Cardiac (all)-41 questions
advertisement
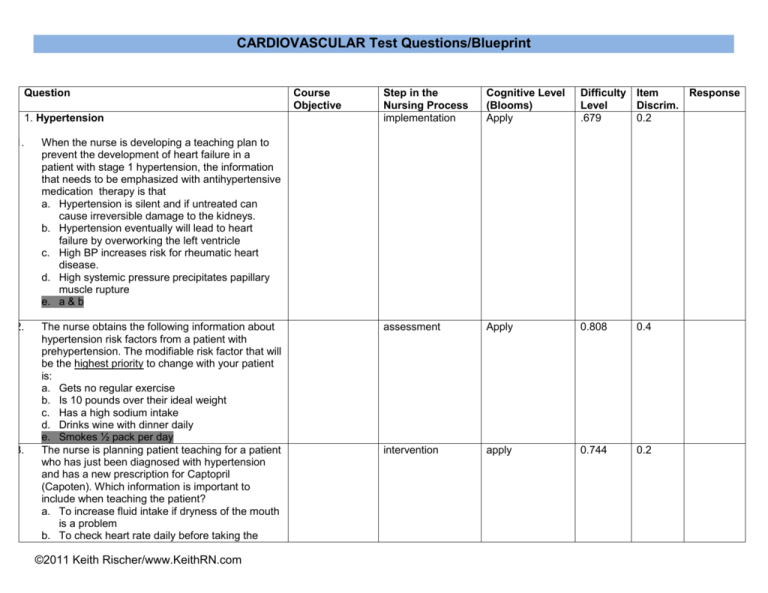
CARDIOVASCULAR Test Questions/Blueprint Question 1. Hypertension 1. When the nurse is developing a teaching plan to prevent the development of heart failure in a patient with stage 1 hypertension, the information that needs to be emphasized with antihypertensive medication therapy is that a. Hypertension is silent and if untreated can cause irreversible damage to the kidneys. b. Hypertension eventually will lead to heart failure by overworking the left ventricle c. High BP increases risk for rheumatic heart disease. d. High systemic pressure precipitates papillary muscle rupture e. a & b 2. The nurse obtains the following information about hypertension risk factors from a patient with prehypertension. The modifiable risk factor that will be the highest priority to change with your patient is: a. Gets no regular exercise b. Is 10 pounds over their ideal weight c. Has a high sodium intake d. Drinks wine with dinner daily e. Smokes ½ pack per day The nurse is planning patient teaching for a patient who has just been diagnosed with hypertension and has a new prescription for Captopril (Capoten). Which information is important to include when teaching the patient? a. To increase fluid intake if dryness of the mouth is a problem b. To check heart rate daily before taking the 3. ©2011 Keith Rischer/www.KeithRN.com Course Objective Step in the Nursing Process implementation Cognitive Level (Blooms) Apply Difficulty Item Response Level Discrim. .679 0.2 assessment Apply 0.808 0.4 intervention apply 0.744 0.2 medication c. To include high-potassium foods such as citrus fruits in the diet d. To change position slowly to help prevent dizziness and falls 4. Laboratory testing is ordered for a patient during a clinic visit for routine assessment of hypertension. When monitoring for target organ damage as a consequence of hypertension, the nurse will be most concerned about a. Blood urea nitrogen (BUN) of 15 mg/dl b. Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) 40 u/L c. Aspartate aminotransferase (AST) 38 u/L d. Serum creatinine of 1.8 mg/dl 5. In teaching a patient with hypertension, the nurse emphasizes that even though you have no symptoms, hypertension needs to be controlled because it can quietly damage many organs in the body. The damage that occurs is primarily related to which effect of hypertension? a. b. Arterial wall changes with progressive development of atherosclerosis c. Hypoxia of organ systems caused by thickening of capillary membranes, which impairs gas exchange. d. Increased viscosity of the blood contributing to intravascular coagulation with necrosis of tissue distal to occlusions. 6. Angina-Coronary Artery Disease 6. Which of the following conditions causes the chest pain seen with angina? a. Increased preload b. Decreased afterload c. Decreased contractility d. Decreased oxygen supply to the myocardium 7. 7. N1120-V-2 Your patient presents to the ©2011 Keith Rischer/www.KeithRN.com assessment Understand/apply 0.962 0.1 Assess/intervention Understand/apply 0.679 0.1 assessment remember understand 0.885 0.3 assessment Understand apply 0.897 0.1 emergency department with complaints of substernal chest pain. 12 hours later, it is noted on the laboratory assessment that troponin levels have not risen. What conclusion can be drawn from this information? a. Your patient has not experienced a myocardial infarction. b. Your patient is experiencing an evolving myocardial infarction. c. Your patient most likely had a myocardial infarction several days ago. d. Your patient has experienced a myocardial infarction within the last 24 hours. 8. Why is the administration of aspirin recommended along with nitroglycerin when a client is experiencing angina-like chest pain? Assess implementation Understand Apply 0.936 0.1 implement Understand apply 0.962 0.1 a. Aspirin has analgestic properties without sedation b. Aspirin can trigger vasodilation and improve blood plow. c. Aspirin inhibits platelet aggregation and clot information d. Aspirin has cardiotonic properties and improves contraction 9. Nitroglycerin is indicated as one of the first medications given for chest pain in angina because it: a. Decreases workload of the heart through decreasing preload and dilates the coronary ©2011 Keith Rischer/www.KeithRN.com arteries b. Decreases workload of the heart through increasing preload and dilates the coronary arteries c. Decreases workload of the heart through decreasing afterload and constricts the coronary arteries d. Decreases workload of the heart through decreasing heartrate and decreasing cardiac contractility 10. A client who has experienced a myocardial infarction develops left ventricular heart failure. Which sign of poor organ perfusion should the nurse remain alert for? assessment Understand Apply 0.628 0.4 Assessment implementation Understand Apply 0.590 0.4 a. Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) 122 u/L b. Serum creatinine of 1.7 mg/dl c. Urine output less than 30mL/hour d. b & c e. a, b, c 11. You are caring for your patient who had coronary angioplasty (PTCA) 1 hour ago. Which complications of this procedure should the nurse remain alert for at this time? a. Hypertensive crisis b. Hyperkalemia c. Infection ©2011 Keith Rischer/www.KeithRN.com d. Bleeding 12. 13. Your patient who is scheduled for echocardiography today asks why this test is being performed. What is the nurse’s best response? a. To assess the structure of the heart and determine left ventricular function b. To assess for abnormal electrical impulses within the heart c. To evaluate the decrease in the cardiac output when the client has PVCs d. To evaluate the coronary arteries for any blockages that may be present You are taking the history of your patient who has chest pain. Recently, he has had episodes of chest discomfort while mowing the lawn with a push mower. The chest discomfort subsides when the patient rests. What conclusion can the nurse draw from this information? implementation Understand Apply 0.628 0.5 Assessment Remember Understand 0.987 0.1 assessment remember understand 0.872 0.4 a. The patient likely has unstable angina. b. The patient likely has stable angina. c. The patient likely has had a myocardial infarction. d. The patient need not be concerned about this pain, because it relieved with rest. 14. The nurse is admitting a patient who is complaining of chest pain to the emergency department (ED). Which information collected by the nurse suggests that the pain is caused by an acute myocardial infarction (AMI)? a. The pain onset was while he was watching TV. b. The pain increases with deep breathing. c. The pain is relieved after the patient takes nitroglycerin. d. The pain has persisted longer than 30 minutes. e. a & d ©2011 Keith Rischer/www.KeithRN.com 15. Which information given by a patient admitted with chronic stable angina will help the nurse confirm this diagnosis? a. The patient rates the pain at a level 3 to 5 (0– 10 scale). b. The patient states that the pain “wakes me up at night.” c. The patient indicates that the pain is resolved after taking one sublingual nitroglycerin tablet. d. The patient says that the frequency of the pain has increased over the last few weeks. 16. 16. Three risk factors that influence the development and progression of coronary artery disease include: a. Smoking, family history of heart disease and diabetes. b. Smoking, active life style, and high density lipoproteins (HDL) of 25. c. Smoking, diabetes and high density lipoproteins (HDL) of 80. d. Obesity, smoking, and low density lipoproteins (LDL) of 80. Heart Failure The initial compensatory mechanism of the body that maintains cardiac output when the heart is in failure is: a. Increased parasympathetic nervous system stimulation b. Increased sympathetic nervous system stimulation c. Decreased sympathetic nervous system stimulation d. Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System 18. An elderly patient with a 40-pack-year history of smoking and a recent myocardial infarction is admitted to the medical unit with acute shortness of breath; the nurse needs to rule out pneumonia versus heart failure. The diagnostic test that the nurse will monitor to help in determining whether the patient has heart failure is: a. 12-lead electrocardiogram (ECG). assessment Understand apply 0.910 0.1 Assessment Understand 0.923 0.1 assessment Understand 0.846 0.2 assessment Understand Apply 0.474 0.4 17. ©2011 Keith Rischer/www.KeithRN.com 19. b. Troponin c. B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP). d. Creatinine phosphokinase (CPK-MB) Which nursing diagnosis would be considered a priority for the client with left sided heart failure? assessment Understand Apply 0.795 0.2 assessment Understand Apply 0.936 -0.2 assessment Understand Apply 0.936 0.1 Assessment Apply 0.423 0.3 a. Anxiety b. Activity Intolerance c. Impaired Gas Exchange d. Fatigue 20. ACE inhibitors such as Lisinopril are often the first drug used to manage heart failure. What aspects of cardiac output are influenced by this medication to decrease the workload of the heart? a. Increases preload and decreases afterload b. Decreases preload and decreases afterload c. Increases preload and increases afterload d. Decreases heart rate and decreases contractility 21. Your patient with left sided heart failure has an ejection fraction of 25%. What pathophysiologic changes would the nurse expect to see? a. An increase in stroke volume b. A decrease in tissue /organ perfusion c. An increase in oxygen saturation d. A decrease in arterial vasoconstriction 22. Questions: 22-26: Ms. Camp, age 65 was ©2011 Keith Rischer/www.KeithRN.com discharged from the hospital 2 weeks ago after a 5day stay for severe dyspnea and congestive heart failure. She now has 2+ pitting edema in lower extremities and a nonproductive cough. Her vital signs are: T-98.9 P-112, R-28 BP 170/110 O2 sats 88% on room air. Ms. Camp has shortness of breath with exertion and used 3 pillows to sleep last night because she became very short of breath after lying flat. Standing or sitting up relieved her shortness of breath. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. Which nursing diagnostic statement(s) are relevant to her current status and will guide your plan of care: a. Impaired gas exchange b. Excess fluid volume c. Fluid volume deficit d. a & b What is the most important assessment for the nurse to accomplish next for Ms. Camp? a. Auscultate the lung sounds. b. Assess the orientation. c. Check the capillary refill. d. Insert an IV. Which assessment finding would most likely indicate that Ms. Camp who has a history of left sided heart failure is now in right-sided heart failure? a. 2+ pitting edema in lower extremities. b. Crackles in lungs. c. Orthopnea. d. Non-productive cough. The physician orders Furosemide (Lasix) 40 mg IV stat. The primary rationale for this medication is to decrease the workload of the heart by: a. Lowering afterload through arterial vasodilation b. Lowering preload through venous vasodilation c. Lowering preload through diuresis d. Lowering preload through diuresis and venous vasodilation When evaluating the effectiveness of your nursing ©2011 Keith Rischer/www.KeithRN.com implement analyze Assessment implement Understand Apply 0.859 0.0 assessment Understand Apply 0.859 0.3 implement Understand Apply 0.821 0.1 evaluation Understand 0.564 0.4 MODIFY intervention, what nursing assessment data supports that Furosemide has been effective to decrease the workload of the heart? a. Urine output of 800 mL in the past hour b. Heart rate 120/minute c. Respiratory rate 16/minute d. a & c e. a,b,c MODIFY 26. N1120-V-2 When evaluating the effectiveness of your nursing intervention, what nursing assessment data supports that Furosemide has been effective? a. Urine output of 800 mL in the past hour b. Heart rate 120/minute c. Respiratory rate 16/minute d. a & c a,b,c PVD-PAD Apply Analyze Evaluate 27. During an assessment of a 63-year-old patient at the clinic, the patient says, “I have always taken an evening walk, but lately my leg cramps and hurts after just a few minutes of walking. The pain goes away after I stop walking, though.” The nurse should: a. Ask about any skin color changes that occur in response to cold. b. Check for the presence of tortuous veins bilaterally on the legs. c. Assess for unilateral swelling, redness, and tenderness of either leg. d. Attempt to palpate the dorsalis pedis and posterial tibial pulses. 29. The nurse performing an assessment with a patient who has chronic peripheral arterial disease (PAD) of the legs would expect to find a. Swollen, dry, scaly ankles. b. A positive Homans’ sign. c. Little to no hair on lower legs d. A draining ulcer on the heel. 30. The health care provider orders a continuous IV Assess implement Understand Apply 0.538 0.3 assess Understand Apply Evaluate 0.962 0.2 Assess Understand 0.846 0.2 28. ©2011 Keith Rischer/www.KeithRN.com 31. 32. 33. heparin infusion for a patient with swelling and pain of the upper leg caused by a DVT. While the patient is receiving the heparin infusion, the nurse should a. Assess for any signs of GI bleeding or unusual bruising. b. Notify the physician if platelets have dropped significantly c. Have vitamin K available in case reversal of the heparin is needed. d. Monitor posterior tibial and dorsalis pedis pulses with the Doppler. e. a&b 30. Your 72-year-old patient is hospitalized for an aortic dissection of the abdominal aorta that stabilizes with treatment. The nurse develops a teaching plan for the patient’s discharge that includes information about a. gradually increasing exercise to improve cardiac function and BP control. b. appropriate use of nonsteroidal antiinflammatory agents (NSAIDs) to control any abdominal pain. c. holding prescribed beta-blockers if systolic blood pressure is <110 mm/Hg. d. the use of antihypertensive medications to lower the risk of further dissection 31. Your patient with a left calf DVT is at high risk of developing a pulmonary embolism. Which physical complaints would be suggestive that this complication has occurred? a. Shortness of breath b. Pleuritic chest pain c. Tachycardia d. All of the above 32. A patient with a DVT is started on IV heparin and oral warfarin (Coumadin). The patient asks the nurse why two medications are necessary. The nurse’s best response to the patient is, a. “Heparin will start to dissolve the clot, and Coumadin will prevent any more clots from occurring.” ©2011 Keith Rischer/www.KeithRN.com implement Apply analyze implement Understand Apply 0.705 0.5 assess Understand Apply Analyze 0.949 0.1 implement Understand apply 0.897 0.2 b. “Because of the potential for a pulmonary embolism, it is important for you to have more than one anticoagulant.” c. “The heparin will work immediately, but the Coumadin takes at least 2-3 days to have an effect on coagulation.” d. “Administration of two anticoagulants reduces the risk for recurrent deep vein thrombosis.” KEY: Cognitive Level: Remembering Understanding Applying Analyzing Evaluating Creating Item Discrimination = how well an item distinguishes between high and low scoring students. 0 is OK if it’s info that everyone absolutely needs to know, i.e. key content. .2 to .3 is desirable for most .4 or higher is OK for just a few questions. If all were .4, most of our students would fail the test. Negative discrimination means a problem, like a poorly written question, mis-speaking in lecture, not fully clarifying a topic, or an error on the answer key. ©2011 Keith Rischer/www.KeithRN.com FINAL EXAM Question 1. ALTERATIONS IN OXYGENATION (CARDIOVASCULAR) (9) 1. Which assessment data is relevant for the nurse to monitor in a patient who is receiving a thiazide diuretic (HCTZ) or a loop diuretic (Furosemide) to manage hypertension? a. Assess most recent serum hemoglobin b. Assess for hypotension. c. Assess most recent serum potassium d. b&c e. a,b,c 2. You are caring for a patient who had symptoms of unstable angina and has been admitted to the hospital. The most appropriate nursing diagnosis for the discomfort associated with angina is what? a. Deficient knowledge about underlying disease and methods for avoiding complications b. Anxiety related to fear of death c. Ineffective cardiopulmonary tissue perfusion as evidenced by chest pain d. Noncompliance related to failure to accept necessary lifestyle changes A patient with an occluded coronary artery is admitted and has an emergency angiogram/PTCA. The patient is admitted to the unit after the PTCA. What is the most important complication to assess this patient for? a. Infection b. Bleeding at insertion site c. Hypertensive crisis d. Congestive heart failure 3. ©2011 Keith Rischer/www.KeithRN.com Course Objective Step in the Nursing Process assess Cognitive Level (Blooms) Understand apply Difficulty Item Response Level Discrim. 0.924 0.1 assessment Understand apply 0.911 0.1 Assessment implement Understand apply 0.759 0.5 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. The nurse is assessing a client whose condition is being stabilized after a myocardial infarction (MI). What data collected by the nurse would indicate likely inadequate renal perfusion? a. Serum blood urea nitrogen (BUN) 20. b. Specific gravity of 1.010. c. Urine output of less than 30 ml/hr. d. Serum creatinine of 1.8 mg/dL e. c&d When discussing angina pectoris secondary to atherosclerotic disease with a patient, the patient asks why he experiences chest pain with exertion. The nurse informs the patient that exertion: a. Increases the heart's oxygen demands b. Causes vasoconstriction of the coronary arteries c. Increases blood flow to the coronary arteries d. Decreases the workload of the heart You are teaching your patient about coronary artery disease (CAD) and its risk factors. What risk factors would you identify that can be controlled or modified? a. Gender, obesity, family history, and smoking b. Inactivity, stress, gender, and smoking c. Obesity, inactivity, diet, and smoking d. Stress, family history, and obesity You are doing discharge teaching with a patient diagnosed with heart failure. What would you teach this patient as the most practical way to assess fluid balance? a. Monitor blood pressure daily b. Assess radial pulses daily c. Monitor weight daily d. Monitor urine output Which assessment finding(s) would indicate that your patient has biventricular heart ©2011 Keith Rischer/www.KeithRN.com assess Understand Apply analyze 0.949 0.1 assess Understand apply 0.911 0.1 implement Understand Apply Analyze 1.000 0.0 implement Understand apply 1.000 0.0 assess Understand Apply 0.949 -0.1 9. failure? a. 2+ pitting edema in lower extremities b. Crackles in bases of lungs bilaterally c. Labored respirations d. b&c e. a,b,c Your patient has received intravenous Heparin therapy for two days for treatment of deep vein thrombophlebitis. He asks why he is receiving Heparin. What is your best response? a. “Heparin will dissolve the clots in your legs.” b. “Heparin will prevent new clots from forming.” c. “Heparin will thin your blood and speeds clotting.” d. “Heparin will prevent the clots from migrating to your lungs.” ©2011 Keith Rischer/www.KeithRN.com Analyze Evaluate implement Understand apply 0.595 0.4