Subject: - Gates County Schools

Subject: Biology
Grade Level/Course: 10th
Unit Title: Structure and Function of Living Things
Timeframe Needed for Completion: 4 – 5 weeks
Grading Period: 1 st
six weeks
Big Idea/Theme: Structure and Functions
Learning Targets: (“I can” or “I will” statements)
1.
I will understand the structure and function of the basic molecules from which all living things are made including: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids.
2.
I will learn the basic structure and function of enzymes and their importance to living things.
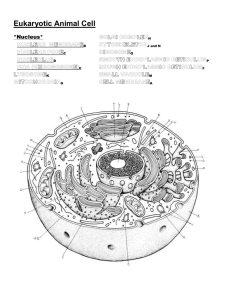
3.
I will learn that cells contain organelles including: the plasma membrane, cell wall, mitochondria, vacuoles, chloroplasts, and ribosomes.
4.
I will learn that cells are specialized to their function and can communicate with one another.
5.
I will investigate how cells move materials in and out including: passive transport (diffusion, osmosis), active transport, and the role of ATP as a source of energy.
Essential Questions: (3-5 questions per unit) – This is not a yes or no question; it must be broad, debatable, and thought-provoking.
Curriculum Goals/Objectives: (Common Core or Essential
Standards)
1.
How can you compare the structure of a cell to the organ systems of a human body
2.
What are the common characteristics of living organisms?
3.
What does the phrase “structure to function relationship”mean?
Bio 1.1.1 Summarize the structure and function of organelles in eukaryotic cells (nucleus, plasma membrane, cell wall, mitochondria, vacuoles, chloroplasts, and ribosomes) and ways these organelles interact with each other to perform the functions of the cell.
Bio 1.1.2 Compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells in terms of their general structures (plasma membrane and genetic material) and degree of complexity.
Bio 1.2.1 Explain how homeostasis is maintained in a cell within an organism in carious environments (including temperature and pH).
Bio 4.1.1 Compare the structures and functions of the major biological molecules (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids) as related to the survival of the living organisms
4.1.3 Explain how enzymes act as catalyst for biological reactions.
Essential Concepts:
Explore and test different mixtures for the presence of various macromolecules.
write examples of products that represent proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids.
Build connections between macromolecules
students learn the features of the microscope, including, total magnification, size of field of view of each objective, reversal of images, and how to estimate size of objects viewed through the microscope
Students will use microscopes to view various cells
Students will investigate the specific functions of each of the types of cells as they relate to the structures.
Students will explain how organelles interact to help cells function as a whole unit.
Students will understand relationships among and between the organelles
Students will compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
understand how changes in surface area/volume ratio affect diffusion in cells
Design and conduct scientific investigations to answer biological questions.
Investigate and analyze cell as a living system
Investigate and describe the structure and function of enzymes and explain their importance in biological systems.
Other Integration Opportunities: (literacy anchor standards,
Information and Technology Essential Standards, 21 st century content and skills, other disciplines)
-Cite specific textual evidence to support analysis of science and technical text…..
-Determine the meaning of symbols, key terms, and ….
-Analyze the structure of relationships among concepts….
-Evaluate the hypothesis, data, analysis, and conclusion in science….
-Students understand that scientific research and experimentation….
-Students collaborate with peers…..
-Students are able to revise their own scientific ideas and hypothesis…
Assessment Tasks: (examples of summative and/or formative assessments)
Quizzes
Tests
Thinking maps
-brace or tree maps for organic chemistry
-bridge maps for organelles
-double bubble prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
-flow maps for steps in scientific method
Diagrams of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
Lab grades
Collaboration with classmates on Labs extended beyond the initial question or problem of the lab ( “What if” scenarios)
Labs (virtual or actual)
Microscope Lab
Enzyme Lab
Qualitative Organic Chemistry
Scientific Method Lab
Resources:
Text book for diagrams, tables, figures
Discovery Education – Microscope Video
The Cell video
Scientific Method Lab
- silly putty lab
- seed germination
Microscope Lab
-10 micrscopes
-microscope slides
-animal cells
-onions or Elodea
Enzyme Lab with Liver
Qualitative Organic Chemistry
-SAS in schools
-starch
-Iodine solution
-simple sugar
- Benedict’s solution
-protein
-Buiret’s Reagent
-oil
Acid/Base Lab
-litmus and pHydrion papers