Climate, Weather, Seasons, Disasters
advertisement

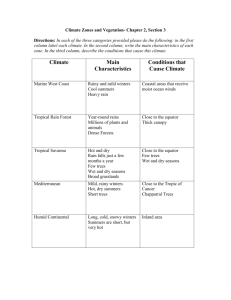
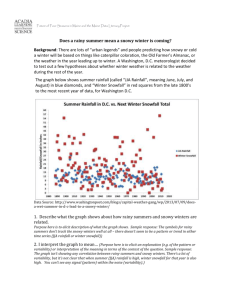
Climate, Weather, Seasons, Disasters CLIMATE is condition of the atmosphere at a particular location over a long period of time. It is the long-term summation of the atmospheric elements that, over short time periods, constitute weather. These elements are solar radiation, temperature, humidity, precipitation, atmospheric pressure and wind (speed and direction) Compare the climate in the Czech Republic, Great Britain, The USA and other English speaking countries: Britain has a temperate, humid climate. Its characteristic features are mild winters (Britain has warmer winters than any other country in the same latitude), not very hot summers, no extremes of temperature, (Extremes of temperature ,above 30°C and below -15°C, are rare), abundant rain all the year round, frequent changes of the weather. The most important factor influencing Britain´s mild climate are southwesterly wind blowing from the Atlantic (mild in winter, cool in summer) and the warm Gulf Stream flowing from the Gulf of Mexico to western Europe. But occasional easterly winds in winter may bring a cold, dry, continental type of climate. The areas of heaviest rainfall are the Western Highlands of Scotland, the Lake district and north Wales. March to June are the driest months, October to January are the wettest. But rain is fairly well distributed throughout the year. A period of as long as three weeks without rain is exceptional. There is occasionally mist and fog, particularly from October to January. Since the 1950s fogs become less frequent and less severe as a result of clean air legislation and the use of smokeless fuel. Compared with Great britain, Ireland has warmer winters and cooler summers, more rain and less sunshine. Due to frequent rains most of the island is beautifully green and therefore it is nicknamed „the emerald island“. The climate of the USA varies with the geography. There are vast climatic differences across the fifty states. The best climates can be found in Hawaii, Florida and California, where there are tropical and semi-tropical regions. In contrast, in the northeast and midwest, the climate is more severe, featuring four seasons and cold winters. However, the most extreme arctic climate can be found, of course, in Alaska. Canada Most of the inhabited part of Canada has a continental climate (warm and sunny summers, long cold winters). On the Pacific coast the climate is milder, in the uninhabited North the winters are very severe. (arctic climate) Australia The northern part of the continent lies in the tropical climate zone, the rest of the continent in the sub-tropical or temperate zone, but there are great differences between individual regions, depending on the distance from the coast and on the altitude. The south-east coast has a pleasant type of climate with warm summers, mild winters and good rainfall all the year round. One third of the continent is desert or semi-desert. New Zealand has a very pleasant, healthy, temperate climate with plenty of sunshine and good rainfall, with warm summers and mild winters. the temperature also depends on the altitude and winters in the mountains are cold with enough snow for skiing. An almost ideal balance of rain and sunshine makes grass and trees grow faster than in most countries. The Czech Republic has a moderate continental climate. How is the global climate changing ? Does the greater industrial pollution affect the global climate ? WEATHER state of the atmosphere at a particular place during a short period of time. It involves such atmospheric phenomena as temperature, humidity, precipitation, air pressure, wind and cloud over. Weather has a tremendous influence on life: Extremes of temperature and humidity may lead to the transmission of disease, heavy rain can cause flooding, thunderstorms, tornadoes, hail and sleet may damage or destroy crops, buildings and roads. Storms may even kill or injure people and livestock. At sea and along the coast tropical cyclones (hurricanes, typhoons and willy-willies) can cause great 1 damage through excessive rainfall and flooding, winds and wave action to ships, buildings, trees, crops, roads, railways, and they may interrupt air service and communications. Heavy snowfall and icy conditions can increase the frequency of accidents. The long absence of rainfall, by contrast, can cause droughts. People have always been concerned with forecasts and predictions of future weather conditions. How reliable are weather forecasts ? Do you follow them on TV, radio, papers or internet ? Why is weather such a popular conversation topic, „small talk“ ? ( easy way of starting conversation, not too personal,...?) What type of weather do you like most ? What type of weather don´t you like at all ? How does various weather affect your moods and emotions ? (I best like sunny weather with temparatures around...degrees. Sunny weather makes me feel happy and cheerful. I dislike rain because rain makes me feel depressed and I get wet. Moreover I hate carrying an umbrella. ...) SEASONS There are four seasons of the year- spring, summer, autumn (fall), winter. Winter is the coldest season. It extends from the winter solstice (year´s shortest day), December 22 or 23, to the spring equinox (day and night equal in length), March 20 or 21. Spring extends from the spring equinox to summer solstice (year´s longest day), June 21 or 22. ...(autumn equinox September 22 or 23) Words associated with each season: SPRING nature begins to awake from winter sleep, new life begins / days get longer, nights get shorter, it becomes warmer/ Easter/ people fall in love (May- the month of love), animals begin their reproducing activities, birds migrate, trees are in blossom /snow and ice melt, danger of floods, mud Weather is unpredictible, changeable, showers, sleet SUMMER two months´ school holiday/ people travel more and take holidays/ swimming, sunbathing, hiking, camping / harvest of corn, picking berries (strawberries, bilberries, raspberries,...) Weather is fair, nice, splendid, lovely / hot and dry, it is sunny, sky is clear and bright, no wind blows / a spell of very hot weather often ends with a thunderstorm (you get thunder and lightning and it pours with rain, afterwards, it is usually cooler) AUTUMN sun sets earlier, days get shorter / fine days of Indian summer/ harvest in the gardens: we pick apples,pears, plums, gather potatoes / grass gets yellow and dry, the leaves become colourful and finally trees shed their leaves / people go mushrooming / birds flock together and set out on the journey southwards / catch a cold or a flu Weather is often awful, wretched, rainy, wet, damp, nasty, chilly, windy, foggy / sky is often cloudy, mornings are dull, temperature continues to drop / it may drizzle, there is mist and fog, cold and strong wind blows WINTER many animals hibernate, some plants and insects die/ people wear heavy clothes like..../ roads are icy and slippery- it makes driving hazardous, for you can skid easily / skiing, sledging, skating, building snowmen / Christmas / lakes and streams are frozen over / Weather is snowy and cold / icy wind/ hard frosts/ sub-zero temperatures / overcast sky/ snowflakes/ icicles/ NATURAL DISASTERS 2 Earthquake: is a tectonic or volcanic disturbance within the Earth. The passage of seismic waves through the Earth often causes violent shaking of its surface. The origin of most major earthquakes can be explained in terms of the plate tectonics theory. The location of the earthquake is determined with a seismograph. The magnitude of an earthquake is usually expressed in terms of the Richter scale. The scale is so arranged that each increase in magnitude of one unit represents a tenfold increase in earthquake size, i.e. an earthquake of Richter magnitude 8 is 10,000 times as large as one of magnitude 4. Large earthquakes have caused some of the worst disasters in history. No other natural phenomenon is as destructive over so large an area in so a short time. People are crushed and buried under the collapsing structures or are burned to death in fires. Destructive, too, are the landslides and mudslides that occasionally accompany an earthquake. Much research has been devoted to earthquake prediction since the mid 1960s, but no method has yet been deviced to predict the time, place or magnitude of quakes. Seismologists have found that major earthquakes are often preceded by certain measurable physical changes in the environment around their epicentres.) Flood high-water stage in which water overflows its natural or artificial banks. Floods commonly results from excessive rainfall over short periods of time, and also from ice jams during the spring rise and from tsunamis (the mountainous sea waves caused by earthquakes) Famine extreme shortage of food, causing widespread and persistent hunger. The causes of famine are numerous, but they are usually divided into natural ( drought, heavy rain and flooding, typhoons, plant disease and insect infestations; drought being the most common natural cause ) and human categories (mainly warfare = destroying crops and food supplies and blockade tactics, overpopulation) Famines sometimes drove some people to cannibalism. Famine continues to be a problem in parts of Latin America, Central Africa and Southeast Asia. The effects of modern famines have been lessened by international relief organizations. Volcanic eruption, hurricane, fires, mudslides, tsunami Fahrenheit thermometric scale (after Gabriel d. Fahrenheit, † 1736, German physisist)- under standard atmospheric pressure the boiling point of water is at 212 degrees and the freezing point at 32 degrees above the zero of the scale. °C= 5/9 (°F-32) °F = 9/5 ( °C+ 32) 0 °C = 32 °F 3 100 °C = 212 °F