ANSWERS TO REVIEW QUESTIONS
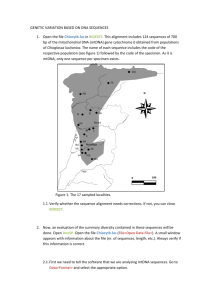
advertisement

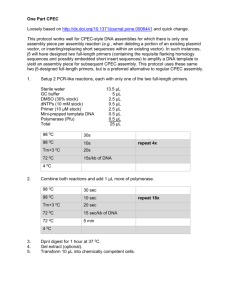
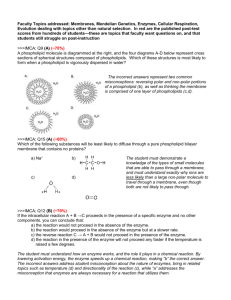
ANSWERS TO REVIEW QUESTIONS CHAPTER 16 1. Dryopithecus, Ardipithecus, Australopithecus anamensis, Australopithecus garhi, Homo habilis, Homo erectus, Homo sapiens idaltu, Denisova hominin, Neanderthals. Overlaps are uncertain due to incomplete evidence. 2. Hominoids are ancestral to apes and humans, whereas hominins are ancestral to humans only. Therefore, hominoids are more ancient. 3. Physically, chimpanzees are not as similar to us as were the australopithecines, yet the australopithecines are in a different genus from us. 4. A single gene can control the rates of development of specific structures, causing enormous differences in the relative sizes of organs in two species. 5. Limited fossil or genetic evidence provides only a partial picture. For example, the sequence of the Neanderthal genome indicated that we share more sequences with them than had been concluded from comparing only some mtDNA sequences. 6. Comparing mtDNA sequences reveals long-ago expansions from Africa. Chapter 15 has several examples of migrations revealed through DNA sequences. 7. Tool use, big brain, bipedalism, cognitive skills 8. Comparing the genomes of indigenous individuals to those of other modern populations can reveal effects on genetic diversity of natural selection, which in turn reflects environmental influences on reproduction. 9. Fossil evidence and mtDNA evidence support an "out of Africa" emergence of modern humans. 10. Y chromosome and mitochondrial DNA sequences enable researchers to trace the genetic contributions of fathers and mothers, respectively. 11. Bipedalism, larger brain, improved fine coordination 12. If the trait is highly conserved, it is very important and therefore unlikely to have changed much through primate evolution. 13. Knowledge of a DNA, RNA, or polypeptide sequence and the mutation rate is necessary to construct an evolutionary tree diagram. An assumption is that mutation rate is constant. A limitation is that only molecular genetics is considered and not large scale characteristics such as behavior and anatomy. 14. SNPs are single nucleotide polymorphisms, indels are insertions and deletions and haplotypes comprise a series of known DNA sequences or SNPs that are linked on a chromosome. ANSWERS TO APPLIED QUESTIONS 1. Our ancestors’ abilities to sweat and run enabled them to survive beyond the treetops. This illustrates natural selection. 2. Answers vary. An example might be selective pressure toward increasing social organization and tool use 1 3. Many species of australopithecines could have arisen because the groups were physically separated and thus could diverge genetically, especially if their environments differed. As Homo evolved, populations met and coalesced, mixing gene pools. 4. a. A small duplication occurred in human chromosome 11 to give rise to the Betazoid karyotype. The Klingon and Romulan karyotypes could have arisen from fusion of human chromosomes 15 and 17. b. The Betazoids are our closest relatives because of greater similarity in chromosome bands and chromosome arrangement. Cytochrome C sequences and intron pattern in the collagen gene are identical between humans and Betazoids. c. They are not distinct species because they can interbreed. d. 3 5. Differences in DNA sequences between chimps and humans are used to estimate the time of divergence of the two species. Such an investigation might also reveal why chimps do not become ill from SIV, their version of HIV. 6. The child would be a modern human. 7. Yes, based on mtDNA evidence, we all descend from Africans. 8. Opinion. Ancestry testing often reveals a more diverse genetic background than people know from family lore. 9. Mitochondrial and genomic DNA from Hatshepsut and reference family members. 10. The Mbuti Pygmies lived happily in Central Africa, until the Alur, Hema, and Nande encroached on the ancestral lands in search of places to plant their crops. Men from the farming communities would occasionally rape Pygmy women. ANSWERS TO WEB ACTIVITIES 1. The Aetas live on the northern Philippine island of Luzon. They were pushed from their lands near the volcano Mount Pinatubo when it erupted in 1991, settling in the city. The Aetas are experts at surviving jungle conditions and helped to train US soldiers during the Viet Nam conflict. The Aetas are all less than five feet tall, a trait with a high heritability. 2 a. Ancestry in one of the major geographic or people groups of the world. b. Only limited lineages are traced. c. By testing a sample from a brother, father or other male from the paternal line d. Opinion based on privacy concerns. ANSWERS TO FORENSICS FOCUS 1. The technology used on the Greenland Eskimo can be used to determine hair, eye, and skin color when there is not enough of a body to see these phenotypes. 2. Opinion. One side is that people entering a country should submit to the practices and laws of that country, such as DNA testing. The other side is that differing cultural definitions, such as that of family, should be recognized and respected. Perhaps immigration officials should be educated about the practices of people from different nations. ANSWERS TO CASE STUDIES AND RESEARCH RESULTS 1. a. Which genes enable a large mammal to survive at high altitude in extreme cold? b. Extract DNA from a frozen mammoth and insert it into an enucleated egg from a modern African elephant. 2 c. A valuable gene variant gave a survival advantage, so its frequency in the population increased over time. d. Elephants and mammoths share a common ancestor. One did not evolve from the other. e. Both elephants and humans expanded out of Africa, founding new populations, while some remained in Africa, where their descendants live today. 2. We share some DNA sequences with Neanderthals. 3. From DNA. 4. a. Divergence of ancestral humans and chimps. Divergence of modern humans from archaic humans. Divergence of modern human populations. b. The similarities support current hypotheses regarding primate and human evolution. c. The divergence of old world and new world lice varieties. Anthropological evidence of contact between archaic and modern humans. d. Conclusions are based on estimates of mutation rates and populations sizes which may be inaccurate. 5. Africa to Western Asia and Europe. Spain and Portugal through Northern Africa. Anthropological evidence. 3