ME 215 Materials Science Quiz Solution - Vacancy & Diffusion
advertisement

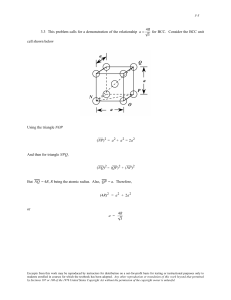
King Fahd University of Petroleum & Minerals MECHANICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT ME 215 : MATERIALS SCIENCE FOR ME Fall Semester 2006-2007 (061) Quiz # (SOLUTION) Name ___________________________ Mr. B. J. Abdul Aleem Student # _________________________ Saturday: November 11, 2006 Section: ME 215.01 Time Allowed: 25 minutes Problem 1 Calculate the energy for vacancy formation in silver, given that the equilibrium number of vacancy at 800°C is 3.6 × 1023 m−3. The atomic weight and density at 800°C for silver are 107.87 g/mole and 10.49 g/cm3, respectively. This problem calls for the computation of the energy for vacancy formation in silver. Upon examination of Equation (4.1), all parameters besides Q are given except N, the total number of v atomic sites. However, N is related to the density, (), Avogadro's number (N ), and the atomic A weight (A) according to Equation (4.2) as N = = 6.023 = 5.86 x 10 NA Ag AAg x 10 23 atoms / mol 10.49 g / cm 3 107.87 g / mol 22 3 28 3 atoms/cm = 5.86 x 10 atoms/m Now, taking natural logarithms of both sides of Equation (4.1), and, after some algebraic manipulation N QV = RT ln V N 3.60 x 10 23 m3 = 8.62 x 10 -5 eV/atom - K (1073 K) ln 28 m 3 5.86 x 10 = 1.11 eV/atom ME 215 – Quiz # 3 (061) Mr. Abdul Aleem 2 Problem 2 Carbon is allowed to diffuse through a steel plate 10 mm thick. The concentration of carbon at the two faces are 0.85 and 0.40 kg C/cm3 Fe, which are maintained constant. If the preexponential and activation energy are 6.2 × 10−7 m2/s and 800,000 J/mole, respectively, compute the temperature at which the diffusion flux is 6.3 × 10−10 kg/m2−s. This problem asks that we compute the temperature at which the diffusion flux is 6.3 x 10 -10 2 kg/m -s. Combining Equations (5.3) and (5.8) yields Q C J = Do exp d x RT Solving for T from this expression leads to Qd 1 T = R D o C ln Jx 1 80, 000 J / mol = 8.31 J / mol- K 7 2 3 6.2 x 10 m / s 0.45 kg / m ln 6.3 x 10 10 kg / m 2 - s 10 2 m = 900 K = 627C 2 (b) - List four important parameters that determine the degree to which the solute atoms replace or substitute the host atoms in forming a substitutional solid solution. (1) Atomic Size Factor (2) Crystal Structure (3) Electro negativity (4) Valences