Year 12 Human Biology Program 2015
advertisement
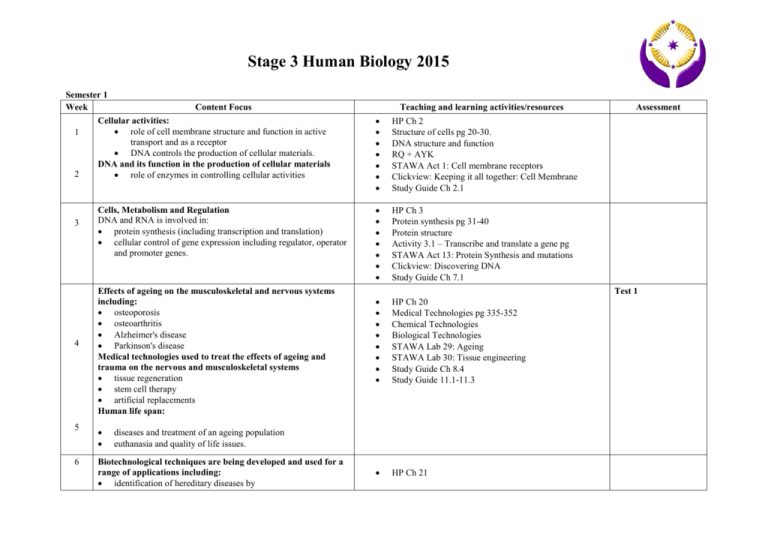
Stage 3 Human Biology 2015 Semester 1 Week Content Focus Cellular activities: role of cell membrane structure and function in active 1 transport and as a receptor DNA controls the production of cellular materials. DNA and its function in the production of cellular materials 2 role of enzymes in controlling cellular activities 3 4 Cells, Metabolism and Regulation DNA and RNA is involved in: protein synthesis (including transcription and translation) cellular control of gene expression including regulator, operator and promoter genes. Effects of ageing on the musculoskeletal and nervous systems including: osteoporosis osteoarthritis Alzheimer's disease Parkinson's disease Medical technologies used to treat the effects of ageing and trauma on the nervous and musculoskeletal systems tissue regeneration stem cell therapy artificial replacements Human life span: 5 6 Biotechnological techniques are being developed and used for a range of applications including: identification of hereditary diseases by Teaching and learning activities/resources HP Ch 2 Structure of cells pg 20-30. DNA structure and function RQ + AYK STAWA Act 1: Cell membrane receptors Clickview: Keeping it all together: Cell Membrane Study Guide Ch 2.1 HP Ch 3 Protein synthesis pg 31-40 Protein structure Activity 3.1 – Transcribe and translate a gene pg STAWA Act 13: Protein Synthesis and mutations Clickview: Discovering DNA Study Guide Ch 7.1 HP Ch 20 Medical Technologies pg 335-352 Chemical Technologies Biological Technologies STAWA Lab 29: Ageing STAWA Lab 30: Tissue engineering Study Guide Ch 8.4 Study Guide 11.1-11.3 HP Ch 21 Assessment Test 1 diseases and treatment of an ageing population euthanasia and quality of life issues. DNA sequencing profiling techniques PCR (polymerase chain reaction) genetic probes production of human proteins, hormones and vaccines by DNA recombinant techniques including restriction and ligase enzymes treatment of genetic disorders by gene therapy cell replacement therapy and tissue engineering by the cloning of stem cells Potential treatment related to individual variations: 7 8 1 information from the Human Genome providing new interventions for common dysfunctions/ disorders Body Systems Central and peripheral nervous system: brain (cerebrum, cerebellum, meninges, medulla oblongata, hypothalamus), spinal cord afferent and efferent systems structure of motor, sensory and inter-neurons the reflex arc including components and their functions in the transmission of messages Biotechnology pg353-373 STAWA Lab 9: Transgenesis and gene therapy STAWA Lab 10: DNA profiling STAWA Lab 11: Human Genome Project STAWA Lab 12:PCR – polymerase chain reaction Clickview: Discovering DNA Clickview: Gene Technology Clickview: Gene Technology Part1 Clickview: The Human Genome Project Study Guide 9.1 (Biotech in a Box Kit is booked November ) HP Ch 5 Nervous system pg 56-68 The brain and spinal cord Extension activity Activity 5.2 Phineas Gage STAWA Act 22: The brain Ch 6 Nervous Tissue Divisions of the nervous system Activity 6.1 Reflexes STAWA Act 23: Reflexes and reactions Clickview: Coordination and Control 1: Animals Study Guide Ch 8.1 The Tools of Biotechnology 2 3 4 5 Body Systems transmission of nerve impulses—generation and propagation control of movement and balance—areas and types of motor control of the body in the cerebrum and cerebellum innervation of muscular contraction. Autonomic nervous system: overview of divisions of the nervous system relationship of the Autonomic NS to the body’s nervous system divisions of the Autonomic NS and their effect on various body organs. HP Ch 7 Transmision of a nerve impulse The autonomic nervous system RQ + AYK Endocrine system: types and location of endocrine glands relationship between the hypothalamus and pituitary production site, target organ and effect of various hormones feedback loops involving endocrine activity regulation of metabolism, blood sugar and body fluid hormonal modes of action – cell recognition lipid soluble –steroid hormones and water soluble-amine hormones Comparison of hormones and nerves in terms of: speed, duration, transmission and specificity. HP Ch 4 Endocrine glands and hormones pg 41-55 Activity 4.1 Endocrine Dysfunction Activity 4.2 The discovery of Insulin RQ + AYK Study Guide The Practice of Human Biology - Investigation protocols: use a personally identified problem to formulate an hypothesis select methodology to plan and conduct a safe and ethical investigation into various aspects of the problem mathematically justify results and use others’ results to support findings justify conclusions taking into account errors and limitations in data prepare and present a balanced report, including discussion of limitations and biases, using information from scientifically reliable sources as well as own data. Approaches to investigating and communicating human biology use a problem identified by the student to formulate an hypothesis plan and conduct a safe and ethical investigation incorporating two different methods to collect data simple analysis of results including factors that influence the Review scientific methodology HP Ch 1 Pg 1-19 Activity 1.1 Validating Pasteur’s experiment RQ + AYK Clickview: Anatomy Functional Body Systems Test 2 Homeostasis: The body's response to vigorous exercise investigation, rates, percentages and frequencies 6 Homeostasis by feedback systems: components of a stimulus-response feedback model homeostatic mechanisms that control: body temperature body fluid concentration blood sugar gas concentrations blood pressure 7 physiological and behavioural mechanisms that influence the maintenance of homeostasis of the above conditions. HP Ch 9 Stimulus response model Pg 101-121 Thermoregulation STAWA Act 2: Introduction to homeostasis STAWA Act 5: Temperature control Clickview: Homeostasis Regulation of body fluids STAWA Act 3: Nephron structure and function STAWA Act 4: Water balance RQ + AYK HP Ch 10 Pg122-140 Regulation of blood sugar Regulation of gas concentrations Control of heart rate and blood pressure RQ + AYK STAWA Act 7: Control of breathing Study Guide Ch 2.2 HP Ch 11 Pg141-155 Study Guide Ch 6.1 STAWA Act 6: Diabetes diagnosis STAWA Act 8: Endocrines – when things go wrong Study Guide Ch 2.3 8 Control of homeostatic dysfunction and hormone replacement therapies to assist treatment of: hyper/hypothyroidism diabetes Risks, ethical concerns and benefits associated with interventions. 9 10 Homeostatic dysfunction and hormone replacement therapies Disruption of homeostasis: causes of disruption hormonal including insulin—diabetes behavioural including. drugs, excessive activity, eating habits disease including thyroid dysfunction treatments for disruption of homeostasis Revision of Content Test 3 Stage 3 Human Biology Semester 2 Week 1 2 3 4 7 8 Teaching and learning activities/resources Syllabus content Cells, Metabolism and Regulation Specific resistance: role of B cells, T cells, memory cells and plasma cells antibody and cell-mediated defence primary and secondary immune response passive and active immunity natural and artificial immunity role of antibiotics and antivirals. HP Ch 12 Pg156-175 Immune Response Types of immunity Vaccines Risks and ethical concerns RQ + AYK STAWA Act 24: Immunity – protection against invaders Study Guide 7.2 Gene expression: the effect of the environment on gene expression e.g. effect of UV light exposure on melanin production and effect of diet on adipose tissue role of epigenetics. mechanisms including histone modification and DNA methylation/acetylation case studies including twin studies Modes of inheritance and variation: polygenic inheritance including human skin colour (no dihybrid crosses) HP Ch 15 Inheritance pg 212-227 Activity 14.1 Polygenic inheritance RQ + AYK Study Guide 4.1 Video: View the on-line video from the Nova website. Activity: Epigenetics (from the Nova website, open the teachers guide, and classroom activity) www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/sciencenow/3411/02.html Gene pools: changes in allele frequencies due to: mutation natural selection random genetic drift including founder effect migration barriers to gene flow e.g. geographical and cultural incidence of genetic diseases in various populations including Tay-Sachs disease and sickle cell anaemia. HP Ch 16 Evidence of Evolution pg 263-275 RQ + AYK STAWA Act 18: Gene pools Clickview: Mechanisms of Evolution Clickview: Natural Selection: Its Place in Modern Society Study Guide 5.1 Speciation: - Theory of evolution by natural selection. refer to other researchers’ findings to analyse and HP Ch 17 HP Ch 18 Assessment Immunity SEMESTER 1 EXAMS Evolution report data using a variety of sources of supporting evidence and scientific concepts. 9 Evidence for evolution: comparative studies of DNA, protein sequences, anatomy including embryology, homologous structures and vestigial organs 10 The Fossil Record fossil formation geological dating and its limitations relative dating including stratigraphy, index fossils and fluorine dating absolute dating including C-14 dating awareness of problems with the fossil record. 11 Body Systems Skeleton—structure and function related to: macro and microscopic structure of bone and cartilage structure and functionality of major joint types Including ball and socket, hinge, pivot, gliding, immovable, cartiliaginous. 1 Body Systems Muscles—structure and function related to: macroscopic including the types (voluntary and involuntary) and resulting movements microscopic including myofibrils molecular including actin and myosin sliding filament theory of contraction. 2 Fossil evidence for evolution pg 251-265 Geological Time Scale Activity 17.1 Radioisotope dating Statigraphy Evidence for human evolution pg266-282 RQ + AYK Activity 18.1 Trends in evolution STAWA Lab 19: Fossils and fossil dating STAWA Lab 20: Evidence for evolution – comparative anatomy STAWA Lab 21: Evidence for evolution –molecular biology Clickview: Understanding Evolution: Inheritance and Change Study Guide 4.2 Study Guide 5.2 Test 4 HP Ch 13 Structure of the bone pg 176-195 Bones of the skeleton pg Joints RQ + AYK STAWA Act 25, 26, 27 Study Guide 8.3 HP Ch 14 Pg 196-211 STAWA Lab 28: Muscle movement Study Guide 8.2 Muscloskeletal Prac Test 3 Primate evolution trends relative size of cerebral cortex olfactory/optical shift gestation time and parental care mobility of the digits teeth shape and dental arrangements. 4 Hominin evolution trends 5 6 bipedalism—feet adaptations, hip and knee joints relative size of cerebral cortex prognathism and dentition spine and pelvis shape. Interaction of evolution mechanisms and the environment effects of environment on early hominid evolution significant cultural advances associated with australopithecines, Homo habilis, Homo erectus and early Homo sapiens including tool cultures and the change in lifestyles up to and including the development of agriculture. Informed debate about human origins. HP Ch 19 Primate evolution pg 283-303 Adaptatations for erect posture and bipedalism Evolutionary trends Cultural evolution of hominins Zoo excursion (Friday 17th August): complete worksheet on primate features suitable for use when introducing hominin features. HP Ch 20 Pg304-319 STAWA Lab 31: Hominin adaptations: Upright stance STAWA Lab 32: Hominin evolutionary trends: Brains and hands STAWA Lab 33: Hominin evolutionary trends: Measuring skulls STAWA Lab 34: Hominin evolutionary trends: Hominin and Pongid skulls STAWA Lab 35: Hominin evolutionary trends: Bipedalism Study Guide 10.1 and 10.2 Hominid Trends Cranial capacity HP Ch 21 Pg 320-334 Study Guide 10.3 7-8 Revision of Semester Content Test 5 9-10 Exams Semester 2 Exam Assessment Outline Stage 3 Human Biological Science Assessment type weighting Tasks Homeostasis: The body's response to vigorous exercise Investigation 20% (15–25%) The Tools of Biotechnology 5% 5% Musculoskeletal Prac Test 5% Cranial Capacity 5% Homeostatic dysfunction and hormone replacement therapies Response (extended) 20% (20–30%) Task weighting Hominid Trends 5% 5% Content and Chapter Reference Your Mark Content Approaches to investigating and communicating human biology: plan and conduct a safe and ethical investigation incorporating two different methods to collect data Homeostasis by feedback systems Human Perspectives Chapter 8 and 9 Biotechnological techniques are being developed and used for a range of applications. Complete Gel Electrophoresis Micropipette skills Uses for biotechnology Human Perspectives Chapter 21 Practical Assessment including the use of microscopes, specimens and models to identify structures and functions of the musculoskeletal system. Human Perspectives Chapter 12 and 13 Compare and contrast hominids trends through measurement of cranial capacity. Human Perspectives Chapter 18 and 19 In-class essay covering control of homeostatic dysfunction and hormone replacement therapies to assist treatment of: hyper/hypothyroidism control of reproduction and menopause risks, ethical concerns and benefits associated with interventions. Human Perspectives Chapter 10 In-class essay covering: Interaction of evolutionary mechanisms and the environment Evidence for evolution Human Perspectives Chapter 18 and 19 3A 3A 3B Evolution 5% In-class essay covering: Interaction of evolutionary mechanisms and the environment Evidence for evolution Human Perspectives Chapter 15 and 16 Immunity 5% In-class essay covering: External defence Specific and Non-specific defence 3B 3B 3A 3A 3B Tests and examinations 60% (40–60%) Human Perspectives Chapter 11 Test 1 3% Cells and Protein Synthesis Human Perspectives Chapter 2-3 3A/B Test 2 6% Technology and Nervous System Human Perspectives Chapter 20, 21, 5-7 3A/B Test 3 7% Homeostasis Human Perspectives Chapter 8-10 Semester 1 Examination 15% Semester 1 Content Test 4 7% Immunity, Inheritance, and Evolution Human Perspectives Chapter 11, 14-17 Test 5 7% Musculoskeletal and Evolutionary Trends Human Perspectives Chapter 12, 13, 18, 19 Semester 2 Examination 15% Semester 2 Content Resources: Biozone Biology Modular Workbook Series Anatomy and physiology. 2009 Biozone International Ltd Harrison, J. (2008). Our human species, 3rd edition. Ecopress Publications. Harrison, J. (2009). Human biological science stage 3 workbook. Ecopress Publications. Newton, T. & Joyce, A. (2009). Human perspectives book 2. McGraw-Hill Australia. Newton, T. & Joyce, A. (2009). The essential dictionary of human biology. McGraw-Hill Australia. Newton, T. & Joyce, A. (2009). Teacher resource CD-ROM. McGraw-Hill Australia. STAWA Exploring Human Biological Science Stage 3 Changing bodies 2009 3A 3A/B 3A/B 3B 3A/B