Isoflurane - Environmental Health & Safety
advertisement

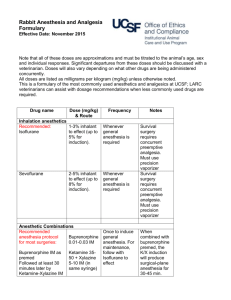
Standard Operating Procedure FoR Isoflurane Isoflurane GHS Classification: Signal Word: Warning Pictograms: General Hazard and Health Hazard Additional Classifications: Purpose: According to the Safety Data Sheet (SDS) special precautions must be taken when working with the chemical described below. The following information includes animal administration, chemical characteristics, followed by recommendations for handling prior to administration, and any paperwork needed in order to use the chemical in the laboratory. This Standard Operating Procedure will be followed along with the requirements of the Chemical Hygiene Plan. Brief description of agent use: Isoflurane is used to anesthetize animals. Isoflurane is a volatile anaesthetic which induces and maintains general anesthesia by depression of the central nervous system. Section 1: Brief Safety Overview The Principal Investigator is responsible for training employees on the proper use of the scavenging equipment prior to use. The training should include a discussion of the known and potential hazards; an explanation of the relevant policies, techniques and procedures including the proper use of personal protective equipment, emergency/spill procedures and containment equipment (engineering controls). Limit access to authorized users. Chemical has been entered in the Chemical Inventory (EHS Assistant) Training in the proper use of anesthesia machines for use with animals is mandatory Vaporizers must be validated annually and calibrated every 3 years. For more information see IACUC policy “Inhalation Anesthesia Machine/Vaporizer/ Waste Gas Maintenance” Controlled Substances in Research. Review the controlled substances policy if in use in your laboratory. Revised 5/3/11 Section 2: Animal Administration Route of Administration: Inhalent Dosage given to animals: Laboratory location where agent is being administered to animals: Section 3: Research Laboratory Procedures Handling: Appropriate PPE will be worn when handling Isoflurane. Wash hands thoroughly after gloves are removed. Storage: When not in use, agents will be stored in room ROOM #, BUILDING at the appropriate temperature, either -80˚C, -20˚C, 4˚C or room temperature. Agents should be dated when opened and checked to verify that the agent is not past the expiration date prior to use. Controlled substances will be secured in an appropriate lock box Location – Engineering controls All procedures using Isoflurane must take place in a chemical fume hood, or with appropriate scavenging equipment. Ventilation (example: Fume Hood, Canopy Hoods, etc): Designated area (specify): Bio-Safety Cabinet PPE required: Skin/Body Protection (example: Lab Coat) Eye protection Face shield Respirator (example: N95): Hand protection (example: Nitrile gloves): Cleanup/Decontamination procedures for work area after use: For clean-up wash area thoroughly with soap and water. Revised 5/3/11 Disposal Procedures Expired or unused bottles of isoflurane must be disposed of by contacting EHS and handled as chemical waste. Empty bottles will be disposed of as chemically contaminated glass. Section 4: Occupational Exposures Routes of Exposure Skin – X Inhalation - X Ingestion- X Eye Contact- X Toxicological Effects Acute Effects/ Precautionary Safety Measures: Cardiovascular effects (may include fluctuations in heart rate, changes in blood pressure, chest pain). Respiratory effects (may include shortness of breath, bronchospasms, laryngospasms, and respiratory depression.) Gastrointestinal effects (may include nausea, upset stomach, and loss of appetite). Nervous System effects (may include ataxia, tremor, disturbance of speech, lethargy, headache, dizziness, blurred vision). Chronic Effects/ Precautionary Safety Measures: Target Organs: Nervous system. Heart. Liver. Occupation Exposure Response and First Aid Measures Skin – In case of contact, immediately flush skin with plenty of water. Remove contaminated clothing and shoes. Get medical attention if irritation develops. Eyes - In case of contact, immediately flush eyes with plenty of water for at least 15 minutes. Get medical attention if irritation develops. Inhalation – If inhaled, move to fresh air. If not breathing or if breathing is difficult, get medical attention. Revised 5/3/11 Ingestion – Do NOT induce vomiting unless directed to do so by medical personnel. Call physician immediately Emergency Procedure for Chemical Spills and Accidental Releases Small spill: Absorb freestanding solution. Large spill: Evacuate room and call EHS 292-1284. This Standard Operating Procedure must be placed in the Chemical Hygiene Plan and the SDS must be accessible. Also, all laboratory personnel must be familiar with safe handling practices (i.e., training with documentation of training) when working with these chemicals. This must be incorporated into the comprehensive chemical hygiene plan of the laboratory. If you have any questions regarding a comprehensive mandatory laboratory chemical hygiene plan please contact your Representative at Environmental Health and Safety (292-1284).For any other questions or concerns, please contact: PI contact information Name: Primary Contact Number: Emergency Contact Number: P.I. Signature _________________ Revised 5/3/11