Article - Nature
advertisement

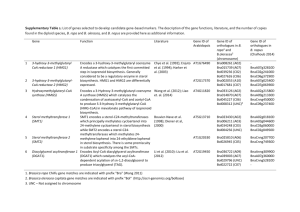
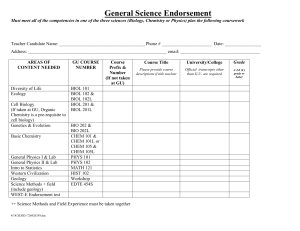
Supplementary Information Substrate Specificity of Benzamide Synthetase Involved in 4-Hydroxy-3-Nitrosobenzamide Biosynthesis Akio Noguchi, Sueharu Horinouchi#, and Yasuo Ohnishi* Department of Biotechnology, Graduate School of Agriculture and Life Sciences, The University of Tokyo. * Correspondence: Yasuo Ohnishi, Department of Biotechnology, Graduate School of Agriculture and Life Sciences, The University of Tokyo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-8657, Japan. E-mail: ayasuo@mail.ecc.u-tokyo.ac.jp # Deceased on 12th July 2009 1 Supplementary Figure S1. Phylogenetic analysis of Gn-ATs. The sequences used for alignment were those of Gn-ATs involved in secondary metabolite synthetic pathways in Streptomyces and other bacteria, as well as the asparagine synthetases from bacteria and mammals (see Table S1). An unrooted tree was constructed by the CLUSTALW multiple alignment program using the following settings: MATRIX blosum, GAPOPEN 10.0, GAPEXT 0.2, GAPDIST 8, MAXDIV 40, bootstrap counts 1000.1 Numbers indicate bootstrap values > 800. Bar = 0.1 amino acid substitutions per site. Among these phylogenetically related bacterial Gn-ATs, NspN,2 OxyD,3 SsfD,4 PcsA,5 PcsB,6 TsrC,7 PhzH-Pa,5 and PhzH-Pc6 had been evaluated for their function in secondary metabolite syntheses in vivo. Only NspN2 and PcsB6 had also been characterized in vitro. In contrast, ORF5,8 SioC, ORF1,9 SfaP, TcsG, FdmV,10 SanV,11 and LlpA12 had not yet been fully characterized. Their involvement in secondary metabolism has been suggested because they are encoded in biosynthetic gene clusters responsible for their respective compounds. GrhP,13 RubR, ORF11,14 and TblS, which belong to the same clade, have no catalytic Cys 2 residue, which is characteristic of the class II glutamine amidotransferase domain. This indicates that these proteins have lost their Gn-AT activity. Apart from the clade including NspN, ORF71x8,15 MoeF5,16 Ste10,17 ORF3, ORF4, ORF16,18 ORF18,19 and ORF2120 also seem to be involved in secondary metabolism processes, however these Gn-ATs have not yet been fully characterized. Asparagine synthetases (AsnB-Ec, AsnB-Vc, ASNS and AS), which catalyze the conversion of aspartic acid to asparagine, are phylogenetically distant from NspN. 3 Supplementary Table S1. Gn-AT enzymes used for phylogenetic analysis. a Amino acid sequence identity to NspN. b These proteins have no catalytic Cys, indicating a loss of Gn-AT activity. 4 REFERENCES 1. 2. 3. Thompson, J.D., Higgins, D.G. & Gibson, T.J. CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22, 4673-4680 (1994). Noguchi, A., Kitamura, T., Onaka, H., Horinouchi, S. & Ohnishi, Y. A copper-containing oxidase catalyzes C-nitrosation in nitrosobenzamide biosynthesis. Nat Chem Biol 6, 641-643 (2010). Zhang, W., Ames, B.D., Tsai, S.C. & Tang, Y. Engineered biosynthesis of a novel amidated polyketide, using the malonamyl-specific initiation module from the oxytetracycline polyketide synthase. Appl Environ Microbiol 72, 2573-2580 (2006). 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. Pickens, L.B. et al. Biochemical analysis of the biosynthetic pathway of an anticancer tetracycline SF2575. J Am Chem Soc 131, 17677-17689 (2009). Seco, E.M., Miranzo, D., Nieto, C. & Malpartida, F. The pcsA gene from Streptomyces diastaticus var. 108 encodes a polyene carboxamide synthase with broad substrate specificity for polyene amides biosynthesis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 85, 1797-1807 (2010). Miranzo, D., Seco, E.M., Cuesta, T. & Malpartida, F. Isolation and characterization of pcsB, the gene for a polyene carboxamide synthase that tailors pimaricin into AB-400. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 85, 1809-1819 (2010). Liao, R. et al. Thiopeptide biosynthesis featuring ribosomally synthesized precursor peptides and conserved posttranslational modifications. Chem Biol 16, 141-147 (2009). Rascher, A., Hu, Z., Buchanan, G.O., Reid, R. & Hutchinson, C.R. Insights into the biosynthesis of the benzoquinone ansamycins geldanamycin and herbimycin, obtained by gene sequencing and disruption. Appl Environ Microbiol 71, 4862-4871 (2005). Hu, Y. et al. Benzodiazepine biosynthesis in Streptomyces refuineus. Chem Biol 14, 691-701 (2007). Wendt-Pienkowski, E. et al. Cloning, sequencing, analysis, and heterologous expression of the fredericamycin biosynthetic gene cluster from Streptomyces griseus. J Am Chem Soc 127, 16442-16452 (2005). Zaleta-Rivera, K., Charkoudian, L.K., Ridley, C.P. & Khosla, C. Cloning, sequencing, heterologous expression, and mechanistic analysis of A-74528 biosynthesis. J Am Chem Soc 132, 9122-9128 (2010). 5 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. Lopez, P. et al. Isolation of the lysolipin gene cluster of Streptomyces tendae Tu 4042. Gene 461, 5-14 (2010). Li, A. & Piel, J. A gene cluster from a marine Streptomyces encoding the biosynthesis of the aromatic spiroketal polyketide griseorhodin A. Chem Biol 9, 1017-1026 (2002). Banskota, A.H. et al. TLN-05220, TLN-05223, new Echinosporamicin-type antibiotics, and proposed revision of the structure of bravomicins. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 62, 565-570 (2009). Stroeher, U.H., Parasivam, G., Dredge, B.K. & Manning, P.A. Novel Vibrio cholerae O139 genes involved in lipopolysaccharide biosynthesis. J Bacteriol 179, 2740-2747 (1997). Ostash, B., Saghatelian, A. & Walker, S. A streamlined metabolic pathway for the biosynthesis of moenomycin A. Chem Biol 14, 257-267 (2007). Wang, L.Y., Li, S.T. & Li, Y. Identification and characterization of a new exopolysaccharide biosynthesis gene cluster from Streptomyces. FEMS Microbiol Lett 220, 21-27 (2003). Galm, U. et al. The biosynthetic gene cluster of zorbamycin, a member of the bleomycin family of antitumor antibiotics, from Streptomyces flavoviridis ATCC 21892. Mol Biosyst 5, 77-90 (2009). Du, L., Sanchez, C., Chen, M., Edwards, D.J. & Shen, B. The biosynthetic gene cluster for the antitumor drug bleomycin from Streptomyces verticillus ATCC15003 supporting functional interactions between nonribosomal peptide synthetases and a polyketide synthase. Chem Biol 7, 623-642 (2000). Tao, M. et al. The tallysomycin biosynthetic gene cluster from Streptoalloteichus hindustanus E465-94 ATCC 31158 unveiling new insights into the biosynthesis of the bleomycin family of antitumor antibiotics. Mol Biosyst 3, 60-74 (2007). 6