Name - Plain Local Schools

Name: _____________________________
Chapter 11: DNA and the Language of Life
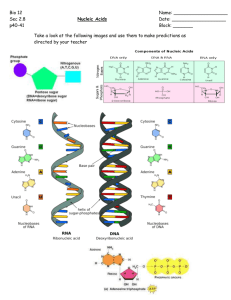
Vocabulary virus: package of nucleic acid wrapped in a protein coat that must use a host cell's machinery to reproduce itself (Concept 11.1) bacteriophage: virus that infects bacteria; also called a "phage" (Concept 11.1) deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA): molecule responsible for inheritance; nucleic acid that contains the sugar deoxyribose (Concepts 1.1, 11.2) nucleotide: building block (monomer) of nucleic acid polymers (Concept 11.2) nitrogenous base: single or double ring of carbon and nitrogen atoms with attached functional groups, found in nucleic acids (Concept 11.2) pyrimidine: single-ring nitrogenous base (Concept 11.2) purine : double-ring nitrogenous base (Concept 11.2) double helix: two strands of nucleotides wound about each other; structure of
DNA (Concept 11.2)
DNA replication: process of copying DNA molecules (Concept 11.3)
DNA polymerase: enzyme that makes the covalent bonds between the nucleotides of new DNA strands (Concept 11.3) ribonucleic acid (RNA): nucleic acid containing the sugar ribose (Concept 11.4) transcription: process by which a DNA template is used to produce a singlestranded RNA molecule (Concept 11.4) translation: process by which a sequence of nucleic acids in RNA is used to direct the production of a chain of specific amino acids (Concept 11.4) codon: in RNA, a three-base "word" that codes for one amino acid (Concept 11.4) messenger RNA (mRNA): RNA molecule transcribed from a DNA template
(Concept 11.5)
RNA polymerase: transcription enzyme that links RNA nucleotides together
(Concept 11.5) intron: internal noncoding region in RNA transcript (Concept 11.5) exon: coding region in RNA transcript (Concept 11.5)
RNA splicing: process by which the introns are removed from RNA transcripts and the remaining exons are joined together (Concept 11.5) transfer RNA (tRNA): RNA that translates the three-letter codons of mRNA to amino acids (Concept 11.5) anticodon: in tRNA, a triplet of nitrogenous bases that is complementary to a specific codon in mRNA (Concept 11.5) ribosomal RNA (rRNA): RNA component of ribosomes (Concept 11.5) mutation: any change in the nucleotide sequence of DNA (Concept 11.6) mutagen: physical or chemical agent that causes mutations (Concept 11.6)