrogen / Total atoms = 49/550 * 100 = 8.9 % Percentage Sulfur / Total atoms = 2/550 *100 = .36% Step 6 Compute the percentage by mass of each atom component. The molar mass of a Villin mole was computed in Step 4 as 4087 g/mol Percentage by mass of Hydrogen / Total mass = 257 mol H * 1 g/molH /4087 g/mol Villin * 100 = 6.29% Percentage by mass of Oxygen / Total mass = 44 mol O* 16 g/molO /4087 g/mol Villin *100 = 17.22% Percentage by mass of Carbon / Total mass = 198 mol C * 12 g/mol C/4087 g/mol Villin *100 = 58.14% Percentage by mass of Nitrogen / Total mass = 49 mol N * 14 g/mol N/4087 g/mol Villin * 100 = 16.78 % Percentage by mass of Sulfur / Total mass = 2 mol S * 32 g/mol S/4087 g/mol Villin *100 = 1.13 % Check for correctness by adding up all percentages: % H = 6.29% % O = 17.22% % C = 58.14% % N = 16.78% % S = 1.13% 6.29 + 17.11+ 58.14 + 16.78 + 1.13 = 99.45 % (this is because of rounding, as we rounded the molar masses of each element) Page 6 Claudia Winkler Molar Mass of Villin: Student’s activity Objective: • Knowing that villin is made of the following sequence of amino acids DEDFKAVFGMTRSAFANLPLWKQQNLKKEKGLFMLS Compute the molar mass of villin. Compute the percentage by number of each atom component. Compute the percentage by mass of each atom component. Step 1: Identify the components of each amino-acid and the number of times that each amino acid appears in the Villin protein. The next few pages give the structure and composition of each amino acid. D – Aspartic Acid Name Aspartic acid, Letter: D Abbreviation: Asp Page 7 Info Looks 4 oxygen 4 carbon 6 hydrogen 1 nitrogen Claudia Winkler E – Glutamic Acid Name Info Glutamic acid Letter: E Abbreviation: Glu 5 carbon 8 hydrogen 4 oxygen 1 nitrogen Looks F – Phenylalanine Name Info Phenylalanine Letter: F Abbreviation: Phe 9 carbon 11 hydrogen 1 nitrogen 2 oxygen Looks K – Lysine Name Info Lysine Letter: K Abbreviation: Lys 6 carbon 14 hydrogen 2 nitrogen 2 oxygen Page 8 Looks Claudia Winkler A – Alanine Name Info Alanine Letter: A Abbreviation: Ala 3 carbon 7 hydrogen 1 nitrogen 2 oxygen Looks V – Valine Name Info Valine Letter: V Abbreviation: Val 5 carbon 11 hydrogen 1 nitrogen 2 oxygen Looks G – Glycine Name Info Glycine Letter: G Abbreviation: Gly 5 carbon 11 hydrogen 1 nitrogen 2 oxygen Page 9 Looks Claudia Winkler M – Methionine Name Info Methionine Letter: M Abbreviation: Met 5 carbon 11 hydrogen 1 nitrogen 2 oxygen 1 suphur Looks T – Threonine Name Info Threonine Letter: T Abbreviation: Thr 4 carbon 9 hydrogen 1 nitrogen 3 oxygen Looks S – Serine Name Info Serine Letter: S Abbreviation: Ser 3 carbon 7 hydrogen 1 nitrogen 3 oxygen Page 10 Looks Claudia Winkler W – Tryptophan Name Info Tryptophan Letter: W Abbreviation: Trp 11 carbon 12 hydrogen 2 nitrogen 2 oxygen Looks Q – Glutamine Name Info Glutamine Letter: Q Abbreviation: Gln 5 carbon 10 hydrogen 2 nitrogen 3 oxygen Looks Count all the atoms that make up villin, by element. To make this task easier, count the individual amino-acids that make up villin and figure out how many times each of them appears. Knowing that villins’s sequence of amino acids is: DEDFKAVFGMTRSAFANLPLWKQQNLKKEKGLFMLS Identify all common amino acids and count all atoms. Show your work in a separate sheet of paper. Here is a hint: D * 2 = 2 * (4*O + 4*C + 6*H+N) = 8O + 8C + 12H + 2N E * 2 = 2* (5*C+8*H+4*O+N) = 10C + 16 H +8O + 2N. Page 11 Claudia Winkler Step 2: Add all carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen, sulfur atoms. This will lead to: ____ Oxygen atoms ____ Carbon atoms ____ Hydrogen atoms ____ Nitrogen atoms ____ Sulfur atoms Step 3: Account for peptide bonds that occur between amino-acids. These bonds cause water molecules to be condensed away from the amino acid chain. A peptide bond occurs between two adjacent pairs. There are 36 amino acids linked by 35 peptide bonds. Each bond releases one molecule of water. A total of ____ * H2O molecules of water needs to be subtracted from the above numbers Total number of Hydrogen atoms = ____ Total number of Oxygen atoms = ____ Step 4: Compute molar mass of Villin knowing that: Molar mass of C = ____ Molar mass of O = ____ Molar mass of H = ____ Molar mass of Nitrogen = ____ Molar mass of Sulfur = ____ Page 12 Claudia Winkler Each molecule of Villin contains: ____ Oxygen atoms ____ Carbon atoms ____ Hydrogen atoms ____ Nitrogen atoms ____ Sulfur atoms Each mole of Villin will contain the above number of moles of the respective atoms. We can now compute the molar mass of one mole of Villin: ____________________________ Step 5 Compute the percentage by number of each atom component. The total number of atoms that make up a Villin molecule can be easily obtained adding the number of the respective Oxygen Hydrogen Carbon, Nitrogen and Sulfur atoms: ____ Percentage Hydrogen / Total atoms = ____ Percentage Oxygen / Total atoms = ____ Percentage Carbon / Total atoms = ____ Percentage Nitrogen / Total atoms = ____ Percentage Sulfur / Total atoms = ____ Page 13 Claudia Winkler Step 6 Compute the percentage by mass of each atom component. The molar mass of a Villin mole was computed in Step 4 ____ Percentage by mass of Hydrogen / Total mass = ____ Percentage by mass of Oxygen / Total mass = ____ Percentage by mass of Carbon / Total mass = ____ Percentage by mass of Nitrogen / Total mass = ________ Percentage by mass of Sulfur / Total mass = ____ Check for correctness by adding up all percentages: % H = ____ % O = ____ % C = ____ % N = ____ % S = ____ Is your total equal 100%? Discuss reasons possible sources of error if your total sum differs from 100 by more than 2%. What did you learn in this lab? Page 14 Claudia Winkler