Word file
advertisement
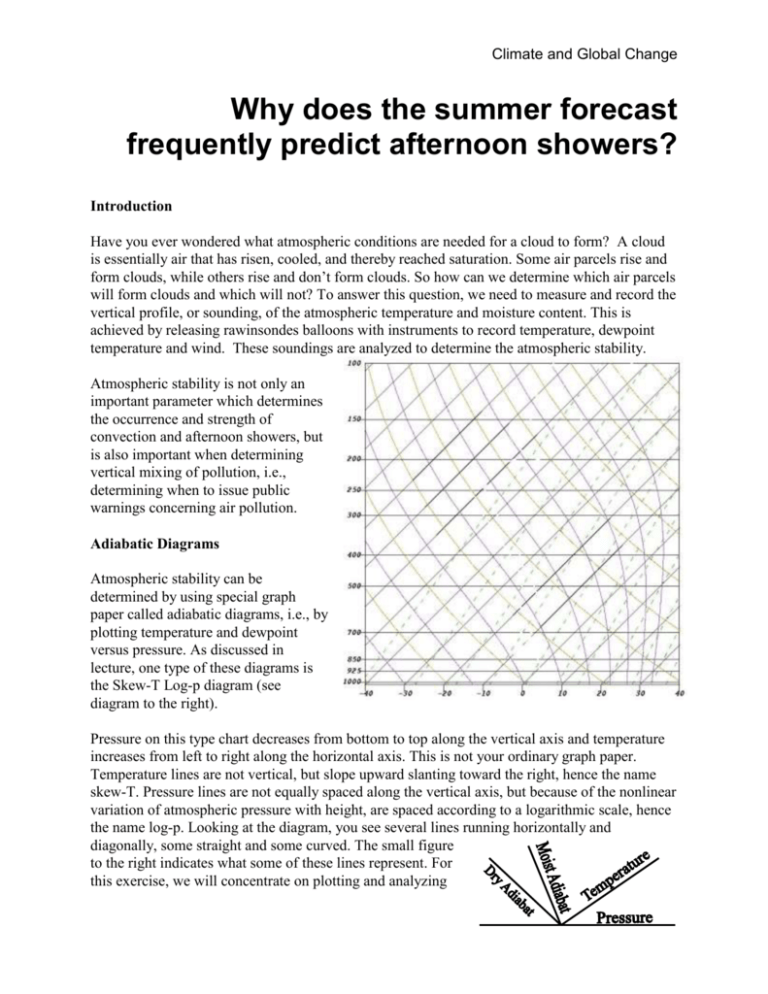
Climate and Global Change Why does the summer forecast frequently predict afternoon showers? Introduction Have you ever wondered what atmospheric conditions are needed for a cloud to form? A cloud is essentially air that has risen, cooled, and thereby reached saturation. Some air parcels rise and form clouds, while others rise and don’t form clouds. So how can we determine which air parcels will form clouds and which will not? To answer this question, we need to measure and record the vertical profile, or sounding, of the atmospheric temperature and moisture content. This is achieved by releasing rawinsondes balloons with instruments to record temperature, dewpoint temperature and wind. These soundings are analyzed to determine the atmospheric stability. Atmospheric stability is not only an important parameter which determines the occurrence and strength of convection and afternoon showers, but is also important when determining vertical mixing of pollution, i.e., determining when to issue public warnings concerning air pollution. Adiabatic Diagrams Atmospheric stability can be determined by using special graph paper called adiabatic diagrams, i.e., by plotting temperature and dewpoint versus pressure. As discussed in lecture, one type of these diagrams is the Skew-T Log-p diagram (see diagram to the right). Pressure on this type chart decreases from bottom to top along the vertical axis and temperature increases from left to right along the horizontal axis. This is not your ordinary graph paper. Temperature lines are not vertical, but slope upward slanting toward the right, hence the name skew-T. Pressure lines are not equally spaced along the vertical axis, but because of the nonlinear variation of atmospheric pressure with height, are spaced according to a logarithmic scale, hence the name log-p. Looking at the diagram, you see several lines running horizontally and diagonally, some straight and some curved. The small figure to the right indicates what some of these lines represent. For this exercise, we will concentrate on plotting and analyzing Climate and Global Change two variables, temperature and dewpoint temperature, versus pressure on skew-T diagrams. Stability and the Skew-T Log-p Diagram Now that we have a method of displaying the environmental conditions, i.e., how temperature and dewpoint temperature vary with height, we can analyze the plot to determine the stability of air parcels rising or sinking in this environment. From lecture, recall the dry and moist adiabatic processes. The word adiabatic means no heat is added or subtracted during the lifting or subsiding of a parcel of air. If a parcel of air is not saturated, it will cool (warm) about 10C / km as it rises (sinks). This rate of temperature change with change of height is called the dry adiabatic lapse rate. On the other hand, if an air parcel is saturated, it will cool (warm) about 5C / km as it rises (sinks) through the lower atmosphere. Recall that the moist adiabatic lapse rate is not constant. It depends on the amount of latent heat being added to the parcel as it rises or sinks. And the latent heat addition depends on vapor being condensed which is temperature dependent. This is referred to as the moist adiabatic (only the latent heat of condensation or evaporation is added or subtracted during the process, no other heating or cooling processes are allowed) lapse rate. If for instance you have a dry (unsaturated) parcel that begins at 1000 mb and is lifted, it will cool at the dry adiabatic (10C / km) rate until the parcel reaches a saturation level, and then it will rise moist adiabatically cooling at about 5C / km thought the lower troposphere. Stability Rules Recall that when a parcel is displaced (moved) from its original altitude to a new level, then • if the net force accelerates the parcel back toward its original position, the atmosphere is considered “stable”. • if the net force accelerates the parcel away from its original position, the atmosphere is considered “unstable”, and • if the net force is zero, the atmosphere is considered “neutral”. Another way to discuss stability is to employ the ideas of we learned from the Buoyancy Lab. For example, a parcel will rise as long as it is less dense (warmer) than its surrounding environment. Conversely, a parcel will sink as long as it is denser (colder) than its surrounding environment. There are three main characterizations of stability - absolute stability, conditional stability and absolute instability (see figure below). In an absolutely stable environment, a rising air parcel becomes denser than the surrounding environmental air as it rises, so a parcel in this environment will not be able to continue to rise by buoyancy alone. In a conditionally unstable environment, a parcel will continue to rise if it is saturated or will sink back to its original position if it is dry (unsaturated). For an absolutely unstable atmosphere, regardless of saturation condition of the parcel, a parcel will continue to rise if it is lifted. See the figure on the next page. To determine stability from a skew-T, one needs to compare the moist and dry adiabatic processes with the environmental sounding and apply the stability rules. If the environmental lapse rate is less (tilted more toward the right) than the moist adiabatic lapse rate, the atmosphere Climate and Global Change is absolutely stable. If the environmental lapse rate is greater (tilted more toward the left) than the dry adiabatic lapse rate, the atmosphere is absolutely unstable. If the environmental lapse rate is greater than the moist adiabatic lapse rate and less than the dry adiabatic lapse rate, the atmosphere is conditionally unstable. 400 Pr es su re ( m b) Dry Adiabat 500 Moist Adiabat Conditional Stability 600 Absolute Stablility 700 800 850 Three Observed or Measured Lapse Rates Absolute Instablility 1000 1050 Temperature (°C) Exercise The following sounding was taken on 11 November 2002 at 0000 UTC in Birmingham, AL. Plot these data on the provided skew-T diagram. Using a pencil draw a dashed line connecting dewpoint temperature data points and a solid line connecting temperature points. Pressure (mb) 986 850 800 762 700 650 585 500 400 300 200 Temp. (C) 25.6 15.8 12.2 12.6 7.6 2.4 -5.1 -9.9 -23.3 -39.3 -53.3 Dewpt. Temp. (C) 20.7 14.0 10.1 -1.4 -9.4 -8.6 -19.1 -40.1 -43.3 -55.3 -70.3 Stable, Unstable or Conditional Stability XXXX XXXX XXXX XXXX XXXX XXXX XXXX Climate and Global Change Using the dry and moist adiabats on the skew-T chart, determine if a parcel is stable or unstable for various layers of the atmosphere. An atmospheric layer is between two or more pressure levels (e.g., 986-850 mb or 850-800 mb, etc.). Complete (the blank locations) the table above by determining the stability of these layers. Now suppose a dry air parcel begins to rise from 986 mb. Assume the parcel begins with the same conditions as its surroundings. Trace the path this parcel would take as it rises to 200 mb. Assume that the parcel reaches saturation at 910 mb, i.e., assume that the parcel first rises dry adiabatic from 986 mb to 910 mb and then moist adiabatically to 200 mb. (The level that a parcel will become saturated can be determined from a Skew-T diagram, but we will not have you learn how this is done in this class.) With the above assumption, is the parcel Stable or Unstable (Circle your answer). At what level is the environmental temperature below 0ºC, i.e., below freezing? Why might this level be critical for airplanes? What kinds of clouds would you expect in this environment, tall thunderstorm-type clouds (i.e., thunderstorms or cumulonimbus clouds) or smaller “fair weather” clouds (cumulus)? Why? Do you recall why this particular sounding might be significant; in other words, what weather event happened around this time in northern Alabama? Climate and Global Change