CP PHYSICS - Brookwood High School
advertisement

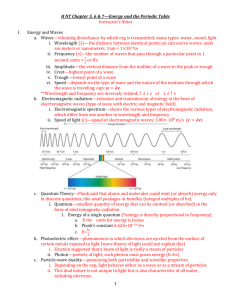
CP PHYSICS ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES (LIGHT) Electromagnetic Waves moving charged particles create a magnetic field that expands as the particles accelerate in one direction magnetic field collapses when particle slows down, stops, and changes direction, causes field to expand again expanding and collapsing magnetic field generates an electric field which expands and collapses to produce another magnetic field and so on travels at 3.0 x 108 m/s through empty space (c = speed of light) travels more slowly through mediums energy depends on frequency 7 Types of Electromagnetic Radiation 1. Radio Waves lowest frequency, longest wavelength, least energy includes TV waves (higher frequencies) VHF = very high frequency, UHF = ultra high frequency radio waves carry sound waves, sound waves changed into electrical signals which change the frequency (FM) or the amplitude (AM) of the radio wave (change back to sound in your radio receiver) each radio station issued wafer shaped quartz crystal that vibrates at a certain frequency, each station has own frequency CP PHYSICS, ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES (LIGHT), page 2 2. Microwaves frequencies match natural frequencies of molecules (fats, proteins, etc.) causes food molecules to vibrate (resonance) making the food cook itself food molecules continue to vibrate even after oven stops generating microwaves – microwave instructions usually include “stand time” icebergs give off microwaves microwaves match natural frequencies of some pacemakers 3. Infrared Waves heat waves – all animals give off infrared uses: heat lamps, night vision, alcohol breath test, remote controls 4. Visible Light only makes up 1/1,000,000 of EM spectrum different frequencies seen as colors (ROY G BIV) red = lowest frequency, longest wavelength, least energy violet = highest frequency, shortest wavelength, most energy produced when electrons make quantum leaps between energy levels 5. Ultraviolet Light causes sunburns, damages tissues, can kill bacteria UV-B ray more dangerous than UV-A because they have higher frequency produced by e-s making larger quantum leaps 6. X-rays produced by high speed electrons slamming into a metal plate uses: medical x-rays (bones, teeth), airport security 7. Gamma Rays highest frequency, shortest wavelengths, highest energy and penetrating power produced by nuclear particles and occur with every nuclear reaction used in radiation therapy (kill healthy cells, but kill cancer cells first) CP PHYSICS VISIBLE LIGHT General Characteristics one type of electromagnetic (EM) radiation frequencies to which human eye is sensitive travels through space in straight line at speed of 3.0 x 108 m/s (c) equation: c = λf transverse wave, but also behaves like a particle interaction with materials: o transparent – all light is transmitted (ex. clear glass) o translucent – scatters light transmitted (ex. frosted glass) o opaque – does not transmit any light (ex. brick) Wave Behavior behaves like wave when travels through medium without interacting with the medium’s particles also behaves as wave when traveling through empty space does everything other waves do: o reflects (stays in old medium when hits boundary to new medium) o refracts (bends as enters new medium) o diffracts (occurs when going through very small opening) o interferes (sent thru 2 slits, constructive interference produces light bands, destructive interference produces dark bands) Particle Behavior discovered in 1900s, occurs when interacts with matter only certain colors (frequencies) of light produce photosynthesis when light absorbed by green leaves when certain colors of light shown on metal plate (ex. solar calculators), electrons jump out of metal atoms and create electric current, violet light always works but red light never does electrons exist in certain energy levels and make quantum leaps to higher levels when they absorb energy, fall back down to ground level and give off certain colors of light CP PHYSICS, VISIBLE LIGHT, page 2 Quantum Theory explains how light interacts with matter all energy is absorbed or given off by atoms in tiny little bundles called quanta photon = quantum of light energy photon’s energy depends on its frequency o violet light has higher frequency so has more energy than red light o red light used in dark rooms to develop film because it does not have enough energy to produce a chemical reaction in photo film cannot explain how light behaves like wave through space but as a particle when interacting with matter result = Dual Theory of Light: Light moves through space as a wave and interacts with matter as a particle. Production of Light Illuminated objects = reflect light, ex. moon Luminous objects = objects which emit light, ex. sun produced by exciting electrons which make quantum leaps and then fall back down to lower energy levels giving off light different methods to produce light based on how they excite the electrons: heating gases, heating metal filaments, electricity, ultraviolet radiation, chemoluminescence, bioluminescence, phosphorescence Polarization of Light only occurs with transverse waves polarized materials have long molecules that only allow EM waves of one direction = polarizing axis blocks waves that are perpendicular to polarizing axis can test for polarization with a polarized filter – every time filter turned 90o over material, should see all light blocked then all light pass through and so on polarized sunglasses – reduce glare of light reflecting off variety of surfaces