Misr language school Second preparatory Model Answer for general
advertisement

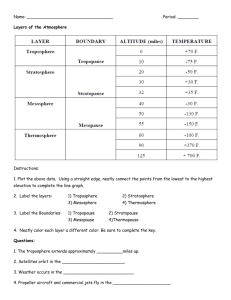
Misr language school Second preparatory Model Answer for general exercises In school book Pages 111, 112: Choose the correct answer: 1- Alkaline earth metals 3- Mesosphere 2- Halogens. 4- Overhunting and environmental pollution. Write the Chemical equations representing the following: 1- MgO + H2O = Mg(OH)2 2- Cl2 + 2KBr = 2KCl + Br2 3- 2H2O = 2H2 + O2 Mention one difference between each of: 1- Fluorine molecule: group 7A, helium molecule: group zero 2- Natural pollutants: it causes by nature (volcanic eruption ) Industrial pollutants: it causes by human (chemical pollution: throwing wastes of factories). 3- Troposphere: air pressure = 100 mb, Stratosphere: air pressure = 1 mb 4- Simple ecosystem: few members (Desert), Complicated ecosystem: multiple members (forests) Give reasons: 1- Due to the difference in electronegativity between its elements is relatively high. 2- To prevent its reaction with moist air 3- The air moves horizontally and no weather conditions 4- Because it feeds on poisonous fish Write brief notes on: 1- Water has a maximum density at 4oC, while water has a lowest density at zero C. 2- As the height increases the atmospheric pressure decreases 3- It is a continuous increase in a temperature of earth's atmosphere due to increase in a ratio of greenhouse gases. To who are these works attributed: 1- Rutherford 2- Van- Allen belts 3- IUCN Pages 113, 114: Complete the following statements : 1- Ascending 2- Protons 3- Monovalent 4- 7A Choose the correct answer for each of the following: 1- 116 2- number of protons 3- B, C are correct 4- Less than its density in liquid state 5- All the previous Mark ( ) or ( x ) : 1- Right 2- False 3- Right 4- Right 5- False. Write the scientific term : 1- Troposphere 2- Fossils (practical) 4- Negative ion 5- Hydrogen bonds. 3- Metalloids Pages 115, 116 , 117 , 118 , 119 ,120 and 121 : Choose the correct answer: 1- Group 2- Mendeleev 3- S 4- Transition 5- Bohr 6- Na, Li 7- Rutherford. 8- Inert gas 9- 7 10- Basic, Amphoteric then acidic . 11- Basic 12- Alkaline 13- Group 1A 14- Barium 15- Thermosphere 16- Mesosphere 17- Stratosphere 18- Barometer 19- Troposphere 20- Altimeter 21- Stratosphere 22- Ionosphere 23- Mesosphere 24- Mesosphere 25- 13 C 26- Weight 27- Mesosphere 28- Thermosphere 29- horizontally 30- Magnetic 31- Is less than 32- 1013.25 33- Troposphere 34- Stratosphere 35- Stratosphere 36- Three oxygen atoms 37- Ultraviolet rays 38- The south pole 39- Halons 40- Chloride 41- Nothing above 42- A and b 43- Infrared rays 44- September 45- Freon 46- Methyl bromide gas 47- Nitrogen oxides 48- A and b together 49- b and c 50- Dobson 51- all the above 52- Polar bears 53- Practical 54- Practical 55-Practical 56- Practical 57- Practical 58- Practical 61- Practical 64- Practical 59- Practical 62- Practical 65- Practical 60- Practical 63- Practical 66- The continuous decrease in number of individuals of the same species without compensation Pages 121 , 122 and 123 : Complete the followings: 1- Rutherford, Moseley 2- Lanthanides and actinides 3- Transition elements 4- fourth 5- 7 and 18 6- Increases 7- Decreases 8- Metal, noble gas 9- 7A (17) 10- 13 km 11- Decreases, 6.5oC 12- 1013.25 13- Measure the atmospheric pressure with day weather. 14- 37 km 15- UV rays, oxygen molecule, oxygen molecule 16- UVA, UVB, UVC. 17- Skin cancer, cataract, and weakness of immune system 18- Spoil eggs, decrease rate of reproduction. 19- Death of plankton, destroy food chain. 20- Upset photosynthesis process, decrease crops production. 21- a) Oxygen molecule of oxygen atoms . b) Oxygen molecule. 22- CFC, Halons, Nitrogen oxides 23- Methyl bromide gas 24- Visible light, UV rays 25- Reduce the use of CFC compounds; stop producing the ultra sound Concorde planes 26- Continuous increase in temperature of earth's atmosphere 27- 10 -9 meters 28- UV rays, visible light 29- Earth's day 30- 38 practical 39- Number, certain, compensation, die 40- Practical 41- Global warming, Extinction 42- Overhunting, reptiles, mammals. 43- 1) Mesosphere, 35 km, hydrogen and helium. 2) Second, 37 km, ozone gas. 3) Thermosphere, fourth, charged ions (ionosphere) Pages 123 , 124 , 125 : Put ( ) or ( x ) : 1- Right 2- False, vertical groups. 3- False, ascending 4- Right. 5- Right 6- Right. 7- Right 8- False, B 9- False, 116 10- Right. 11- Right 12- False, 1.7 13- False, difficult 14- False, strong metal. 15- Right 16- Right. 17- Right 18- False, troposphere. 19- Right 20- Right. 21- 1013.25 miilibar 22- Right. 23- Right 24- False, second 25- Right 26- Right. 27- Right 28- Right. 29- False, stratosphere 30- False, horizontally. 31- Right 32- False, Dobson. 33- Right 34- Right. 35- Right 36- False, near only. 37- Right 38- False, nitrogen oxide 39- False September 40- False, Halons 41- Right 42- Right. 43- False, methane and CO2 44- Right. 45- False, 20 to 40 Km 46- Right. 47- Right 48- Right. 49- Right 50- Right. Pages 125 , 126 ,127 , 128 Correct the underlined words: 1- Moseley 2- Bohr 3- Increase in atomic no. 4- Decreases 5- Noble gas 6- 7 group ( 7A ). 7- Acidic oxides 8- Second group. 9- Mammoth 10- Practical 11- Practical 12- Practical. 13- Practical 14- Practical. 15- Practical 16- Practical. 17- Practical 18- Practical. 19- Dinosaur 20- Quagga 21- Dodo bird 22- Endangered 23- Protectorates Write the scientific terms: 1- Mendeleev's periodic table. 2- Moseley's periodic table. 3- Periods. 4- Groups. 5- Energy levels. 6- Sub levels 7- Transition elements. 8- P- block. 9- F - block. 10- Electronegativity 11- Amphoteric oxides. 12- Metals. 13- Non metals. 14- Group 7A 15- P- block. 16- Mesopause. 17- Thermosphere. 18- Altimeter. 19- Troposphere 20- Van Allen belts. 21- Aurora phenomena. 22- Mesosphere. 23- Exosphere. 24- Global warming. 25- Ozone gas. 26- Oxygen gas. 27- Infrared rays. 28- to 33 practical . 34- Extinction. 35- Overhunting. 36- Food chain. 37- Simple ecosystem. 38- Complicated ecosystem. 39- Protectorates. Pages 128 , 129: 1- 1- c 2- a 3- e 4- b 6- f 2- 1- e 2- c 3- b 4- d 3- Practical. 4- 1- b ( practical ). 2- a ( practical). 3- d 4- e. Page 130 Give reasons : 1- Because it has highest electronegativity and the largest atomic size non metal. 2- Because it has the largest atomic size. 3- Because it dissolves in water forming acids , changing the colour of litmus paper into red. 4- Because it dissolves in water forming bases , changing the colour of litmus paper into blue. 5- Because it has both properties of acidic oxides and basic oxides . 6- Due to the attraction force between nucleus and the electrons in outermost energy level increases. 7- Due to the difference in electronegativity between its elements is relatively high. 8- Because the outermost energy level may be ends with 3 , 4 , 5 or 6 electrons. 9- Because it contains 75% of atmospheric mass . 10- Because it contains charged ions which reflect radio waves. 11- Due to 2 magnetic belts surrounds ionosphere. 12- Because it contains charged ions. 13- Because the ozone layer absorbs UV rays . 14- Due to pollutants which affects ozone layer such as CFC compounds , Methyl bromide gas , Halons and nitrogen oxides. 15- Because it protects earth from harmful UV rays 16- Because of cutting trees, burning fuels and burning forests. 17- To avoid erosion of ozone layer. 18- Practical. 19- Practical. 20- It causes extinction of more than 300 species. 21- Because it has a few members or alternatives. 22- It causes extinction. 23- Because it feeds on their sheep's and chickens . 24- Because it has short wings so it can't fly and short legs so it can't run. 25- Because of overhunting and changing its habitat to cultivated lands. 26- To protect the living organisms from extinction. 27- Because it has a large amount of skeletons of whales. Page 131 : What happens in the followings : 1- The colour changes into blue. 2- The colour changes into red. 3- It forms magnesium hydroxide. 4- The water molecule will be a non polar compound 5- It reaches maximum density 6- We cannot use it in putting off fires 7- It will change into water vapour 8- Water decomposes by electricity into hydrogen gas and oxygen gas . 9- It causes water pollution. 10- Practical . 11- Practical. 12- Practical . 13- Extinction of many species. 14- Extinct of passenger pigeons. 15- Disturbance in ecosystem. 16- Destroy natural habitat lead to extinction of species. 17- Extinct of passenger pigeons. Page 131: Compare between : 1- Alkalis: Group 1A, Monovalent; lose 1 electron during chemical reactions. Earth alkaline: Group 2A, Divalent; lose 2 electrons during chemical reactions. 2- Group: elements have the same no. of electrons in outermost energy level. Period: elements have the same no. of energy levels . 3- Atomic volume ( size ) : distance between nucleus and the outermost energy level. Electronegativity: ability of an atom to attract the electrons in a covalent bond toward itself 4- Altimeter: measure atmospheric pressure with height from sea level. Aneroid: measure atmospheric pressure with day weather. 5- Troposphere: 100mb, decreases till it reaches – 60 C at its end. Ionosphere: very low, increases till it reaches 1200oC at its end. 6- Mesosphere: 0.01mb, decreases till it reach – 90oC at its end. Thermosphere: very low, increases till it reaches 1200oC at its end. 7- Atmospheric pressure: weight of air column over unit area Atmospheric envelope: mixture of gases surrounds the earth and it extends to 1000 kms Pages 131 , 132: Mention one difference: 1- Practical 2- Practical. 3- Practical. 4- Practical. 5- Simple ecosystem: few members Complicated ecosystem: multiple members 6- Ras Mohamed: collection of coloured fish and coral reefs Waadi Hetan: collection of skeletons of whales Page 132 : What is meant by: 1- Group of recommendations to protect ozone layer. 2- Chloro- fluoro carbon compounds 3- Intergovernmental panel on climate change. 4- Continuous increase in temperature of earth's atmosphere. 5- Standard Temperature and pressure. 6- Losing parts of ozone layer. 7- Measuring unit of ozone layer. 8- No Chloro fluoro carbon compounds 9- CO2, CH4, H2O and CFC compounds. 10- Lamps protect your environment and save your money. 11- Trapping infrared rays by plastic or galss. 12- Temperature = zero oC and Pressure = 1013.25mb. 13- 10-9 meters. 14- practical. 15- Practical. 16- Continuous decrease in number of living organisms of certain species without compensation. 17- Practical. 18- List of endangered species and the level of danger of each species. 19- Practical. 20- Practical. 21- International union conservation of nature. 22- Practical 23- Practical. Page 132: What is the importance: 1- Scattering the harmful cosmic radiations away from earth. 2- Protecting earth from harmful UV rays. 3- Measure the atmospheric pressure with height from sea level. 4- Regulate the temperature of earth's atmosphere. 5- Wireless communications and radio stations. 6- Area in which satellites are rotating. 7- Transmit weather condition information and TV programs. 8- Measure the atmospheric pressure with day weather 9- Burning meteors before reaching earth. Mention one example: 1- to 6 Practical. 7- Ibis bird. 8- Papyrus plant. 9- Dodo bird. 10- Passenger pigeon. 11- Panda. Page 133: Choose: 1- e 2- d 3- b 4- c 5- Ras Mohamed a. 6- No choices. 7- F (practical). Model answer Exam 1 Question one: Complete the followings: 1- Properties. 2- Harmful 3- Dinosaur, mammoth. 4- Kerosene, moist air. Question two: Choose the right answer: 1- C 2- A 3- A 4- Practical 5- Practical 6- A Question Three: Give reasons for : 1- Due to its low boiling point – 196 C. 2- Because the air moves horizontally and no weather conditions . 3- Practical. Question Four: Put right or false: 1- false. 2- practical. 3- false. 4- right. 5- right. 6- right. Model Answer Exam 2 Question one: A) Choose the right answer: 1- C 2- B 3- B 4- B B) Element Y 17: 1- 2,8,7. 2- 7A 3- 3. Question two: A) Put true or false : 1- true. 2- true. 3- true in groups. 4- Practical. 5- true. B) See the figure: 1- A 2- B neutral atom. 3- period 2 , group 2A. Question Three: Write scientific term: 1- Extinction. 2- Dodo bird. 3- Electronegativity. 4- Alkaline earth metals . 5- Natural protectorates. Question Four: Complete the followings: 1- bottom to up. 2- less , more. 3- stratosphere. 4- Practical. 5- halogens. 6- natural protectorates. 7- hydrogen . 8- Practical.