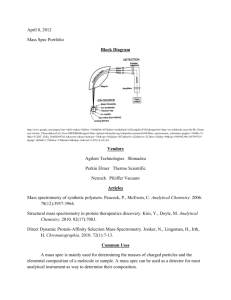
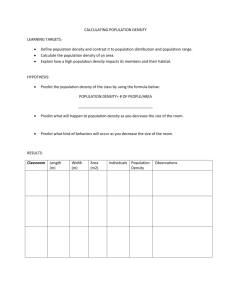
A Level Learning Objectives WJEC
advertisement

Learning Objectives WJEC A2 Introduction to Ecology Understand the concept of ecosystems Define habitat and community Describe how climate change can affect species distribution Define and give examples of inter and intra-specific competition Spec links: BY5 5.5 Variation and evolution Inter and intra-specific competition for breeding success and survival (e.g. supply of food, breeding sites, climate) Spec links: BY5 5.7 Energy and Ecosystems The concept of ecosystems The concept of habitat and community Spec links: BY5 5.8 Effects of Human activities and sustainability Global warming and climate change affect distribution of species and are a possible cause of extinction. Sheltered Rocky Shore Investigation Collect quantitative data from at least one habitat use percentage cover and frequency as measures of abundance Spec links: Fieldwork skills collection of quantitative data from at least one habitat the use of percentage cover and frequency as measures of abundance Gastropod Microhabitat Investigation Use frame quadrats to collect quantitative data Construct an appropriate null hypothesis Use a statistical test to analyse the data, Chi Squared Spec links: Fieldwork Skills the use of frame quadrats and line transects the application of elementary statistical analysis to the results Spec links: Practical and Investigative Skills Null hypothesis Chi squared Effect of Exposure Investigation Environmental factors produce variation between individuals Construct an appropriate null hypothesis Use a statistical test to analyse the data, t-test Spec links: BY5 5.5 Variation and evolution Genetic and environmental factors produce variation between individuals Spec links: Fieldwork Skills the application of elementary statistical analysis to the results Spec links: Practical and Investigative Skills Null hypothesis Standard deviation T-test Saltmarsh Investigation Describe the process of succession Use the terms primary and secondary succession, pioneers, sere and climax community Collect quantitative data from at least one habitat Spec links: BY5 5.7 Energy and Ecosystems Principles of succession as illustrated by the change from bare rock to woodland. Use of terms primary and secondary succession, pioneers, sere and climax community. Spec links: Fieldwork Skills collection of quantitative data from at least one habitat Quadrat Comparison Construct an appropriate a null hypothesis Calculate the Spearman’s Rank test statistic Spec links: Practical and Investigative Skills Null hypothesis Correlation Energy Flow Investigation (Freshwater/Rocky Shore) Explain how energy enters the ecosystem Explain what happens to energy as it is transferred through a food chain Describe gross and net production Draw pyramids of number, biomass and energy Spec links: BY5 5.7 Energy and Ecosystems The sun is the source of energy for the ecosystem Transfer of energy from plants to animals. Trophic levels and the efficiency of energy transfer. Gross and net production Pyramids of energy Conservation Study Explain conflicts between production and conservation and possible solutions Provide reasons for deforestation and describe the impacts on biodiversity Explain how forests are managed Explain why environmental monitoring is needed for conservation Spec links:BY5 5.8 Effects of Human activities and sustainability The conservation of gene pools in the wild and in captivity Conflicts between production and conservation and possible means to resolve such conflicts forests: reasons for and scale of forest destruction, consequences, managed forests, ecotourism. Native woodlands and biodiversity oceans: the problems of over-fishing and attempts at regulation as illustrated by the principle of quotas, exclusion zones and restricted net mesh size, human choices. Fish farming and associated issues. Increased human pressures on the environment. The need to achieve sustainability by changes in human attitudes and informed choices. The need for political decision making to be informed by knowledge based on sound scientific principles. Environmental monitoring and the need to provide data which is reliable and valid