El Nino and East Asian monsoon
advertisement

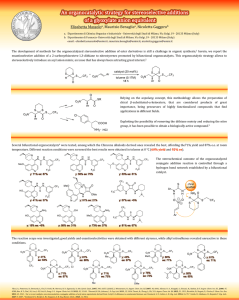
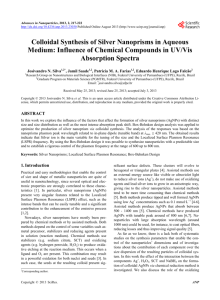
Department of Physics and Materials Science Seminar Oxidation in Silver Nanoparticles: Some Chemical and Biological Aspects Prof Chi-Ming HO Department of Chemistry and Open Laboratory of Chemical Biology of the Institute of Molecular Technology for Drug Discovery and Synthesis, The University of Hong Kong, Pokfulam Road, Hong Kong. Email: rickyho@hkucc.hku.hk Date: 27 May 2011 (Friday) Time: 3:30 pm (tea reception: 3:15 pm) Venue: B5-207 Academic Building City University of Hong Kong Enquiry: 3442-7787 Oxidation in Silver Nanoparticles: Some Chemical and Biological Aspects Prof Chi-Ming HO Department of Chemistry and Open Laboratory of Chemical Biology of the Institute of Molecular Technology for Drug Discovery and Synthesis, The University of Hong Kong, Pokfulam Road, Hong Kong. Email: rickyho@hkucc.hku.hk ABSTRACT Oxidation of metal complexes is a crucial reaction in many biological systems and chemical processes.[1] Likewise, oxidation of metal nanoparticles is important to the advancement of nanotechnology because oxidative dissolution of metal nanoparticles to metal ions is a powerful tool for the synthesis of well-defined nanostructured materials, and is also related to their biological activity.[2] However, little is known about parameters that govern the oxidative dissolution rate of nanostructured materials and its mechanism. We are particularly interested in studying the oxidation chemistry of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) and its relationship to biological activities. It is because AgNPs are widely incorporated into biomedical and everyday applications owing to their potent antibacterial and antiviral activities. In addition, AgNPs are highly coloured rendering the ease of spectrometric measurement. In this presentation, we will first present some biological activities of AgNPs studied at HKU.[3] We will also disclose our recent progress on the oxidative dissolution of AgNPs by biologically relevant oxidants in aqueous media.[4] References [1] R. A Sheldon, J. K. Kochi, Metal-Catalyzed Oxidations of Organic Compounds, Academic Press, New York, 1981. [2] Xia Y. Y. Xiong, B. Lim, S. E. Skrabalak, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 60; Angew. Chem. 2009, 121, 62. b) J. Park, J. Joo. S. G. Kwon, Y. Jang, T. Hyeon, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 4630. [3] (a) C.-N. Lok, C.-M. Ho, R. Chen, Q.-Y. He, W.-Y. Yu, H. Sun, P. K.-H. Tam, J.-F. Chiu, C.-M. Che, J. Proteome Res. 2006, 5, 916; (b) C.-N. Lok, C.-M. Ho, R. Chen, Q.-Y. He, W.-Y. Yu, H. Sun, P. K.-H. Tam, J.-F. Chiu, C.-M. Che, J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2007, 12, 527. [4] C.-M. Ho, S. K.-W. Yau, C.-N. Lok, M.-H. So, C.-M. Che, Chem. Asian J. 2010, 5, 285.