SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS
advertisement

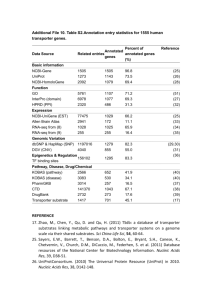
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS Figure S1 Process Diagram of Semi-auto Data Retrieval from External Data Sources Table S1. Integrated external databases Integrated Databases NCBI Genbank NCBI Homologene NCBI PubMed Gene Ontology UniProt PDB Ensembl BIND Description Gene information Collection of groups of homolog sequences Collection of biomedical literature citations and abstracts Gene annotations Protein information Protein structure Annotation of large eukaryotic genomes Molecular interactions Literature cited [1] [2] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] [7] [1] Benson,D.A., Karsch-Mizrachi,I., Lipman,D.J., Ostell,J. and Wheeler,D.L. (2006) GenBank. Nucleic Acids Res., 34, D16-D20. [2] Wheeler,D.L., Barrett,T., Benson,D.A., Bryant,S.H., Canese,K., Chetvernin,V., Church,D.M., DiCuccio,M., Edgar,R., Federhen,S. et al. (2006) Database resources of the National Center for Biotechnology Information. Nucleic Acids Res., 34, D173-D180. [3] Gene Ontology Consortium. (2001) Creating the gene ontology resource: design and implementation. Genome Res., 11, 1425-1433. [4] Wu,C.H., Apweiler,R., Bairoch,A., Natale,D.A., Barker,W.C., Boeckmann,B., Ferro,S., Gasteiger,E., Huang,H., Lopez,R. et al. (2006) The Universal Protein Resource (UniProt): an expanding universe of protein information. Nucleic Acids Res., 34, D187-D191. [5] Deshpande,N., Addess,K.J., Bluhm,W.F., Merino-Ott,J.C., Townsend-Merino,W., Zhang,Q., Knezevich,C., Xie,L., Chen,L. Feng,Z. et al. (2005) The RCSB Protein Data Bank: a redesigned query system and relational database based on the mmCIF schema. Nucleic Acids Res., 33, D233-D237. [6] Birney,E., Andrews,D., Caccamo,M., Chen,Y., Clarke,L., Coates,G., Cox,T., Cunningham,F., Curwen,V., Cutts,T. et al. (2006) Ensembl 2006. Nucleic Acids Res., 34, D556-D561. [7] Alfarano,C., Andrade,C.E., Anthony,K., Bahroos,N., Bajec,M., Bantoft,K., Betel,D., Bobechko,B., Boutilier,K., Burgess,E. et al. (2005) The Biomolecular Interaction Network Database and related tools 2005 update. Nucleic Acids Res., 33, D418-D424. Figure S2 Animated TLR Signaling Pathways Descriptions of labels in the Figure S2 are listed in the below: Steps to run the animated signaling pathway 1 Choose the ligands 2 Click here to show the pathway components 3 Click here to start the simulation Description of functionality of the buttons A Click one of the button to set status of the selected pathway component. WT: set the status of the component as wild type M: set the status of the component as mutant KO: set the status of the component as knockout B Click to view details of mutant/knockout phenotype C Click to view description of the selected pathway component