Sultan Qaboos University Collage of Science Department of
advertisement

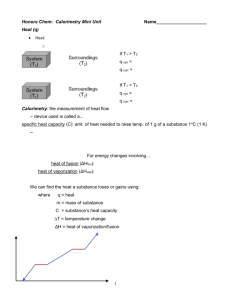
Sultan Qaboos University Collage of Science Department of Chemistry Physical Chemistry Laboratory (CHEM3335) THERMODYNAMIC PROPERTIES OF WATER Name:Al Hamdani. ID: Date: 27/4/2010. 0 Objective: The purpose of this experiment is to study the thermodynamic properties of water by determining the enthalpy. Introduction: Thermodynamic is the study of the heat, work, energy and the changes they produce in the state of the system. By knowing the thermodynamic properties e.g. heat capacity(C), change in enthalpy (∆H) and many other properties we can measure the energy change of the system. Water (H2O) is a fundamental features in our life. It has a special characteristics due to dipolar molecular structure. The change of water into different states include either absorb heat(endothermic process) as in this chemical equation: (melting) H2O(s)→H2O(l) Or release heat(exothermic process) as in this chemical equation: (freezing) H2O(s)→H2O(l) The specific heat is the amount of heat in joule per gram required to raise the temperature by one degree Celsius. forwater the specific heat is 4.186J/g 0C which is higher than any other common substance. From the product of the average specific heat capisity cp and the Celsius temperature .we can find the enthalpy relative to 0 0C for water which is the energy needed to heat water. The enthalpy conservationon mixing(A+B)is (ab)in KJ/Kg is defined by 1 ( A) ( a ) ( B ) (b) ( A B ) ( ab) sin ce A is liquid water ( a ) C T p1 a 0 sin ce below 80C , CP indepenent of temperature so ( a ) CP1Ta so ( ab) CPTab (1 B / A)Tab (b) B Ta CP1 A where the plot of (1 B / A)Tabversus B / A will give us linear graph with a slope (b) and the int ercept Ta CP1 Experimental: Apparatus and chemicals: *Volumetric flask *water bath *Dewar flask *Balance *plastic cup *device to measure the temperature. Condition: *Room Temperature *Pressure= 1 atm 2 Procedure: 1-pour 250ml of distilled water in volumetric flask and put it in water bath and record the temperature of the water(Ta). 2-weigh10.0g of ice and then put it inside the provided dewar flask and you must be accurate and don not touch the ice by your finger. 3-pour the prepared water in step1in the dewar flask and stir it untind all the ice melts and then record the temperature of the mixture(Tab). 4-repeats steps 2,3by using amount of ice (20,30,40,50,55,60,65,70,75) Results: A(g) Table1: the result that we got it from our experiment. B(g) B/A Tab 1+B/A (1+B/A)*Tab Ta 247.51 10.08 0.040726 30.02 1.040726 31.2 35 247.23 20.03 0.081018 27.2 1.081018 29.4 35 247.27 30 0.121325 23.3 1.121325 26.1 35 247.31 40.1 0.162145 20.9 1.162145 24.3 35 247.23 50.28 0.203373 17.8 1.203373 21.4 35 247.29 55.14 0.222977 16.2 1.222977 19.8 35 247.67 60.04 0.242419 14.5 1.242419 18.0 35 246.82 65.33 0.264687 13.9 1.264687 17.6 35 247.58 70.1 0.283141 12.2 1.283141 15.7 35.1 247.42 75.05 0.30333 12.1 1.30333 15.8 34.9 3 B/A vs (1+B/A)*Tab 35.0 (1+B/A)*Tab 30.0 25.0 20.0 15.0 10.0 5.0 0.0 0 0.05 0.1 0.15 0.2 0.25 0.3 B/A Fig(1) shows the plot of (1+B/A)Tabvs B/A Calculations: Mass of water(A) Mass of ice(B) B 10.08 0.04073 g A 247.51 B 1 1 0.04073 1.04073 g A B (1 )Tab 1.04073 g 30.02 C 31.24 g . C A B (b) B (1 )Tab Ta A C P1 A (b) 0.04073 g 35.0 C 4.2 KJ / Kg. C (b) 387 J if we det er min e the enthaply change from the det er min e slop : (b) 62.9138 C P1 31.24 g . C (b) 264 KJ / Kg 4 0.35 Discussion In this experiment we determined the enthalpy which is needed to melt the ice by calculating the slop of the graph (1+B/A)TabvsB/A. we notice that there is different between the measured value and the literature value that is indicated to uncertainty in our result, there is some error during the experiment. Answers of questions: a- The different sign of vap and freeze because the system gains energy to break the intermolecular force of water to evaporate .But it loses energy to make the bonds and solidifying the water. b- we use distilled water to obtain pure ice because the impurities affect the freezing point of water. c-we don not use our hand to transfer the ice because the heat can flow from our hand and affect the Tb, so it will effect and it may contaminate with ice and affect the mass. Error analysis: Slop is -62.9138± 1.991735 Intercept is 34.0431± 0.418415 The source of error which occur in the experiment is 1- Inaccuracy in reading the temperature 2- Exceeded the time given (20-30s) for weighing the ice, so the ice started to melt and this is leads to affect the results. 5