Mapping
advertisement

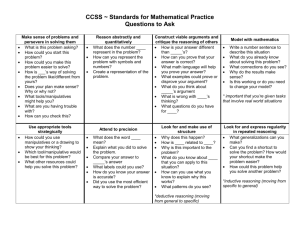
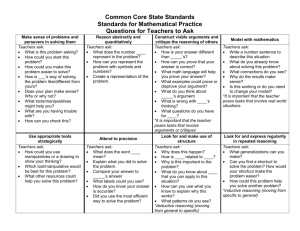
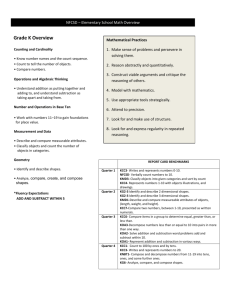
Horizontal Curriculum Mapping 2012/2013 Math Common Core Standards Kindergarten Dates Aug. 6-7 Aug. 8-10 Aug. 13-17 Aug. 20-24 Aug. 27-31 Concept (Big Ideas) Focus Standards Including Standard Type (K), (R), (S), (P) PD & Opening Day Start Smart Readiness Compare & Sort K.MD.3 (S) Knowledge Targets Know how to count objects. Classify objects according to attributes. Understand >, <, = Reasoning Targets Classify objects by attributes. Sort into groups. Compare & Sort Numbers 0 to 5 K.CC.1(K) Knowledge Targets Count from 0-5 Count from 0-10 Count from 0-20 Count from 0-50 Count from 0-100 Count by tens to 100 KCC.3(K) Knowledge Targets Write numbers 0-20 Count numbers 0-20 Count 0-20 objects with one to one correspondence and write the number. I Can Statements Critical Vocabulary I can compare and sort objects by attribute. Classify (alike, different, same number, more than, less than) Count Sort Chapter 1 Success Maker, Compass Literature List, CD-Rom Manipulatives, Work Books Count Sequence(order) How Many? Identify, Greater than, less than, or equal Number Words (Zero-Five) Chapter 2 Success Maker, Compass Literature List, CD-Rom Manipulatives, Work Books I can identify a group with more, less, or equal. I can name recognize and count the numbers (0,1,2,3,4,5) Instructional Resources K.CC.4(P) Knowledge Targets Count objects with one to one correspondence. Understand that the last number name said tells the number of objects counted. Understand that the arrangement of the objects does not change the number of objects. Understand that each successive number refers to a quantity that is one larger. K.CC.5 (P) Knowledge Targets Count up to 20 items arranged in lines, a rectangular array, or a circle. Count as many as 10 items in a scattered configuration. Given a number from 1-20, count out that many objects. K.CC.6(R) Knowledge Targets Understand Vocabulary terms: equal, greater than, less than Reasoning Targets Use matching and counting strategies to identify whether a group is greater than, less than, or equal. K.CC.7(R) Knowledge Targets Understand Vocabulary terms: equal, greater than, less than Reasoning Targets Use matching and counting strategies to identify whether a number is greater than, less than, or equal to another number. Sept. 3-7 Sept. 10-14 Sept. 17-21 Numbers 0 to 5 Numbers 0 to 5 Positions & Patterns K Sept. 24-28 Sept. 30 – Oct. 5 Positions & Patterns Numbers to 10 K.G.1 (R) Knowledge Targets Identify objects in the environment and name their shape. Use position words to describe objects in the environment. I can identify a pattern above, below, beside, in front of, behind, and next to. After, before, Top, middle, bottom, Over, under Pattern(lesson 3-4) Predict(Lesson 3-9) K.CC.1 (k)Knowledge Targets Count from 0-5 Count from 0-10 Count from 0-20 Count from 0-50 Count from 0-100 Count by tens to 100 I can name, recognize and count the numbers 0-10. Count sequence How Many? Identify, Greater than, less than, or equal Number words (six-ten) Ordinal numbers K.CC.3(K) Knowledge Targets Write numbers 0-20 Count numbers 0-20 Count 0-20 objects with one to one correspondence and write the number. K.CC.4 (P) Knowledge Targets Count objects with one to one correspondence. Understand that the last number name said tells the number of objects counted. Understand that the arrangement of the objects does not change the number of objects. Understand that each Chapter 3 Success Maker, Compass Literature List, CD-Rom Manipulatives, Work Books Common Assessment 1 Chapter 4 Success Maker, Compass Literature List, CD-Rom Manipulatives, Work Books successive number refers to a quantity that is one larger K.CC.5 (P) Knowledge Targets Count up to 20 items arranged in lines, a rectangular array, or a circle. Count as many as 10 items in a scattered configuration. Given a number from 1-20, count out that many objects K.CC.6(R) Knowledge Targets Understand Vocabulary terms: equal, greater than, less than Reasoning Targets Use matching and counting strategies to identify whether a group is greater than, less than, or equal. K.CC7(R) Understand Vocabulary terms: equal, greater than, less than Reasoning Targets Use matching and counting strategies to identify whether a number is greater than, less than, or equal to another number. Oct. 8-12 Numbers to 10 Oct. 15-19 Oct. 22-26 Numbers to 10 Graphs Know how to count objects. Classify objects according to attributes. Understand >, <, = Reasoning Targets Classify objects by attributes. Sort into groups. Knowledge Targets Know how to count objects. Classify objects according I can make and read a graph. Data,graph,survey picture graph real graph, Chapter 5 Success Maker, Compass Literature List, CD-Rom to attributes. Understand >, <, = Manipulatives, Work Books Reasoning Targets Oct. 29Nov. 2 Nov. 5-9 Classify objects by attributes. Sort into groups. Graphs Numbers to 20 K.CC.1(K) Knowledge Targets Count from 0-5 Count from 0-10 Count from 0-20 Count from 0-50 Count from 0-100 Count by tens to 100 K.CC.2(K) Knowledge Targets Given any number within the known sequence (0100)– count forward K.CC.3(K) Knowledge Targets Write numbers 0-20 Count numbers 0-20 Count 0-20 objects with one to one correspondence and write the number. K.CC.4 (P) Knowledge Targets a. Count objects with one to one correspondence. b. Understand that the last number name said tells the number of objects counted. Understand that the arrangement of the objects does not change the number of objects. Understand that each successive number refers to a quantity that is one larger I can name, recognize and count objects and numbers to 20. Count sequence How Many? Identify, Greater than, less than, or equal Count forward Number Words (eleventwenty) Chapter 6 Success Maker, Compass Literature List, CD-Rom Manipulatives, Work Books K.CC 5(P) Knowledge Targets Count up to 20 items arranged in lines, a rectangular array, or a circle. Count as many as 10 items in a scattered configuration. Given a number from 1-20, count out that many objects. K.CC.6(R) Knowledge Targets Understand Vocabulary terms: equal, greater than, less than Reasoning Targets Use matching and counting strategies to identify whether a group is greater than, less than, or equal. K.CC 7(R) Knowledge Targets Understand Vocabulary terms: equal, greater than, less than Reasoning Targets Use matching and counting strategies to identify whether a number is greater than, less than, or equal to another number. Nov. 12-16 Nov. 19-23 Nov. 26-30 Numbers to 20 Numbers to 20 Numbers to 20 Dec. 3-7 Measurement K.MD.1 (K) Knowledge Targets (Kmd.1) Know the word attribute Know that objects have measurable attributes Describe objects by the attributes of length and weight using related terms. Identify terms related to length and weight such as: long, short, heavy, light I can identify units of length, weight, capacity, temperature and area. Length weight. attributes temperature, Area, Capacity Chapter 7 Success Maker, Compass Literature List, CD-Rom Manipulatives, Work Books Reasoning Targets discriminate between lengths using long and short discriminate between weights using heavy and light K.MD 2 (R) Knowledge Targets (Kmd.2 Understand measurable attributes, such as shorter, taller Reasoning Targets compare/contrast objects with common measurable attributes, such as shorter/taller. Dec. 10-14 Dec. 17-21 Measurement Numbers Beyond 20 Jan. 2-4 Numbers Beyond 20 Jan. 7-11 Numbers Beyond 20 K.CC.1(K) Count from 0-5 Count from 0-10 Count from 0-20 Count from 0-50 Count from 0-100 Count by tens to 100 I can identify numbers beyond 20. Count sequence How Many?(About, Estimate) Greater than, less than, or equal Count forward Chapter 8 Success Maker, Compass Literature List, CD-Rom Manipulatives, Work Books Common Assessment 2 Knowledge Targets (Kcc.2) Given any number within the known sequence (0-100)– count forward Knowledge Targets (Kcc.4) Count objects with one to one correspondence. Understand that the last number name said tells the number of objects counted. Understand that the arrangement of the objects does not change the number of objects. Understand that each successive number refers to a quantity Knowledge Targets( Kcc.5) Count up to 20 items arranged in lines, a rectangular array, or a circle. Count as many as 10 items in a scattered configuration. Given a number from 1-20, count out that many objects. Knowledge Targets (Kcc.6) Understand Vocabulary terms: equal, greater than, less than Reasoning Targets Use matching and counting strategies to identify whether a group is greater than, less than, or equal. Knowledge Targets Kcc.7 Understand Vocabulary terms: equal, greater than, less than Reasoning Targets Use matching and counting strategies to identify whether a number is greater than, less than, or equal to another number. Jan. 14-18 Addition Knowledge Targets (KOA.1) Know Key words and concepts for addition and subtraction. Reasoning Targets Represent addition and subtraction with mental images, verbal explanations, expressions, or equations. Performance Skills Targets Represent addition and subtraction stories using objects, drawings, fingers, sounds, or acting. Knowledge Targets (KOA.2) I can add objects. Understand addition (Plus Sign, Join, In all) Solve addition Equal values Pairs Chapter 11 Success Maker, Compass Literature List, CD-Rom Manipulatives, Work Books Know key words for addition and subtraction. Reasoning Targets Evaluate word problems to determine the operation needed. Performance Skills Targets Represent word problems with objects or drawings. Jan. 21-25 Addition Knowledge Targets (KOA.3) Know the value of each number Know “equal” values Know the meaning of pairs Reasoning Targets Evaluate addition with mental images, verbal explanations, expressions, or equations Performance Skills Targets Decompose numbers, less than or equal to 10, into a pair of sets using objects or drawings then record each decomposition using a drawing or equation. Knowledge Targets (KOA.4) Know how to count forward from a given number 1-9 Reasoning Targets Evaluate the addition of numbers forward to the sum of 10 Performance Skills Targets Using a given number add on to make 10 by using objects or drawings then record the answer with a drawing or equation Jan. 28 – Feb. 1 Addition Knowledge Targets (KOA.5) Fluently add within 5 Fluently subtract within 5 Knowledge Targets (KNBT.1) Be able to count 0-19 Recognize numbers 11-19 Understand tens and ones (place value) Reasoning Targets Discriminate between tens and ones. Performance Skills Targets Model numbers 11 to 19 using objects or drawings to represent tens and ones Record composition or decomposition using a drawing or equation Feb. 4-8 Addition Feb. 11-15 Subtraction K.OA.1 (P) Know Key words and concepts for addition and subtraction. Reasoning Targets Represent addition and subtraction with mental images, verbal explanations, expressions, or equations. Performance Skills Targets Represent addition and subtraction stories using objects, drawings, fingers, sounds, or acting. K.OA.2 (R) Know key words for addition and subtraction. Reasoning Targets Evaluate word problems to determine the operation needed. Performance Skills Targets Represent word problems with objects or drawings. K.OA 3 (P) Know the value of each number Know “equal” values Know the meaning of pairs Reasoning Targets Evaluate addition with I can subtract objects. understand subtraction (Minus sign, subtact, are left, Solve subtraction Equal values/sign Pairs Chapter 12 Success Maker, Compass Literature List, CD-Rom Manipulatives, Work Books mental images, verbal explanations, expressions, or equations Performance Skills Targets Decompose numbers, less than or equal to 10, into a pair of sets using objects or drawings then record each decomposition using a drawing or equation. K.OA.4 (R) Know how to count forward from a given number 1-9 Reasoning Targets Evaluate the addition of numbers forward to the sum of 10 Performance Skills Targets Using a given number add on to make 10 by using objects or drawings then record the answer with a drawing or equation. K.OA.5 (K) Fluently add within 5 Fluently subtract within 5 K.NBT.1(P) Be able to count 0-19 Recognize numbers 11-19 Understand tens and ones (place value) Reasoning Targets Discriminate between tens and ones. Performance Skills Targets Model numbers 11 to 19 using objects or drawings to represent tens and ones Record composition or decomposition using a drawing or equation Feb. 18-22 Feb. 25 – Mar. 1 Mar. 4-8 Mar. 11-15 Subtraction Subtraction Subtraction Using Time I can tell time to the hour. Hour, clock, o’clock Morning, afternoon, evening, Common Assessment 3 Chapter 9 Success Maker, Compass Mar. 18-22 Mar. 25-29 Using Time Geometric Figures K.G.1(R) Identify objects in the environment and name their shape. Use position words to describe objects in the environment. K.G.2 (K) Recognize two-dimensional shapes (any position or size) Recognize threedimensional shapes (any position or size) K.G.3(K) Recognize two-dimensional shapes (lying in a plane, “flat”) Recognize threedimensional shapes (“solid”) K.G.4(R) Recognize two-dimensional shapes Recognize threedimensional shapes Identify and count number of sides Identify and count number of vertices. Identify sides of equal length Reasoning Targets Describe similarities and differences of various twoand three-dimensional shapes Analyze two-dimensional shapes, in different sizes and orientations. I can identify and sort two dimensional shapes and three dimensional shapes. today, yesterday, tomorrow, week, month, year Literature List, CD-Rom Manipulatives, Work Books squares, circles, triangles, rectangles, hexagons, cubes, cones, cylinders, and spheres (round) Identify shapes as twodimensional (lying in a plane, “flat”) or three-dimensional shapes(“solid”). Analyze Model Simple and larger shapes. Chapter 10 Success Maker, Compass Literature List, CD-Rom Manipulatives, Work Books Compare two-dimensional shapes, in different sizes and orientations, using informal language to describe their similarities, differences, parts (e.g. number of sides and vertices/”corners”) and other attributes (e.g. having sides of equal length). Analyze three-dimensional shapes, in different sizes and orientations. Compare three-dimensional shapes, in different sizes and orientations, using informal language to describe their similarities, differences, parts (e.g. number of sides and vertices/”corners”) and other attributes (e.g. having sides of equal length). K.G.5 (P) Recognize and identify (square, circles, triangles, rectangles, hexagons, cubes, cones, cylinders, spheres) Identify shapes in the real world Reasoning Targets Analyze the attributes of real world objects to identify shapes. Performance Skills Targets Construct shapes from components (e.g., sticks and clay balls) Draw shapes K.G.6(P) Identify the attributes of shapes Reasoning Targets Analyze which simple shapes can be put together to compose a new or larger shape. Performance Skills Targets Compose a new or larger shape using more than one simple shape. Apr. 1-5 Spring Break Apr. 8-12 Apr. 15-19 Apr. 22-26 Apr. 29May 3 May 6-10 May 13-17 May 20-21 Geometric Figures End of Year Review End of Year Review Looking Ahead Testing 21 Closing Day