How do detergents clean? Read the text and fill in the gaps with
advertisement

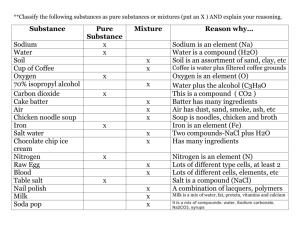
How do detergents clean? 1. Read the text and fill in the gaps with these words. detergent soapless droplet soluble hydrogen hydrophilic hydrophobic A detergent molecule, whether soapy or 1 ______________ , consists of two parts. There is a polar, 2 _______________ (water-loving) end. Which is soluble in water and is often called the ‘head’. There is also a non-polar, 3 _____________ (water- hating) end, which is soluble in fats and oils and is called the ‘tail’. The tail is a long hydrocarbon chain, that is, a chain of carbon atoms with 4 ______________ atoms attached to them. Dirt clings to surfaces, skin or fabric, by an oil film that surrounds the dirt particle. The tail end of 5 ______________ molecules will attach to the oil film around the dirt particle and completely surround it, making a tiny 6 ______________ or micelle. As all the tail ends are attached to the oil around the dirt particle, only the hydrophilic end of the detergent molecules will be exposed to the surface. As these are 7_______________ in water, you can now wash away the dirt. Common chemical substances and their uses in the home 2. Put the word and phrases in the correct places in the table. One item appears twice. alum ●antacid ● citric acid ● Glauber’s salt ● insect stings ●laxative ●monosodium glutamate ●oven cleaner ● raising agent ●salt ●sodium chloride ● sodium hydrogencarbonate ●sodium hydroxide ●vinegar ●washing soda Common name caustic soda Milk of magnesia 4 _____________ Chemical name (of active ingredient) Type of chemical Uses 1 _______________________ alkali drain cleaner, 2___________ grease remover magnesium hydroxide alkali 3 ____________________ acid cooking, pickling, cleaning and treating some 5______________ salt raising agent in baking, an antacid, in dry powder fire extinguishers, treating insect bites, for cleaning salt 7____________ in baking salt to make soaps and glass cleaners, also used as a water softener salt and acid antacid 10 _______________________ salt cooking and preserving foods. magnesium sulphate salt 11 _________________ sodium sulphate salt laxative acetic acid solution (ethanoic acid) 6 __________________________ baking soda __________________________ baking powder 8______________ sodium hydrogencarbonate sodium carbonate sodium hydrogencarbonate and Enos salts 9 _________________________ table (common) salt Epson salts 12 ____________ sodium aluminium sulphate salt water purification, also baking powder toothpaste sodium monofluoroposphate 14 ________ prevents tooth decay MSG 15 ____________________ salt enhances flavour in food 13 ____________ Solutions 3. Underline the correct word in each sentence. 1 Solutions are (homogenous/ heterogeneous) mixtures, which are formed when a solute completely dissolves in a solvent. 2 The (solute/ solvent) is the substance that dissolves, while the (solute/ solvent) is the substance that does the dissolving. 3 It is generally present in the (lesser/ greater) quantity in the mixture. 4 When the solvent used to make the solution is water then the solution is said to be (aqueous/ non-aqueous). 5 However when the solvent used is liquid other than water, then the solution is said to be (aqueous/ non-aqueous). 6 Liquid solutions are (translucent/ transparent) but not necessarily colourless. 7 They allow (light/ dark) to pass through without being scattered. 8 The dissolved particles are very small, from 0.1 nanometre to 1 nanometre therefore they cannot be seen with the (nude eye/ naked eye) or even be removed by normal filter paper. 9 The dissolved (articles/ particles) do not settle out if the solution is allowed to stand for some time. Solvents in stain removal 4. Match these stains with the correct paragraph to show the stain can be removed. blood ●chocolate ● paint ●varnish ●coffee/tea ● grease/oil ● ink ●nail polish 1 _________________ - Gloss is best removed whilst wet with turpentine or white spirit. Some water –based versions can be removed with hot water and detergent. 2 _________________ - If the stain cannot be removed by warm and soap, pour on boiling water, provided that this will not damage the fabric. Or use biological washing powder. If this does not work, dab with dilute hydrogen peroxide. 3 _________________ - If stains cannot be removed with soap and hot water, try biological detergent which contains bleach. 4 _________________ - Water-soluble versions of this substance can be removed by washing with soap and water. However, many stains made by this substance can be removed by soaking the stain in milk for 1 or 2 days, changing the milk as it becomes discoloured. Ethanoic acid and methanol are non- aqueous solvents that can dissolve these stains. 5 _________________ - Rub with alcohol. The wash with warm water and soap. 6 _________________ - Soak in cold water until stain turns lighter brown. Then wash in warm water and detergent. 7 _________________ - Remove with acetone which is an organic solvent. 8 _________________ - Wash in warm water and soap, or use clean white blotting paper, a piece on each side of the stain, and iron with a warm iron to remove as much of it as possible. Gasoline is non-aqueous solvent that removes these stains. Properties of acids and alkalis 5. Sort the characteristics of acids and alkalis in the correct columns. One of the characteristics applies to both. Acids…. Alkalis… 1 7 2 8 3 9 4 10 5 11 6 12 a …. are corrosive b …. are slippery when touched, that is they feel soapy. c ….. are soluble in water. d …. are the oxide or hydroxide of a metal. e …. have a sour taste. f …. react with acids to give a salt and water only. g …. react with bases/alkalis to produce a salt and water only. h …. react with fatty acids in the skin to form soap. I … react with many materials and some can damage human tissue. j … release hydrogen ions when dissolved in water. k … turn blue litmus paper red. Types of solutions 6. Read the text and complete the table. There are different types of solutions. We often think of solutions as being formed between a solid solute and a liquid solvent. However, gases and liquids can be solutes and solvents too. There are solutions which are made up of a solid in a liquid where the solute is a solid and the solvent is a liquid. Examples of this are sugar in water, salt in water and iodine in ethanol. Oxygen in water, carbon dioxide in water in fizzy drinks are examples of solutions where there is gas in a liquid. This is where the solute is a gas and the solvent is liquid. It is also possible to have a solution which is a liquid in a liquid where both the solute and the solvent are liquids. Examples of this are alcohol in water and syrup in water. Type of solution solid in liquid gas in liquid liquid in liquid Solute solvent examples 7. Choose the correct answers. Formic acid is an acid in the juice of fruits such as oranges that irritates the skin. It is present in ant bites. that is the main part of vinegar. Sodium stearate is a compound used for making soap, paper, etc. a sulphuric acid that is used to make soapless detergents. the chemical name for soap. Ascorbic acid is a compound containing carbon and oxygen a chemical compound produced from sulphuric acid. vitamin C. A disinfectant is a liquid used for washing clothes or dishes. A colloid is a type of alcohol used as a fuel. substance that is between a solution and a suspension. solid fatty acid. Aqueous means not mixing together to form a solution. substance used for cleaning injured skin. containing water. chemical substance that kills bacteria etc. not containing water. 8. Match the sentence beginnings and endings by reordering the endings on the right. Citric acid Lactic acid Lactic acid Lactic acid is found in sour milk. is also formed during anaerobic respiration in animals and bacteria. is found in citrus fruits. in is found in grapes. Hydrochloric acid causes muscle cramps. Ethanoic acid is vitamin C, so can be found in many green, leafy vegetables. Tartaric acid Ascorbic acid is made in the stomach where it aids digestion. is found in vinegar. 9. Use the words to complete the statements that follow: acidity Calcium hydroxide neutralize citric alkaline carbonates neutralization oxide In most cases acids and alkalis are used in the home for reactions. Rust stains can be removed by treatment with lime juice. Lime juice contains acid while rust is an of iron. Therefore the two react to form a salt and water. Acidic soils are less fertile, so farmers neutralize the soil, usually with slaked lime or before using it. Wasp stings are , so they can be treated with a mild acid such as vinegar, which contains acetic acid to neutralize the alkali in the sting. This helps to reduce the pain. The term ‘neutralization’ is used to describe any reaction which reduces For example, when a carbonate reacts with an acid to form salt, water and carbon dioxide, the carbonate is said to have neutralized the acid. are commonly used in home remedies. For example, bee stings and ant bites which are acidic can be treated with baking soda (sodium hydrogencarbonate) to them and so reduce the irritating effect. 10. Use the words to complete the statements that follow: neutral hydrogen oxide or hydroxide salt filtration combination Acids are substances that release Acids turn litmus paper A base is the red homogenous ions in solution. . of a metal. A neutralization reaction occurs when an acid reacts with a base to form and water only. On the pH scale pH7 is A mixture is a combined. Solutions are . of substances which are not chemically mixtures. The components of a suspension can be separated by 11. Suspensions In a suspension the solid particles do not dissolve but are suspended in the liquid. They will eventually separate or settle out if the mixture is left to stand. So, a suspension is an example of a heterogeneous mixture because the solid component can be seen separately from the liquid component in the mixture. The solid particles are also large enough to be filtered out. Examples of suspensions are soil and water and powdered chalk in the water. Suspensions scatter light that is they do not allow light to pass through completely. So they look cloudy.