Chapter 4 ()
advertisement

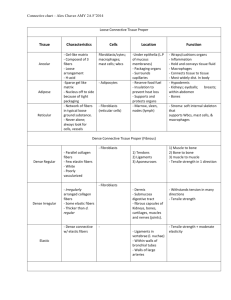
Anatomy Lecture Notes Chapter 4 I. tissue components A. cells that perform related functions and are similar in structure B. extracellular material - made by cells and secreted into interstitial space II. tissue types A. epithelium (e.) = sheet of cells that covers a body surface or lines a body cavity or forms glands 1. characteristics a. cellularity - cells directly attached to other cells, very little extracellular material b. cell junctions - attach cells to each other c. polarity - apical surface is free (not attached to other cells) and basal surface is attached to c.t. d. supported by c.t. on basal surface (basement membrane) e. avascular - contains no blood vessels f. regenerate easily 2. classification a. number of cell layers simple - 1 layer stratified - more than 1 layer Strong/Fall 2008 page 1 Anatomy Lecture Notes Chapter 4 pseudostratified - 1 layer but looks like more than one b. shape of cells squamous - flat, wider than they are tall; nucleus flattened horizontally cuboidal - as tall as they are wide; nucleus rounded and central columnar - taller than they are wide; nucleus flattened vertically 3. common types a. simple squamous structure: functions: diffusion, filtration locations: lungs, kidneys endothelium = lining of vascular system, walls of capillaries mesothelium = component of serous membranes b. simple cuboidal structure: functions: secretion, absorption, transport locations: kidney tubules, ducts and secretory portions of many glands c. simple columnar structure: ciliated: specialized to move materials across apical surface of cells with microvilli: specialized to increase surface area functions: absorption, secretion, transport Strong/Fall 2008 page 2 Anatomy Lecture Notes Chapter 4 locations: nonciliated - stomach ciliated - oviduct, small bronchi with microvilli - small intestine d. pseudostratified ciliated structure: cells vary in height all cells rest on basement membrane not all cells reach apical surface of tissue short cells are precursors for tall cells nuclei are at several levels goblet cells are unicellular mucous glands cilia move mucus functions: secretion and movement of mucus locations: trachea and large bronchi e. stratified squamous structure: surface cells are squamous basal cells are cuboidal or columnar basal cells undergo mitosis; replace surface cells keratinized - surface cells dead (no nuclei); contain the protein keratin non-keratinized - surface cells alive (nuclei) and do not contain keratin function: protection location: nonkeratinized - esophagus, vagina keratinized - skin f. transitional Strong/Fall 2008 page 3 Anatomy Lecture Notes Chapter 4 structure: stratified basal cells cuboidal or columnar surface cells vary in shape depending on amount of stretch function: locations: 4. gland = cell or group of cells that secretes a product, usually containing proteins a. endocrine = no ducts, releases secretory product (hormone) via tissue fluid into blood b. exocrine = secretes product onto surface of epithelial membrane; may have ducts unicellular = one cell goblet cells - secrete mucus multicellular = many cells ducts: simple vs branched (compound) secretory units: tubular vs alveolar or acinar 5. epithelial surface features: a. cell junctions desmosomes =adhesive spots that hold cells together along their lateral surfaces plaques cadherins/linker proteins intermediate filaments tight junctions = belt-like junctions that form tight seals between adjacent cells fusion of plasma membrane proteins no space between cells Strong/Fall 2008 page 4 Anatomy Lecture Notes Chapter 4 gap junctions = hollow cylinder of proteins (connexons) forms opening between cytoplasm of two adjacent cells also found in smooth muscle and neural tissue b. basal lamina noncellular material on basal surface consists of proteins secreted by epithelial cells acts as filter, guides regenerating epithelium with reticular fibers from underlying c.t., forms basement membrane c. microvilli = fingerlike extensions of apical membrane; increase surface area d. cilia = whip-like extensions of apical membrane; core of microtubules; move materials B. connective tissue (c.t.) connective tissue proper loose dense cartilage bone blood 1. characteristics a. cells separated by extracellular matrix b. all types originate from mesencyme 2. extracellular matrix secreted by c.t. cells consists of fibers and ground substance a. there are 3 types of fibers collagen fibers - proteins that withstand tension reticular fibers - proteins that act as scaffolding for cells elastic fibers - proteins that recoil after being stretched b. ground substance is amorphous composition varies with specific type of c.t. in loose c.t. it is made of proteins and glycoproteins and holds tissue fluid Strong/Fall 2008 page 5 Anatomy Lecture Notes Chapter 4 glycosaminoglycans proteoglycans 3. mesenchyme = embryonic c.t. cells are undifferentiated and multipotent 4. common types a. areolar c.t. fibroblasts gel-like ground substance consists of hyaluronic acid; holds fluid collagen, reticular, and elastic fibers defense cells: macrophages (phagocytes) plasma cells (antibodies) mast cells (histamine) adipose cells located under epithelia, around organs, between muscles, blood vessels, and nerves b. adipose c.t. adipocytes - store fat matrix sparse located under skin, around organs stores energy, insulates, protects brown fat = non-shivering thermogenesis c. reticular c.t. fibroblasts (reticular cells) loose matrix network of fine reticular fibers location - lymphoid organs, bone marrow, spleen Strong/Fall 2008 page 6 Anatomy Lecture Notes Chapter 4 d. dense irregular c.t. fibroblasts collagen fibers running in all directions located in dermis, organ and joint capsules withstands tension in several directions e. dense regular c.t. fibroblasts collagen fibers in parallel bundles located in tendons and ligaments withstands tension in one direction f. hyaline cartilage chondroblasts are immature cells that are secreting matrix chondrocytes are mature cells that are surrounded by matrix these cells occupy spaces in the matrix, the spaces are called lacunae ground substance = chondroitin sulfate collagen fibers avascular located at ends of bones, between ribs and sternum, supports nose and trachea support with flexibility g. fibrocartilage chondroblasts/chondrocytes in lacunae ground substance = chondroitin sulfate collagen fibers avascular located in intervertebral discs and other joints strength and compression Strong/Fall 2008 page 7 Anatomy Lecture Notes Chapter 4 h. elastic cartilage chondroblasts/chondrocytes in lacunae ground substance = chondroitin sulfate elastin fibers and collagen avascular located in external ear and epiglottis flexibility and support i. blood matrix is a liquid called plasma formed elements include erythrocytes, leukocytes, and thrombocytes main function is transport j. bone (Chapter 6) C. muscle tissue cells vary in size and shape but all contain the contractile proteins actin and myosin 1. skeletal cells are multinucleate, cylindrical and very long (run from one end of the muscle to the other) striations seen under microscope due to arrangement of contractile proteins under voluntary nervous control 2. cardiac cells are cylindrical, but branch and join each other end to end gap junctions occur where cells join each other at intercalated discs cells have only one nucleus each and are striated 3. smooth Strong/Fall 2008 page 8 Anatomy Lecture Notes Chapter 4 cells are spindle shaped and uninucleate no striations usually arranged in sheets in each sheet the cells are usually parallel D. nervous tissue consists of neurons and supporting cells (neuroglia) neurons are characterized by long processes that carry electrical impulses throughout the body III. epithelial membranes A. definition: epithelial sheet + underlying c.t. B. types 1. cutaneous = skin (Chapter 5) 2. mucous line organs that open to outside of body: respiratory, digestive, urinary and reproductive surface layer moistened by mucus secreted by goblet cells or glands in underlying c.t. c.t. layer usually called lamina propria 3. serous line the closed ventral body cavity simple squamous e. (mesothelium) on areolar c.t. fluid produced by filtration from capillaries in c.t. Strong/Fall 2008 page 9 Anatomy Lecture Notes Chapter 4 IV. tissue repair regeneration = replacement by same tissue fibrosis = replacement by fibrous c.t. repair of skin injury: scab formed by drying of fibrin in blood clot clot is replaced by granulation tissue (capillaries, fibroblasts, phagocytes) epithelium regenerates under scab scab falls off scar under e. is composed of fibrous c.t. tissues that regenerate well include epithelia, bone, areolar c.t., dense irregular c.t. and blood-forming tissue tissues that do not regenerate well or at all include skeletal and cardiac muscle, cartilage, nervous tissue Strong/Fall 2008 page 10