UAB Nurse Anesthesia Program
advertisement

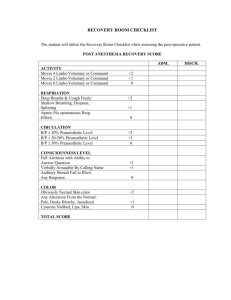
Appendix XI UAB Nurse Anesthesia Program School of Health Related Professions Anesthesia Management Plan Date: August 6, 2002 Student Name: x Prospective Retrospective Patient DX: Desires Sterilization Proposed Procedure: Laparoscopic BTL Age: 34 Sex: F Allergies: NKDA Medications: None Height: 5’1” Weight: 74kg ASA Status: 1 Medical/Surgical History Significant Review of Systems Med. Hx: Para 3003 All deliveries uncomplicated vaginal Surgical Hx: None Social Hx: Smokes ½ ppd. Occasional ETOH. Denies drug use. Dental: Good. No loose teeth or Partials. Neuro: Alert and oriented x3. No gross deficit. Resp: BBS CTA. Chest x-ray without opacities or gross Abnormalities. CV: S1 and S2. RRR. No ectopy. . GU: H/o UTI’s Airway: Class 2; FROM of head and neck. Lab Values Na: 139 Hgb: 13.2 Cl: 106 BUN: 10 K: 4.1 Plt: 212 Cr: 0.6 CO2: 25 HCT: 39.5 Glu: 98 Fluid Management Maint: 148 cc/hr Deficit: 1780 cc 3rd Space: minimal ABL: 960cc Evaluation Anesthetic Management Adequate anesthetic depth attained as evidenced by stable vital signs throughout the procedure and during induction and emergence. Adequate muscle relaxation as monitored per nerve stimulator. Postoperative Evaluation To PACU with HOB elevated Extubated without difficulty after sustained lift following reversal. VSS and O2 saturation holds at 97% on 40% OFM. - Sample - Scheduled Procedure: Laparoscopic BTL Position: Supine with arms on bilateral padded armboards < ninety degrees from sides. Exposure: Zyphoid to pubis. Table to table Incision: 1-4 incisions approximately 1-2 cm long below the umbilicus. Blood bank: Type & screen EBL: < 10 cc Surgical time: 10-30 minutes Nerves: Cutaneous branches of T10-12. Overview Laparoscopy is a technique widely used to visualize abdominal and pelvic structures without a large incision thus promoting quicker recovery from surgery. It involves several small incisions through which trocars are inserted for insufflation of CO2 into the peritoneal cavity, and rigid instrumentation support.The laparoscope is a rigid long camera with a fiberoptic lightsource attached to the end that is inserted through one of the trocars to provide visualization. Several procedures may be performed with the use of the laparoscope, one of which is tubal ligation for sterilization. Lithotomy is used to allow for uterine manipulation from a vaginal approach. The procedure is usually performed under GETA but may also be done with regional techniques. This patient preferred General. Reglan 10mg IV slow with Pepcid 20mg IV slow were given preoperatively for aspiration prophylaxis. Pre-op Assessment Complete history including assessment for GERD. This pt’s history was relatively benign with the exception of fibroadenomatous reproductive organs. She had irregular periods with some heavy bleeding and pain. Her exercise tolerance was good and her BP was within normal limits. Anesthesia Implications With the insufflation of large quantities of air into the peritoneum, ventilation can become more challenging. Residual volume decreases and peak inspiratory pressures increase. O2 saturations may decrease a bit and you may need to deliver smaller tidal volumes with higher respiratory rates to keep the patient from becoming hypercapneic. There may also be some intraperitoneal absorption of CO2 which may also contribute. Dysrhythmias such as ST or SB may occur with CO2 insufflation as well. Postoperatively, the pt may have some abdominal discomfort that may radiate to the shoulders due primarily to quantities of CO2 in the peritoneum and or gut. Anesthetic Management Upon entering the room and monitor attachment, 2mg Versed and 100mcg Fentanyl were given. We also administered a defasciculating dose of 5mg Zemuron at this time. Induction was performed with 80mg Propofol and 120mg Anectine. A 7.0 Fr ETT was placed without difficulty of trauma and Isoflurane with O2 /N2O were utilized for maintenance. Zemuron 15-20mg boluses for continuous relaxation as monitored per PNS. 1 liter of LR was given intraoperatively via #18 PIV. Reversal attained with Neostigmine 3mg and Robinul .6mg as evidenced by Full 4/4 TOF and sustained DBS. Isoflurane turned off with closing of fascial layer and N2O with O2 utilized to aid in blowing off volatile until skin is closed. Ventilator turned off at .27% ET agent and pt. allowed to begin spontaneous respirations. Oropharynx suctioned and pt. extubated with + Pressure after sustained head lift displayed and following commands. Little BP or HR lability intraop. With smooth induction and emergence.








![Basic Final Guide[1] - dan](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/009547503_1-41d303ca818815348cebf203860b39ba-300x300.png)