ACTIVITY SERIES
advertisement

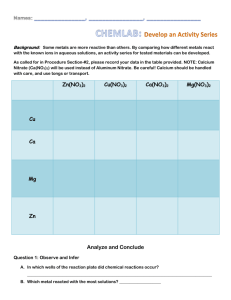
ACTIVITY SERIES Introduction Oxidation-reduction reactions, also known as redox reactions, comprise an extremely important area of study in chemistry. These reactions provide energy in electrochemical cells and have a veriety of commercial uses in batteries and solar cells. In addition, oxidation-reduction reactions are involved in rusting, cleaning agents, photography, and many other processes. Redox reactions can be thought of as reactions in which electrons are exchanged between one species that is oxidized and another that is recuded. Reduction involves the gain of electrons, while oxidation involves the loss of electrons. A reduction reaction for a metal ion can be written in the following manner: *Diagram* The oxidation reaction is written: *Diagram* *MR. STREIB: Fill in blank spots with correct characters* ____ is typically a metal with +n oxidation state, and n represents the number of electrons (e-) gained. _____ is the metal in its reduced form. An activity series of metals is a list that ranks metals accroding to their relative activity. Metals at the top of the list are oxidized most readily to their metallic ion. They tend to remain in ionic ____ form. Conversely, metals at the bottom of the list are oxidized with difficulty. Their metallic ion is relatively active so they tend to be in the reduced ____ form. In his investigation, you will establish any activity series based on the ease with which metallic ions are reduced. The ions to be studied are Cu2+, Fe2+, H+, Mg2+, Ag+, and Zn2+. The metals to be studied are Zn, Cu, Mg, and Fe. Pre-Lab Discussion Read the entire laboratory investigation and the relevant pages of your textbook. Then answer the questions that follow. 1. Define the terms oxidation and reduction. ________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 2. Are metallic ions the oxidized or reduced form of metals? Explain. ____________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 3. What safety hazards are involved in this investigation and what precautions should be followed? _________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 4. What will be the major information gained from this investigation? ___________ __________________________________________________________________ 5. Write an example of a typical reduction half reaction for a metal ion. __________ __________________________________________________________________ Problem Can an activity series for metals be developed based on the reduction of certain ions in solution? Materials chemical splash goggles laboratory apron latex gloves well plate marking pen 6 micropipets, filled with the following solutions: magnesium sulfate (MgSO4), 0.1 M copper sulfate (CuSO4), 0.1 M silver nitrate (AgNO3), 0.1 M zinc sulfate (ZnSO4), 0.1 M iron sulfate (FeSO4), 0.1 M sulfuric acid (H2SO4), 3.0 M steel wool tweezers zinc (Zn) strip copper (Cu) strip magnesium (Mg) strip iron (Fe) strip Safety Wear your goggles and lab apron at all times during the investigation. Sulfuric acid is extremely corrosive. Silver nitrate is toxic if ingested. It will cause stains to skin and clothing. Wear gloves when handling silver nitrate or sulfuric acid. Wash any area of contact with plenty of cold water. Procedure 1. Put on your goggles and lab apron. Set up and label the 24-well reaction plate as shown in Figure 58-1. Place the well plate on a sheet of white paper so you can more easily view the dark precipitates. *Diagram* Figure 58-1 2. 3. 4. 5. Put on your latex gloves. Using the appropriate micropipet, place 20 drops of 0.1 M zinc sulfate solution into the four wells in column 1. In a similar fashion, place 20 drops each of 3.0 M sulfuric acid, iron sulfate, silver nitrate, copper sulfate, and magnesium sulfate into the wells in columns 26 respectively. CAUTION: Sulfuric acid is extremely corrosive. Silver nitrate is toxic if ingested. It will stain skin and clothing. Wear gloves when handling these solutions. Wash any spills with plenty of cold water and tell your teacher. Using steel wool, clean strips of zinc, copper, magnesium, and iron. Place the strips in wells A1-D1 as shown in Figure 58-1. Wait for two minutes and check for a reaction. Record your observations in the Data Table. Rinse and dry the strips. In a similar fashion, repeat the process for columns 2-6. Continue to record your observations in the Data Table. Using a micropipet, dispose of the contents of the wells in column 4 in a labeled container provided by your teacher. Rinse the rest of the solutions down the drain. Clean up your work area and wash your hands before leaving the laboratory. Observations DATA TABLE 1 ZnSO4 A B C D 2 H2SO4 3 FeSO4 4 AgNO3 5 CuSO4 6 MgSO4 Zn Cu Mg Fe Critical Thinking: Analysis and Conclusions 1. Which metal reacted with the largest number of solutions? (Interpreting data) ___ __________________________________________________________________ 2. Which metal was the least reactive? (Interpreting data) _____________________ __________________________________________________________________ 3. Which metal(s) reacted with sulfuric acid? (Interpreting data) _______________ __________________________________________________________________ 4. Which metal ion reacted with all metals and what is the significance of these results? (Drawing conclusions) ________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 5. Rank the positive ions from the most easily recuded to least easily reduced and write the reduction half reactions for each. (Making comparisons) __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ Critical Thinking: Applications 1. Magnesium blocks are often attached to iron storage tanks by a wire prior to placing these tanks underground. What is the purpose of this? (Developing hypotheses) ________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 2. By convention, eight metals (ruthenium, rhodium, palladium, silver, osmium, iridium, platinum, and gold) have been classified as “precious.” Would you expect them to be easy or difficult to oxidize? (Making judgements) ___________ __________________________________________________________________ 3. The element fluorine is one of the most reactive elements. Predict where it might fit in the list in Analysis and Conculsions Question 5. (Hint: it reacts with metallic silver to make silver fluoride.) (Making predictions) _______________________ __________________________________________________________________ Going Further 1. There are a number of “sacrificial” metals used to protect other metals. If possible, contact boat, boat motor, and metal fabricators, find out how these metals are utilized, then do a report on the topic.