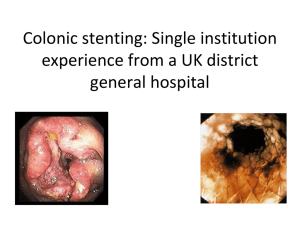
A novel lumen-apposing stent for endoscopic ultrasonography
advertisement

Placement of a fully covered metal stent (AXIOS) for EUS-guided drainage of peripancreactic fluid collections; a prospective European cohort study D. Walter1, U. Will2, A. Sanchez-Yague3, D. Brenke4, J. Hampe5, J.M. H. Wollny6, J.M. Esteban López-Jamar7, G. Jechart8, P. Vilmann9, J.B. Gornals10, H.S. Ullrich11, M. Fähndrich12, A. Herreros de Tejada13, F. Junquera14, H. Schlieker15, F. Gonzalez-Huix16, P.D. Siersema1, F.P. Vleggaar1 1 Dept. Gastroenterology and Hepatology, UMC Utrecht, Utrecht, Netherlands Dept. of Gastroenterology, Municipal Hospital, Gera, Germany 3 Endoscopy Unit, Hospital Costa del Sol, Marbella, Spain 4 Dept. of Internal Medicine II, Department of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Diabetology, SKK Teaching Hospital , Karlsruhe, Germany 5 Dept. of Internal Medicine I, UKSH, Kiel, Germany 6 Dept. of Internal Medicine and Gastroenterology, Medical Center Städte Region, Aachen, Germany 7 Dept. of Endoscopy, Hospital Clinico San Carlos, Madrid, Spain 8 Dept. of Gastroenterology, Klinikum Augsburg, Augsburg, Germany 9 Dept. of Surgery, University Hospital Herlev, Copenhagen, Denmark. 10 Dept. of Endoscopy, Hospital Universitari de Bellvitge-IDIBELL, Barcelona, Spain 11 Dept. of Internal Medicine I, Klinikum Asklepios Altona, Hamburg, Germany 12 Dept. of Interventional Endoscopy, Klinikum Dortmund, University Münster, Dortmund, Germany 13 Dept. of Gastroenterology, Puerta de Hierro University Hospital, Madrid, Spain 14 Dept. of Digestive Disease, Hospital Parc Tauli , Barcelona, Spain 15 Dept. of Gastroenterology, Klinikum Lippe-Detmold , Detmold, Germany 16 Endoscopy Unit, Clinica Girona, Girona, Spain 2 Endoscopic ultrasonography (EUS)-guided transmural drainage with placement of double-pigtail plastic stents is an important treatment for symptomatic peripancreatic fluid collections (PFC). The limitation of small-diameter plastic stents (7/10F) is the high risk of stent occlusion, especially in PFCs containing necrotic debris. Stent occlusion may result in infection and delayed PFC resolution. A novel large-diameter (10/15mm) fully-covered self- expanding metal stent, the AXIOS stent, has been developed to overcome these limitations. We evaluated technical and clinical success, stent migration and safety of EUS-guided PFC drainage using the AXIOS stent. From May 2011 until November 2012 patients who underwent EUS-guided drainage of PFCs with the AXIOS stent in 16 European medical centers were prospectively enrolled in a web-based database. In total, 62 patients (39 men, median age 54 (range 22 - 88) years) were included. PFCs were classified as walled-of pancreatic necrosis (n=47) or pancreatic pseudocyst (n=15) and almost half of the PFCs were infected (n=29; 47%). The median diameter of the PFC was 90 mm (range 40-230). A transgastric approach was used in the 59 patients (94%) and in 3 patients (6%) a transduodenal drainage was performed. Stent placement was technically successful in 61 patients (98%) while in 1 patient the entire stent was deployed inside the PFC and was removed during a subsequent endoscopy. Resolution of the PFC was achieved in 51 patients (82%) after a median of 29 days (range 1-136) days. In 5 patients (8%), the PFC has not yet been resolved, 3 patients (5%) required surgery because of severe sepsis, 1 patient (2%) died due to an unrelated cause before resolution and 2 patients (3%) were lost to follow up. Stent removal was successfully performed in 43 patients (70%) after a median of 32 days (range 2-178), 13 stents (21%) are still in situ, 4 stents (6%) dislodged during endoscopic transmural necrosectomy and 2 stents (3%) migrated to the GI-tract without complications. Stent removal was rated as easy in 42 patients (98%), but in 1 patient hyperplastic tissue ingrowth made removal difficult. In total, 13 major complications were reported in 12 patients (19%), including stent dislodgement (n=4), infection of the PFC (n=4), stent migration (n=2), bleeding (n=1), retroperitoneal abscess (n=1) and abdominal pain after stent removal (n=1). We concluded that placement and removal of the AXIOS stent is technically feasible for drainage of PFCs with an acceptable complication rate. Clinical success seems promising but further studies with longer follow-up and a direct comparison with plastic stents are needed.