Surface morphology analysis and AFM study of silica gel
advertisement

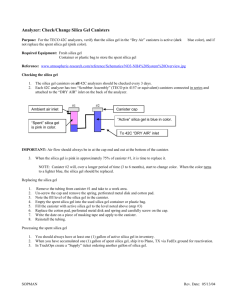
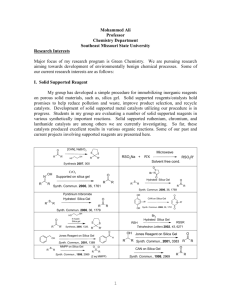
014 SURFACE MORPHOLOGY ANALYSIS AND AFM STUDY OF SILICA GEL PARTICLES AFTER MECHANICAL DRY COATING WITH MAGNESIUM STEARATE. Y. Ouabbas1, A.M. Danna1, G. Thomas1, B. Guilhot1, P. Grosseau1, M. Baron2, L. Galet2, A. Chamayou2 : Ecole Nationale Supérieure des Mines de Saint Etienne, Centre SPIN – LPMG -UMR CNRS 5148, 158 Cours Fauriel - 42023 Saint-Etienne, France. ouabbas@emse.fr 1 : Ecole Nationale Supérieure des Techniques Industrielles et des Mines d’Albi-Carmaux, Centre RAPSODEE - UMR CNRS 2392, Campus Jarlard - 81013 Albi, France. galet@enstimac.fr 2 ABSTRACT Dry coating technique has been realized to change the surface properties of silica gel particles (d50 = 55 µm) coated with different mass ratio of magnesium stearate (MgSt; d50 = 4.6 µm): 1%, 5% and 15%. The dry coating experiments were performed by using a high-speed dry impact blending coater. This device, called “the Hybridizer”, is manufactured by Nara Machinery from Japan. The surface morphology of the uncoated and coated silica gel particles were observed by environmental scanning electron microscopy (ESEM). The images have shown that a greater MgSt coverage was observed on the surface of silica gel as the MgSt mass ratio is increased to 15%. In addition, Atomic force microscopy (AFM) analysis revealed how this coating process makes possible to obtain a discrete and uniform dispersion of the MgSt particles. AFM studies were carried out with a scanning probe microscope Multimode Nanoscope IIIA (Digital Instruments/Veeco Metrology Group). All measurements have been carried out at ambient conditions in tapping mode with a phosphorus (n) doped Si probe (stiffness 40 N.m-1). Height, amplitude and phase images were simultaneously recorded for each sample. Beyond the classical height imaging, the phase contrast mode is quite efficient to exhibit the main surface property differences between de silica gel and MgSt. For the coated particles, the part of the image characterized by high phase angles can be attributed to the presence of MgSt layers on the surface of silica gel. Phase contrast image of silica gel coated with 15% of MgSt To examine the mechanism of interaction between silica gel and MgSt particles, The AFM Picoforce option has been used in contact mode with silicon nitride probe (stiffness 0.32 N.m -1). The adhesion forces were measured between the MgSt particles attached on the end of the cantilever and the different samples of uncoated and coated particles. For each sample 450 force curves were obtained. The mean adhesion force between the MgSt particles attached on the end of the cantilever and the MgSt sample (70 nN) was stronger than for the silica gel sample (8 nN). For the coated particles, the number of high adhesion increased as the mass ratio of MgSt increased. Phase contrast image of silica gel Phase contrast image of MgSt 350 MgST-Silica gel MgSt - SG+15%MgSt MgSt-MgSt 300 Frequency 250 200 150 100 50 0 0 50 100 150 200 250 adhesion force (nN) Adhesion force distributions for different particulate systems. Keywords dry coating, surface morphology, AFM phase imaging, adhesion force


![LAB 4 FB Safety [BH]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/007109339_1-10edf2f99cf9e3f5eb5770ce96c065cf-300x300.png)