02 GW Content Representation - Meteorology Lesson
advertisement
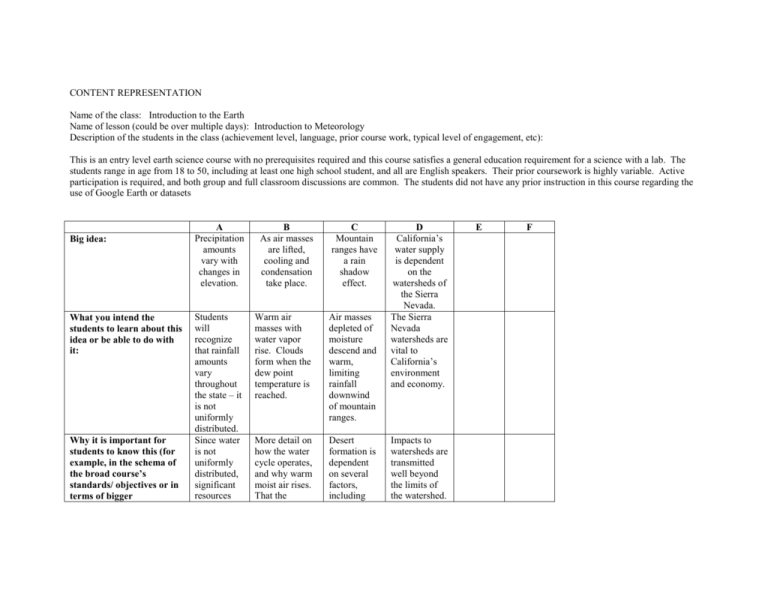
CONTENT REPRESENTATION Name of the class: Introduction to the Earth Name of lesson (could be over multiple days): Introduction to Meteorology Description of the students in the class (achievement level, language, prior course work, typical level of engagement, etc): This is an entry level earth science course with no prerequisites required and this course satisfies a general education requirement for a science with a lab. The students range in age from 18 to 50, including at least one high school student, and all are English speakers. Their prior coursework is highly variable. Active participation is required, and both group and full classroom discussions are common. The students did not have any prior instruction in this course regarding the use of Google Earth or datasets Big idea: What you intend the students to learn about this idea or be able to do with it: Why it is important for students to know this (for example, in the schema of the broad course’s standards/ objectives or in terms of bigger A Precipitation amounts vary with changes in elevation. B As air masses are lifted, cooling and condensation take place. C Mountain ranges have a rain shadow effect. Students will recognize that rainfall amounts vary throughout the state – it is not uniformly distributed. Since water is not uniformly distributed, significant resources Warm air masses with water vapor rise. Clouds form when the dew point temperature is reached. Air masses depleted of moisture descend and warm, limiting rainfall downwind of mountain ranges. More detail on how the water cycle operates, and why warm moist air rises. That the Desert formation is dependent on several factors, including D California’s water supply is dependent on the watersheds of the Sierra Nevada. The Sierra Nevada watersheds are vital to California’s environment and economy. Impacts to watersheds are transmitted well beyond the limits of the watershed. E F educational/civic/social goals): Anticipated student misconceptions and difficulties understanding this: Teaching procedures (and reasons why): Formative assessment: Specific ways of ascertaining students’ understanding or confusion around this idea (include likely range of responses): are expended to transmit water from one location to another, impacting ecosystems. Rainfall is relatively uniform across a broad area. Provide Google Earth map with elevation and rainfall totals for specific sites. Have students graph the data using two y axes to compare elevation and rainfall data. Activity: Draw a crosssection of a mountain range and addition of water vapor to air lowers density is counterintuitive. rain shadows. Water vapor will add to the density of air and cause it to sink rather than rise. Use a “cloudin-a-bottle” demonstration to help illustrate condensation. Refer to condensation on cold surfaces. Discuss other instances where students have witnessed condensation. Mountain ranges do not influence desert climates. Water is not collected in discrete watersheds. Use diagrams to illustrate the concept. Ask for observations that students have made in travels to the east side of the Sierra. Show map of the California Water Project. Have discussion of why water is being stored, moved, and how utilized at various locations in the state. Discuss local watersheds and issues. Discussion: Describe what happens as an air mass rises. Quiz: Describe the influence that the Sierra Nevada have Group projects: Students research and present findings on Correct: As air plot relative rainfall totals at several elevation points. Correct Response would indicate an increasing amount of rainfall with elevation, and rapid decrease on the downwind side. Incorrect responses could include no change in rainfall amount with elevation, a decrease in rainfall amount with an increase in elevation, or no significant decrease in rises, it expands and cools, when it reaches the dew point temperature condensation occurs. Incorrect: Water vapor comes in contact with cold air and condensation takes place. Water vapor makes air more dense. on rainfall totals on both the west and east sides of the range. Describe how that influence affects the ecosystems. Correct: Generally, with an increase in elevation comes an increase in precipitation. On the downwind side, precipitation is greatly reduced because of the rain shadow effect. Vegetation is adapted to precipitation amounts, rates of weathering Central California watersheds, impoundments and distribution system, as well as various uses of water throughout the Central Valley. Assessed on accuracy, completeness, and organization. rainfall amounts on the downwind side of mountain range. and erosion are also greatly influenced. Incorrect: Precipitation amounts are not affected by mountains. Vegetation, weathering and erosion are not significantly affected.