BIO 340
advertisement
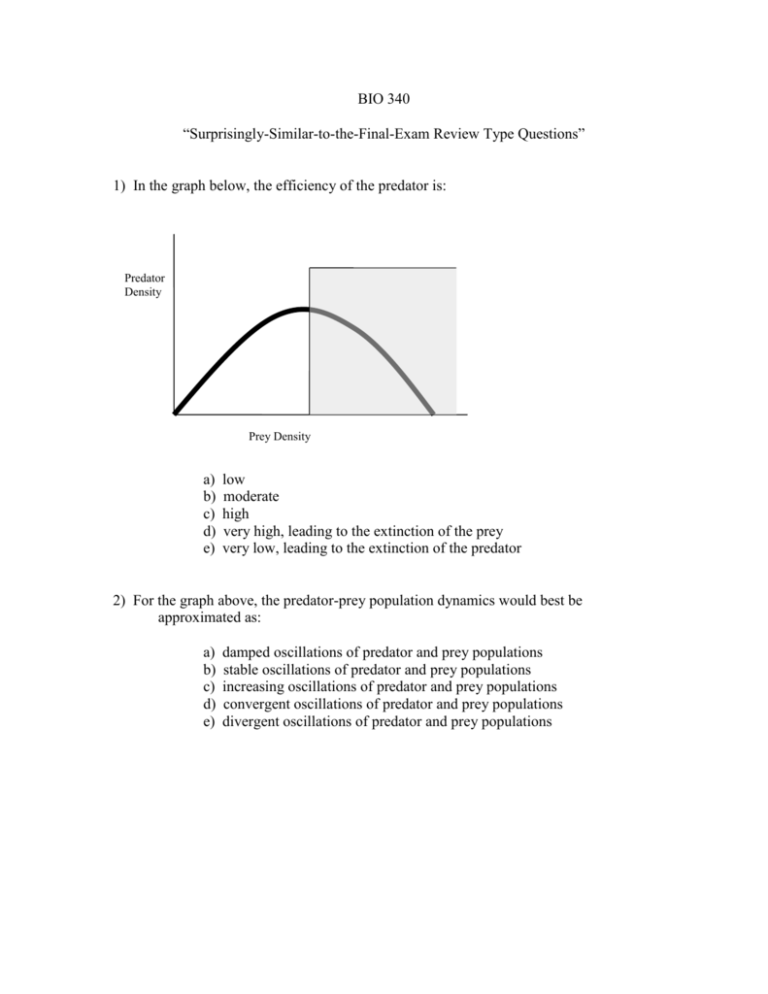
BIO 340 “Surprisingly-Similar-to-the-Final-Exam Review Type Questions” 1) In the graph below, the efficiency of the predator is: Predator Density Prey Density a) b) c) d) e) low moderate high very high, leading to the extinction of the prey very low, leading to the extinction of the predator 2) For the graph above, the predator-prey population dynamics would best be approximated as: a) b) c) d) e) damped oscillations of predator and prey populations stable oscillations of predator and prey populations increasing oscillations of predator and prey populations convergent oscillations of predator and prey populations divergent oscillations of predator and prey populations 3) What type of functional response is identified in this figure. Number Prey killed per predator per unit time Prey Density a) b) c) d) e) Type I Type II Type III Type IV Type A 4) Why does the curve, in the graph above, reach an asymptote or level off? a) b) c) d) e) the predator has difficulty finding more prey the prey become elusive the predator becomes satiated the predator’s begin to compete all of the above 5) Ecologist who described a model of an ecosystem as an energy-transforming machine: a) b) c) d) e) Volterra Elton Lindeman Lotka Paine 6) Habitat fragmentation typically results in: a) increased patch area b) decreased patch isolation c) increased edge habitat d) increased dispersal rates e) decreased population density Additional Example Questions for the Final Exam 1. All are considered ecological spatial elements EXCEPT: a. matrix b. ecosystems c. patches d. corridors 2. T/F Fragmenting can take place in aquatic environments as well as terrestrial environments. (true) 3. Brown headed cowbirds highly contribute to: a. net primary production b. nutrient cycling c. nest parasitism d. extreme predation 4. Choosing sites that look good to organisms at a certain time to live, but eventually become traps for predation is part of the: a. Ecological Trap Hypothesis b. Ecological Predation Hypothesis c. Wrong Decision Hypothesis d. Ecological Accountability Hypothesis 5. T/F Higher-order effects is the process of which fragmentation leads to a change in a species’ abundance or distribution. (false) 6. About what percent of energy is efficient between trophic levels? a. 3% b. 10% c. 25% d. 50% 7. Which statement is true dealing with energy? a. Herbivores and carnivores expend more energy on maintenance than plants. b. Plants use about 95% of light energy assimilated for maintenance. c. Lower trophic levels have higher energy levels than the levels above it. d. Energy is put into the ecosystems via metabolism. 8. T/F Assimilation efficiency increases are higher trophic levels. (true) 9. The scientist that came up with the Energy Flux Model popularizing ecology to a new generation is: a. Lindeman b. Odum c. Lotka d. Elton e. Volterra 10. Bacteria are an example of what type of trophic structure? a. decomposers b. autotrophs c. secondary consumers d. two of the above e. none of the above








