Section 5a worksheet extraction metals answers
advertisement
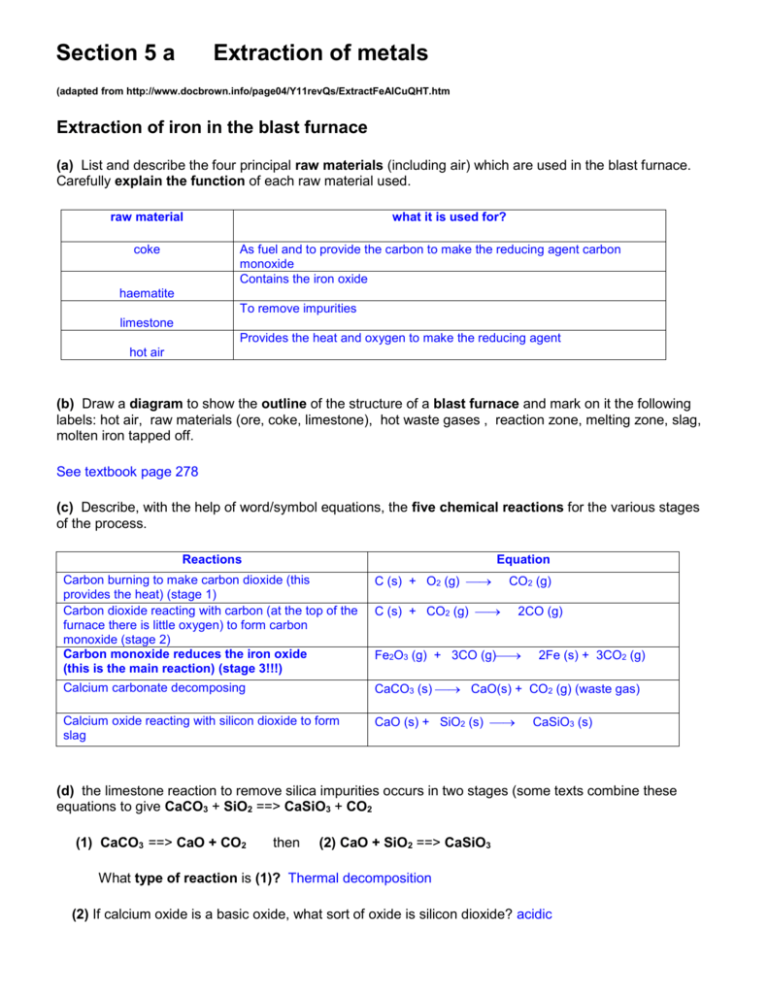
Section 5 a Extraction of metals (adapted from http://www.docbrown.info/page04/Y11revQs/ExtractFeAlCuQHT.htm Extraction of iron in the blast furnace (a) List and describe the four principal raw materials (including air) which are used in the blast furnace. Carefully explain the function of each raw material used. raw material coke what it is used for? As fuel and to provide the carbon to make the reducing agent carbon monoxide Contains the iron oxide haematite To remove impurities limestone Provides the heat and oxygen to make the reducing agent hot air (b) Draw a diagram to show the outline of the structure of a blast furnace and mark on it the following labels: hot air, raw materials (ore, coke, limestone), hot waste gases , reaction zone, melting zone, slag, molten iron tapped off. See textbook page 278 (c) Describe, with the help of word/symbol equations, the five chemical reactions for the various stages of the process. Reactions Equation Carbon burning to make carbon dioxide (this provides the heat) (stage 1) Carbon dioxide reacting with carbon (at the top of the furnace there is little oxygen) to form carbon monoxide (stage 2) Carbon monoxide reduces the iron oxide (this is the main reaction) (stage 3!!!) C (s) + O2 (g) Calcium carbonate decomposing CaCO3 (s) CaO(s) + CO2 (g) (waste gas) Calcium oxide reacting with silicon dioxide to form slag CaO (s) + SiO2 (s) CO2 (g) C (s) + CO2 (g) 2CO (g) Fe2O3 (g) + 3CO (g) 2Fe (s) + 3CO2 (g) CaSiO3 (s) (d) the limestone reaction to remove silica impurities occurs in two stages (some texts combine these equations to give CaCO3 + SiO2 ==> CaSiO3 + CO2 (1) CaCO3 ==> CaO + CO2 then (2) CaO + SiO2 ==> CaSiO3 What type of reaction is (1)? Thermal decomposition (2) If calcium oxide is a basic oxide, what sort of oxide is silicon dioxide? acidic Why do they react together and what sort of compound is calcium silicate? Neutralization and salt (e) Carefully explain why reaction for stage 3: iron(III) oxide + carbon monoxide ==> …. is an example of a REDOX reaction i.e. it involves an oxidation and a reduction. Carbon monoxide is oxidized as it reduces the iron oxide. (f) (i) State what is oxidised in the reaction for stage 1. Carbon is oxidized. (ii) State what is oxidised, and to what, and what is reduced, and to what, in the reaction for stage 2 Carbon is oxidized to carbon monoxide whilst carbon dioxide is reduced to carbon monoxide. (g) Describe several uses of iron including steel. Car bodies, construction, cutlery, machine parts, .. Extraction of aluminium (a) What is the main ore of aluminium called? What is the name and formula of the principal aluminium compound in it? Bauxite, aluminium oxide, Al2O3 (b) Aluminium is extracted from its ore by electrolysis. What does this mean? Aluminium oxide is broken down into aluminium and oxygen using electricity. (c) Sketch in outline the electrolysis cell, add labels to show: bauxite input, carbon anodes (+), electricity supply, aluminium output, carbon cathode (-), waste gases See text book p 117 (d) Questions on the electrolysis process: (1) Why is cryolite added to the bauxite ore in the electrolysis cell? To lower the temperature at which the mixture melts/lower operating temperature. (2) Why is it expensive to produce aluminium by this method? Needs large amounts of current to both heat the mixture and provide electrons for the reaction. (3) Give the names and symbols of the two ions free to move in the molten ore. Where and why do theses ions move to? Al3+ to the cathode and O2- to the anode as they are attracted to the oppositely charged electrode. (4) Give the two electrode equations to show the formation of aluminium at the cathode(-) and oxygen at the anode(+). Explain the changes in terms of oxidation and reduction cathode: reduction: Al3+(l) + 3e- Al (s) anode: oxidation: 2O2- (l) O2 (g) + 4e- (5) Why do the carbon anodes have to be replaced regularly? Is there any danger of a toxic gas being produced? Carbon form the anode reacts with oxygen to form carbon dioxide; there is the possibility of formation of carbon monoxide which is toxic. (6) Is the electrolysis of molten aluminium oxide an exothermic or endothermic chemical change and explain your answer. Endothermic process as it needs energy to keep the reaction going. (e) The uses of aluminium (1) Describe some everyday uses of aluminium. Airplanes, car bodies, step ladders, food cans, window frames, (2) Give two good reasons for recycling aluminium cans. Reduce mining of bauxite and lower carbon dioxide emissions as less electricity is needed. (3) Give three good reasons for using aluminium alloys for aircraft wings. Low density, strong and does not corrode (4) Aluminium is used for window frames but theoretically it is reactive enough to corrode away fairly rapidly. Explain why this does not happen. Aluminium forms an oxide layer on the outside which protects it against corrosion of reagents such as water.