Proposal for the Collecting and Sorting Out Related National
advertisement

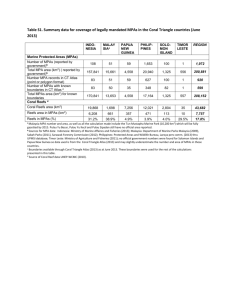
NOWPAP United Nations Environment Programme Northwest Pacific Action Plan Distr. RESTRICTED UNEP/NOWPAP/DINRAC FPM 8/12 7 April 2009 Original: English Northwest Pacific Action Plan Data and Information Network Regional Activity Centre The 8th NOWPAP DINRAC Focal Points Meeting Beijing, the People’s Republic of China, 19 - 21 May 2009 PROPOSAL FOR THE COLLECTING AND SORTING OUT RELATED NATIONAL INFORMATION ON MARINE PROTECTED AREAS IN THE NOWPAP REGION UNEP/NOWPAP/DINRAC FPM 8/12 Page 1 PROPOSAL FOR THE COLLECTING AND SORTING OUT RELATED NATIONAL INFORMATION ON MARINE PROTECTED AREAS IN THE NOWPAP REGION 1. Definitions “Marine and coastal protected area“ means any defined area within or adjacent to the marine environment, together with its overlying waters and associated flora, fauna and historical and cultural features, which has been reserved by legislation or other effective means, including custom, with the effect that its marine and/or coastal biodiversity enjoys a higher level of protection (Convention on Biological Diversity, 2004). “Areas within the marine environment” include permanent shallow marine waters, sea bays, straits, lagoons, estuaries, subtidal aquatic beds (kelp beds, tropical marine meadows), coral reefs, intertidal muds, sand or salt flats and marshes, deep-water coral reef, deep-water vents, and open ocean habitats (Convention on Biological Diversity, 2004). 2. Background One of the reasons why marine and costal biodiversity is declining or being lost at the national, regional and global level is the very low level of establishment of Marine and Coastal Protected Areas. Marine Protected Areas (MPAs) are among the five key elements of the programme of work of the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) on marine and coastal biodiversity. The CBD target of developing MPA networks by the year 2012 was set, together with other target to significantly reduce the current rate of biodiversity loss at global, regional and national levels in marine areas. 3. Objectives of the proposed project The proposed project is aiming at collecting and sorting out related national information on MPAs to facilitate the exchange of and access to information on national, regional and global initiatives, using the existing databases (e.g. MPA Global database - http://www.mpaglobal.org, World Database on Protected Areas - http://www.wdpa.org). DINRAC will serve as a switchboard to provide information on MPAs in the NOWPAP region to the MPA Global Database and others and share the benefit of providing such information that is comparable across countries and regions. Based on the national inputs, a regional report on MPAs in the NOWPAP region will be developed, which will facilitate establishment of MPA networks at national, regional and global level. 4. Tasks To collect and classify national information on MPAs, using international classification and requirements, which will be shared with the existing global MPA-related database systems and contribute to establishing MPA networks. UNEP/NOWPAP/DINRAC FPM 8/12 Page 2 5. Expected outputs • National and regional information on MPAs available in the global databases (will be managed by database and published on DINRAC website as NowpapMPA) • A regional report on MPAs in the NOWPAP region (will be publish on DINRAC website and printed as hard copy) ※ NowpapMPA will be shared with the global databases. 6. Estimated budget and time • Project period: 1 year - Compile national information (6 months) - Review national information provided (2 months) - Develop a regional report on MPAs in the NOWPAP region (2 months) - Finalize a regional report, taking into account comments and suggestions to be raised by the member states (2 months) • Estimated budget: US$ 20,000 - National Focal Points (or national experts) (US$ 14,000, US$ 3,500 X 4 member states) - Regional consultant (US$ 5,000) - Publication (US$ 1,000) ※ It is suggested that the National Focal Points or the national experts nominated by the Focal Points to compile the Form to collect the information on Marine Protected Areas (see Annex I), in addition, qualified consultant will be hired by DINRAC to develop the regional report based on collected information. 7. Actions required Draft and sign the MOUs between DINRAC and National Focal Points of member states (or national experts nominated by the Focal Points) Create a list of MAP in NOWPAP. The list will be created based on the global databases (e.g. MAP Global databases, WDPA) and NowpapNR by DINRAC and confirmed/update/supplemented by National Focal Points or national experts. Finalize the Form to collect the information on MAP by DINRAC with the support of National Focal Points or national experts. Collect the information and submit the Forms by National Focal Points. Harmonize the data, establish and publish the database by DINRAC. Hire a regional consultant to compile the regional report by DINRAC based on collected national information. Publish the regional report on the DINRAC website and print as hard copy by DINRAC. Disseminate the hard copies and share the outputs with concerned organizations. UNEP/NOWPAP/DINRAC FPM 8/12 Page 3 Annex I: Information on Marine Protected Areas (MPAs) Site name Location Latitude: Longitude: Total size of the MPA (Km 2) Total sea’s surface area (Km2) of the country Total EEZ area (Km2) of the country Geographic region Select a geographical region type and cross (X) ( ) FAO Fisheries Area: ( ) Large Marine Ecosystem: ( ) MEOW Ecoregion ( ) Ocean ( ) WWF G200 Ecoregion MPA designated under international convention/programme Select a convention/programme and cross (X) ( ) Convention on Biological Diversity ( ) Ramsar Convention ( ) World Heritage Convention ( ) UNESCO Man and Biosphere Programme ( ) Habitats Directive MPA designated under national law 1. Name of law/regulations (in English): Name of law/regulation (in national language): Date of entry into force: A brief summary of relevant articles: 2. Name of law/regulations (in English): Name of law/regulation (in national language): Date of entry into force: A brief summary of relevant articles: If more, describe in the same manner: Designation Status Cross (X) one of the following IUCN categories ( ) Designated ( ) informally designated ( ) Degazetted* ( ) Proposed ( ) Recommended ( ) Unknown UNEP/NOWPAP/DINRAC FPM 8/12 Page 4 * No longer (legally or non-legally) recognised as a MPA Marine Components Cross (X) one of the following categories ( ) Intertidal ( ) Subtidal ( ) Both ( ) No Data Available Type of protection and management (proposed or being implemented) Cross (x) one of the following categories: ( ) Representative highly-protected areas where extractive uses are excluded ( ) Additional marine and coastal protected areas ( ) Sustainable-management practices in the wider marine and coastal environment No-take regulation ( ) All of the MPA is no-take ( ) Part of the MPA is no-take ( ) None of the MPA is no-take ( ) Unknown if any part of the MPA is no-take Temporal aspects (e.g. permanency or seasonality of protection or management) IUCN Category Cross (X) one of the following categories (details as attached below) ( ) Ia – Strict nature reserve ( ) Ib – Widerness area ( ) II – National (marine) park ( ) III – Natural monument ( ) IV – Habitat/species management area ( ) V - Protected landscape/seascape ( ) VI – Management resource protected area ( ) None ( ) Unset ( ) Unapplicable Effectiveness of protection and management gauged against the regime being proposed or being implemented Cross (X) one of the following categories: ( ) Currently fully effective – no significant problems known ( ) Currently partially effective – some deficiencies ( ) Currently ineffective – significant implementation problems Habitats and species specially excluded from protection/management within the marine and coastal protected area (i.e., that have no legal protection) Nature of threats to habitats/species Cross (X) one or more of the following categories where appropriate ( ) Physical loss: removal (e.g., harvesting, draining to create dry land) and smothering (e.g., by artificial structures, disposal of dredged spoil) ( ) Physical damage: siltation (e.g., run-off, outfalls), abrasion (e.g. boating, anchoring, trampling) and selective extraction (e.g. aggregating dredging, entanglement, turf cutting) ( ) Non-physical disturbance: noise (e.g. boat activity) and visual (e.g., recreation activity)] ( ) Toxic contamination: introduction of synthetic compounds (e.g., pesticides, antifoulants, PCBs), introduction of non-synthetic compounds (e.g., heavy metals, hydrocarbons), and introduction of radio nuclides UNEP/NOWPAP/DINRAC FPM 8/12 Page 5 ( ( ) Non-toxic contamination: nutrient enrichment (e.g., agricultural run-off, outfalls), organic enrichment (e.g., mariculture, outfalls), changes in thermal regime (e.g., outfalls , power stations), changes in turbidity (e.g., run-off, dredging) and changes in salinity (e.g., water abstraction, outfalls) ) Biological disturbances: introduction of microbial pathogens; introduction of non-native species and translocations, and selective extraction of species (e.g., bait collection, wildfowling, commercial and recreational fishing) Knowledge and research efforts on MPAs (if any) National information initiative on MPAs including online system (if any) Further plan to submit national information on MPAs to the international organization (e.g. Convention on Biological Diversity) and related programmes (e.g. MPA Global Database) National strength to address MPAs National weakness to address MPAs Gaps to follow-up the global initiatives dealing with MPAs Need for national capacity building to address MPAs Annex II: IUCN has defined a series of six protected area management categories, based on primary management objective. A summary of categories and their definitions is provided below. Definitions of these categories, and examples of each, are provided in Guidelines for Protected Area Management Categories (IUCN, 1994). Categories and definitions on Marine Protected Areas (MPAs) (IUCN) CATEGORY Ia: Strict Nature Reserve: protected area managed mainly for science Definition Area of land and/or sea possessing some outstanding or representative ecosystems, geological or physiological features and/or species, available primarily for scientific research and/or environmental monitoring. CATEGORY Ib Wilderness Area: protected area managed mainly for wilderness protection Definition Large area of unmodified or slightly modified land, and/or sea, retaining its natural character and influence, without permanent or significant habitation, which is protected and managed so as to preserve its natural condition. CATEGORY II National Park: protected area managed mainly for ecosystem protection and UNEP/NOWPAP/DINRAC FPM 8/12 Page 6 recreation Definition Natural area of land and/or sea, designated to (a) protect the ecological integrity of one or more ecosystems for present and future generations, (b) exclude exploitation or occupation inimical to the purposes of designation of the area and (c) provide a foundation for spiritual, scientific, educational, recreational and visitor opportunities, all of which must be environmentally and culturally compatible. CATEGORY III Natural Monument: protected area managed mainly for conservation of specific natural features Definition Area containing one, or more, specific natural or natural/cultural feature which is of outstanding or unique value because of its inherent rarity, representative or aesthetic qualities or cultural significance. CATEGORY IV Habitat/Species Management Area: protected area managed mainly for conservation through management intervention Definition Area of land and/or sea subject to active intervention for management purposes so as to ensure the maintenance of habitats and/or to meet the requirements of specific species. CATEGORY V Protected Landscape/Seascape: protected area landscape/seascape conservation and recreation Definition Area of land, with coast and sea as appropriate, where the interaction of people and nature over time has produced an area of distinct character with significant aesthetic, ecological and/or cultural value, and often with high biological diversity. Safeguarding the integrity of this traditional interaction is vital to the protection, maintenance and evolution of such an area. CATEGORY VI Managed Resource Protected Area: protected area managed mainly for the sustainable use of natural ecosystems Definition Area containing predominantly unmodified natural systems, managed to ensure long term protection and maintenance of biological diversity, while providing at the same time a sustainable flow of natural products and services to meet community needs. managed mainly for