Chemistry 199 - Oregon State University
advertisement

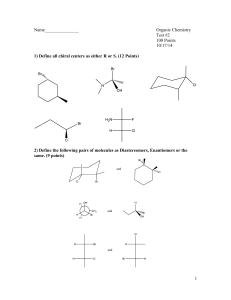
Chemistry 123 Worksheet 10 Notes 1. Spring 2004 May 26, 2004 Oregon State University Dr. Richard Nafshun Draw the line structure of an alkane that contains ten carbon atoms. What is the chemical formula of this compound? What is the condensed structural formula of this compound? Draw the line structures of two isomers of this compound. What are their chemical formulae (explain)? What are their condensed structural formulae? What are the names of these three structures? C10H22 (CnH2n+2) CH3(CH2)8CH3 C10H22 (CnH2n+2) CH3CH(CH3)(CH2)6CH3 C10H22 (CnH2n+2) CH3CH2CH(CH3)(CH2)5CH3 decane 2-methyl nonane 3-methyl nonane These are three isomers of C10H22 (there are many more). 2. Sketch an alkene that contains three carbon atoms. Name it. Write a reaction for your alkene and Br2 in UV. Br + Br2 (in UV) → propene Br 1,2-dibromopropane This reaction is an example of the addition to an alkene. The pi-bond is broken. 3. Sketch an alkyne that contains three carbon atoms. Name it. Write a reaction for your alkyne and two moles of Cl2 in UV. Cl Cl + propyne 2 Cl2 (in UV) → Cl Cl 1,1,2,2-tetrachloropropane 4. Sketch an alcohol that contains six carbon atoms. OH 2-hexanol Sketch a carboxylic acid that contains five carbon atoms. O OH (Name happens to be pentanoic acid) Sketch an aldehyde that contains six carbon atoms. O H (Name happens to be hexanal) Sketch a ketone that contains five carbon atoms. O (Name happens to be 2-pentanone) Sketch an ether that contains three carbon atoms. O (Name happens to be ethyl methyl ether) 5. Sketch an ester that contains six carbon atoms. Identify the alcohol and carboxylic acid that form this ester with the loss of water. O O One of the six-carbon esters... O OH and the alcohol... HO and the carboxylic acid that can produce it. 6. Sketch a carboxylic acid that is a benzene derivative. Sketch the ester that is formed when your carboxylic acid reacts with ethanol. O O OH O OH Benzoic acid (the carboxylic acid) 7. ethanol the ester formed from benzoic acid and ethanol Sketch an amine that contains six atoms. Sketch the amide that is formed when your amine reacts with ethanol acetic acid (note this change). N O N A six-carbon amine 8. O OH acetic acid the amide formed What is meant by a condensation reaction? Give an example. Water is lost during a condensation reaction. Examples include: the formation of an ester from an alcohol and a carboxylic acid, the formation of an amide from an amine and a carboxylic acid. 9. What is meant by an addition reaction? Give an example. Addition is to make an addition to a molecule. An example is the addition of a small molecule (such as Br2) to an alkene. Br + Br2 propene 10. (in UV) → Br 1,2-dibromopropane What is meant by a substitution reaction? Give an example of one. Substitution is to substitute an atom on a molecule. An example is electrophilic aromatic substitution. Cl + in the presence of AlCl3 → + HCl 11. The reaction of hydrochloric acid and ethene produces: HCl Cl → + 12. C6H12O6 (aq) 2 CH3CH2OH (aq) + 2 CO2 (g) occurs in the absence of air and in the presence of yeast. This is fermentation. 13. The building blocks of proteins are amino acids. 14. What is chiral? Sketch a molecule that contains three chiral carbons. A molecule is chiral if it cannot be superimposed on its mirror image. A carbon in a molecule is chiral if it has four different groups attached to it. CH2BrF is not chiral. CHBrClF is. 15. What are the products of benzene and chloroethane in the presence of AlCl3? Cl in the presence of AlCl3 → + 16. Sketch Ala-Ala-Gly-Cys-Tyr. H R1 O H R2 O H R3 O H R4 O H R5 O H N C C N C C N C C N C C N C C OH H H H H Where: R1 is CH3 R2 is CH3 R3 is H R4 is CH2SH R5 is CH2 OH H + HCl 17. Write the mechanism for the electrophilic aromatic substitution of benzene with 3chloropentane in the presence of AlCl3. H H H H H H Cl + in the presence of AlCl3 → Step1: The catalyst strips Cl- from 3-chloropentane: Cl + AlCl3 → + AlCl4- Step 2: The electrophile attacks the benzene ring. The new bond is formed using a pair of pi-electrons from benzene: H H H H H H Step 3: The leaving group H+ leaves. The pi-electrons are returned: + H H H H H H Step 4: The catalyst is regenerated: AlCl4- + H+ → AlCl3 + HCl Net Reaction: H H H H H H Cl + in the presence of AlCl3 → H H H H H 18. + HCl What polymer is formed by the reaction of HOCH2OH and HOOCCH2CH2CH2CH2COOH? This is a condensation polymerization. Water is lost between the alcohol and carboxylic acid: O O O O || || || || HOCH2OH + HOCCH2CH2CH2CH2COH → HOCH2OCCH2CH2CH2CH2COH water will leave The carboxylic acid group on the right is still in tact and will react with an alcohol group from another HOCH2OH molecule. The alcohol group on the left is still in tact and will react with a carboxylic acid group from another HOOCCH2CH2CH2CH2COOH molecule. The polymer may be represented as: O O || || -[-CH2OCCH2CH2CH2CH2CO-]nWhere n is a large number representing a large number of these repeat units make up the polymer. 19. Define: trans-, unsaturated, saturated, and omega-3 fats. What is meant by partially hydrogenated vegetable oil? trans- fats have the trans- conformation about a double bond. unsaturated fats have double bonds (they are not saturated with hydrogens). saturated fats have no double bonds (any double bonds have been saturated with hydrogen). omega-3 fats have a double bond located at the third carbon from the end of the chain. The term omega-3 is used because omega indicates the first carbon at the end of the chain and the 3 indicates the third carbon atom in. partially hydrogenated vegetable oil some, but not all, of the double bonds present in the carbon chains have been hydrogenated (had hydrogen added across the pi-bond). 20. What polymer is formed by the reaction of a radical initiator and CF(C6H5)CF2? -[-CF(C6H5)CF2-]nThe radical initiator breaks the pi-bond in the monomer causing it to become a larger radical and attacking another monomer unit. F F C F R C C F F + monomer F C R• initiator → new, larger, radical (The dot inside the right carbon is to represent the radical electron) (This new radical will attack a monomer unit and this process will continue...) 21. What polymer is formed by the reaction of HOOCH2CH2CH2COOH and HNCH2CH2CH2CH2NH? This is a condensation polymerization. Water is lost between the amine and carboxylic acid: H H O O | | || || HNCH2CH2CH2CH2NH + HOCCH2CH2COH → water will leave H H O O | | || || HNCH2CH2CH2CH2NCCH2CH2COH new amide The carboxylic acid group on the right is still in tact and will react with an amine group from another HNCH2CH2CH2CH2NH molecule. The amine group on the left is still in tact and will react with a carboxylic acid group from another HOOCCH2CH2COOH molecule. What two dipeptides can be formed from Tyr and Gly? H R1 O H N C C H R2 O N C C OH H H Tyr-Gly has the above structure where R1 is: CH2 OH and R2 is:H. Gly-Tyr has the above structure where R2 is: CH2 OH and R1 is:H. Are Tyr-Gly and Gly-Tyr different molecules? Yes. Identify a tripeptide that can be formed from Glu, Asn, and Val. H R1 O H N C C H R2 O H R3 O N C C N C C OH H H H Glu-Asn-Val has the above structure where: R1 is CH2CH2COOH and R2 is CH2CONH2 and R3 is CH(CH3)2. How many tripeptides can be made from a single Glu, a single Asn, and a single Val? (The answer is in my name at the top of the first page :-) 22. Below are the structure of Talose and Gulose: HO HO HO H CHO H H H OH CH 2OH H H HO H CHO OH OH H OH CH 2OH How many chiral centers are there in each sugar? Label them. Assign D or L to each sugar and explain how you arrived at that conclusion. There are 4 Chiral centers in each sugar (all the carbons between the aldehyde and alcohol part at the bottom). The very bottom carbon is not chiral since it has 2 Hydrogens on it. Both sugars are D sugars since the very bottom chiral carbon has the OH on the right side.