8th Grade Science Curriculum Map: 2009-2010
advertisement

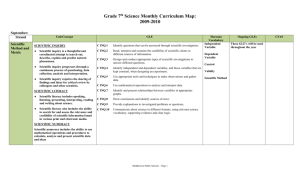
Grade 8th Science Monthly Curriculum Map: 2009-2010 September 15- November 23 Unit/Concept Strand Scientific Method and Metric GLE Marzano Vocabulary Independent Variable SCIENTIFIC INQUIRY C INQ.1 Identify questions that can be answered through scientific investigation. Scientific inquiry is a thoughtful and coordinated attempt to search out, describe, explain and predict natural phenomena. C INQ.2 Read, interpret and examine the credibility of scientific claims in different sources of information. C INQ.3 Design and conduct appropriate types of scientific investigations to answer different questions. Scientific inquiry progresses through a continuous process of questioning, data collection, analysis and interpretation. C INQ.4 Identify independent and dependent variables, and those variables that are kept constant, when designing an experiment. Validity C INQ.5 Use appropriate tools and techniques to make observations and gather data. Scientific Method Scientific inquiry requires the sharing of findings and ideas for critical review by colleagues and other scientists. C INQ.6 Use mathematical operations to analyze and interpret data. C INQ.7 Identify and present relationships between variables in appropriate graphs. C INQ.8 Draw conclusions and identify sources of error. SCIENTIFIC LITERACY C INQ.9 Provide explanations to investigated problems or questions. Scientific literacy includes speaking, listening, presenting, interpreting, reading and writing about science. C INQ.10 Communicate about science in different formats, using relevant science vocabulary, supporting evidence and clear logic. Scientific literacy also includes the ability to search for and assess the relevance and credibility of scientific information found in various print and electronic media. SCIENTIFIC NUMERACY Scientific numeracy includes the ability to use mathematical operations and procedures to calculate, analyze and present scientific data and ideas Middletown Public Schools – Page 1 Dependent Variable Control Ongoing GLEs CFAS Grade 8th Science Monthly Curriculum Map: 2009-2010 Heredity and Evolution 1. Describe the structure, location and function of chromosomes, genes Heredity, and DNA and how they relate to each other in the living cell. species, 2. Illustrate and chart the purpose, cell type (somatic and germ) reproduce, and resulting chromosome count during cell division in asexual/sexual, mitosis and meiosis. reproduction, 3. Identify the major structures in human male and female reproductive chromosome, systems and explain where meiosis and gamete formation take place. gene, DNA, 4. Investigate and report on the role of hormone production as it initiates and regulates 5. the creation of male and female germ cells from birth trait, body through adolescence and into adulthood. (somatic) cell, 5. Compare and contrast the events and processes that occur germ cell, when a human egg is fertilized or not fertilized. gamete, 6. Demonstrate the relationship of corresponding genes on pairs meiosis, of chromosomes to traits inherited by offspring. 7. Describe in writing the role of the germ cells in the formation of the human zygote and its resulting 23 pairs of chromosomes, the 23rd of which determines gender and the other 22 of which determine the characteristics of that offspring. 8.2.a Heredity is the passage of genetic information from one generation to another. 8.2.b Some of the characteristics of an organism are inherited and some result from interactions with the environment. Relate the continued existence of any species to its successful reproduction hormone, adolescence, and explain 1. in writing the factors that contribute to successful reproduction. zygote, fetus Middletown Public Schools – Page 2 Grade 8th Science Monthly Curriculum Map: 2009-2010 Strand Unit/Concept GLE Middletown Public Schools – Page 3 Marzano Vocabulary Textbook Correlation/Materials CFAS Grade 8th Science Monthly Curriculum Map: 2009-2010 November 26 – January 15 Unit/Concept Strand GLE Middletown Public Schools – Page 4 Marzano Vocabulary Textbook Correlation/Materials CFAS Grade 8th Science Monthly Curriculum Map: 2009-2010 Earth and the Solar System 1. Relate the strength of gravitational force between two objects to their mass and the 1. distance between the centers of the two objects and provide Force, gravity, examples. orbit, 2. Describe in writing how gravitational attraction and the inertia of objects in the solar 2. system keep them on a predictable elliptical pathway. 8.3.a Gravity is the force that governs the motions of objects in the solar system. revolution, year, 1. Distinguish between rotation of Earth on its axis and its elliptical revolution around the sun. period, mass, 2. Investigate and report in writing how the Earth’s revolution around the sun weight, rotation, affects changes in daylight and seasons. hemisphere, 3. Compare the revolution times of all the planets and relate it to their distance season, phase, from the sun. new moon, solar 4. Conduct and report on an investigation that shows how the Earth’s tilt on its eclipse, axis andlunar 6. position around the sun relates to the intensity of light striking the Earth’s surface. eclipse, tides 5. Use a model to demonstrate the phases of the moon relative to the position of the sun, Earth and moon. 6. Develop a model or illustration to show the relative positions of the Earth, sun and moon during a lunar and solar eclipse and explain how those positions influence the view from Earth. 8.3.b The motion of the Earth and moon relative to the sun causes daily, monthly and yearly cycles on Earth. Middletown Public Schools – Page 5 Grade 8th Science Monthly Curriculum Map: 2009-2010 Strand Unit/Concept GLE Middletown Public Schools – Page 6 Marzano Vocabulary Textbook Correlation/Materials CFAS Grade 8th Science Monthly Curriculum Map: 2009-2010 January 16 – March 7 Strand Unit/Concept GLE Middletown Public Schools – Page 7 Marzano Vocabulary Textbook Correlation/Materials CFAS Grade 8th Science Monthly Curriculum Map: 2009-2010 Energy in the Earth’s System , core, Illustrate and describe in writing the composition of the three major layers of the Earth’s 1.mantle, interior. folds, .fault/fault Explain how Earth’s internal energy is transferred to move tectonic plates.2. line, continent, Demonstrate the processes of folding and faulting of the Earth’s crust. 3. tectonic Correlate common geological features/events (deep sea trenches, mountains, earthquakes, 4. plate, volcanoes) with the location of plate boundaries. boundary, Compare geological features that result from constructive forces (e.g., mountains andplate 5. ridges) with geological features that result from destructive convection, forces (e.g., canyons and flood plains). Analyze and interpret data about the location, frequency and intensity of earthquakes.mountains, volcano, earthquake 7.3.a Volcanic activity and the folding and faulting of rock layers during the shifting of the Earth’s crust affect the formation of mountains, ridges and valleys. . Erosion, Compare and contrast the major agents of erosion and deposition of sediments: running 7. water, moving ice, wave action, wind and mass movement due 7.3.b Glaciation, weathering weathering, to gravity. and erosion change the Earth’s surface by moving earth materials from place to place. glacier,8.valley, Investigate and determine how glaciers form and affect the Earth’s surface as they change over time. floodplain Distinguish between weathering and erosion.9. Observe and report on the geological events that are responsible for having shaped 10. Connecticut’s landscape. Middletown Public Schools – Page 8 Grade 8th Science Monthly Curriculum Map: 2009-2010 February: Strand Unit/Concept GLE Middletown Public Schools – Page 9 Marzano Vocabulary Textbook Correlation/Materials CFAS Grade 8th Science Monthly Curriculum Map: 2009-2010 March: Strand Unit/Concept GLE Middletown Public Schools – Page 10 Marzano Vocabulary Textbook Correlation/Materials CFAS Grade 8th Science Monthly Curriculum Map: 2009-2010 March 8 – June 20 Unit/Concept The Changing Earth- How do materials cycle through Earth’s Systems 9.7 - Elements on Earth move among reservoirs in the solid earth, oceans, atmosphere and organisms as part of biogeochemical cycles. GLE Middletown Public Schools – Page 11 Marzano Vocabulary Textbook Correlation/Materials CFAS Grade 8th Science Monthly Curriculum Map: 2009-2010 9.7.a- Elements on Earth exist in essentially fixed amounts and are located in various chemical reservoirs. Explain how chemical and physical processes cause carbon to cycle through the major earth reservoirs. 9.7.b- The cyclical movement of Explain how solar energy causes water to cycle through the major earth reservoirs. matter between reservoirs is Explain how internal energy of the Earth causes matter to cycle through the magma driven by the Earth’s internal and the solid earth. and external sources of energy. Middletown Public Schools – Page 12 Carbon cycle, greenhouse effect, photosynthesis, decomposition, combustion, fossil fuels Reservoir, convection currents Grade 8th Science Monthly Curriculum Map: 2009-2010 May: Unit/Concept GLE Middletown Public Schools – Page 13 Marzano Vocabulary Textbook Correlation/Materials CFAS Grade 8th Science Monthly Curriculum Map: 2009-2010 June: Unit/Concept GLE Middletown Public Schools – Page 14 Marzano Vocabulary Textbook Correlation/Materials CFAS