The Axial Skeleton
advertisement

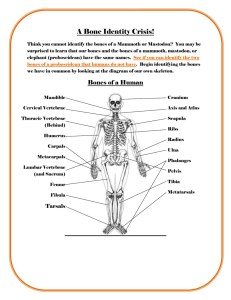
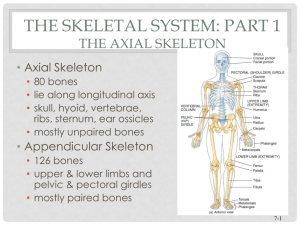
Name ____________________________________________________________ Period_____ The Axial Skeleton The Axial Skeleton Forms the __________________________________ of the body Divided into _______________________ _________________________________ _________________________________ _________________________________ The Skull Two sets of bones o __________________ – encloses & protects brain o ______________________________ – holds eyes in anterior position & allows the facial muscles to show emotions. All but 1 of the bones are joined by __________________________________________ Only the ___________________ is attached by a freely movable joint The Cranium ________________ – forms ____________________, brow bone, superior eye orbit ____________________(___) – form most of the ______________________________ of the cranium o Meet in midline = _______________________________________ o Meet frontal = _______________________________________ ____________________(___)– inferior to parietals & join to them at the _____________ _________________________ o Important bone markings found here ___________________________________________________ – ______________ leading to eardrum _________________________________ – sharp needle-like projection inferior to external auditory meatus (______________________________ for many __________________________________________________) _________________________________ – thin ____________________ that joins w/ the zygomatic (_____________) bone _________________________________ – rough projection posterior & inferior to the external auditory meatus ____________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________ Close to middle ear & __________________________________ ________________________________ – junction of occipital & temporal Allows for ____________________________________________ Largest vein of the head – _______________________________ ___________________________________ – anterior to jugular foramen Transmits ______________________________ (facial & vestibulocochlear) _________________________________ - anterior to jugular foramen ____________________________________________________ ________________________– most posterior bone of cranium forming _____________ __________________________________________ o Joins parietals anteriorly at _________________________________ o ___________________________________ = large opening in base of the occipitals (_______________________________________________________) Lateral to the foramen magnum are rockerlike _____________________ _____________________ which rest on the 1st vertebra ___________________________ – butterfly-shaped – spans the width of the skull and forms part of ________________________________________________ o __________________________________ “Turk’s saddle” = small depression on the midline of the sphenoid, holds the ________________________________ o _________________________________ = large oval opening in line w/ the posterior end of the sella turcica (allows _______________________ (trigeminal) to pass to _______________________ muscles of mandible o Parts of the ________________________ form part of the eye orbits 2 important openings: 1. ___________________________ (optic nerve) 2. __________________________________________ (cranial nerves 3, 4 & 6 – eye movements) o Central part of the sphenoid riddled w/ air cavities = _______________________ _____________________ – irregularly shaped, anterior to sphenoid – forms _________ _______________________ and ___________________________________________. o ______________________________ “cock’s comb” = superior ethmoid surface projection – ______________________________________________________ o _____________________________________ – holey areas on sides of crista galli= ________________________________________ pass through from nose o ________________________________________________ – extensions of the ethmoid – form part of _________________________________________ & ____________________________________________ of air flowing Facial Bones *________________________ *________________________, only the _______________ and ____________are _________ ________________________(___) / maxillary bones – fused to form _______________ o Upper teeth carried in the ________________________________________ o ___________________________________– extensions that form the ________ part of the _____________________________ o ___________________________________ – ___________________________ _________________, lighten the skull bones, ___________________________ as we speak Hollow portions of bones surrounding the nasal cavity _____________________ (infection of sinuses) – can result in ________ ________________________________ pain ______________________ (___) – posterior to palatine processes of maxillae – form ____________________ part of __________________________________ o ________________________________ = failure of these to fuse ___________________________(___) – cheek bones – form portion of _____________ _____________________________________ ___________________________(___) – fingernail sized bones forming part of _______ _____________________________________ o Groove serves as ________________________________________________ _______________(___) – small rectangular bones – form ________________________ – lower part of nose made of cartilage _______________ “_____________” (1) – median line of nasal cavity – forms _______ __________________________________________ _________________________________________ (___) – thin, ___________________ ________________________ from lateral walls of the nasal cavity ________________________ (lower jaw) – largest, _____________________________ – ________________________________________ on each side of face, forming the _____________________________________________________________ (find them!) o Horizontal part (body) forms the ________________ o 2 upright bars of bone (rami) extend from the body to connect the mandible with the temporal bone. o __________________________ lie in ________________________________ The Hyoid Bone ______________________________________ _______________________________ w/ a body and 2 pair of horns (cornua) Closely related to mandible and temporal bones ______________________________________ ______________________________________ Suspended in mid–neck region 2 cm above the larynx, ________________________________ ______________________________________ Serves as a movable ____________________ ____________ & attachment point for neck muscles (lower and raise larynx when we swallow & speak) The Fetal Skull Face small compared to size of cranium (skull is large compared to body length) ____________________________________ _______________; newborn is _________ ______________________ – fibrous membranes connecting the cranial bones o Baby’s pulse can be ______________ _______________ spots (explains their name “little fountain”) o Allow fetal skull to be _____________ ______________________________ o Allow infants ____________________ o Largest fontanels are diamond shaped anterior shaped fontanel and smaller triangular shaped posterior o ________________________________ _____________________ after birth The Vertebral Column Serves as ____________________ of the body Extends ______________________, which it supports, _______________________, where it transmits the weight of the body to the legs. ____________________________________ connected & __________________________ creating a flexible, curved structure. _________________________ runs through central cavity, protected by vertebrae ___________________ = ________________ ___________________ but _______________ ________________________________ – the ____________ (5 fused) & the ___________ (4 fused). Each vertebrae is given a _________________ ______________________________________ . 24 single vertebrae o __________________________ vertebrae o __________________________vertebrae o __________________________vertebrae Vertebrae separated by pads of __________________________________ – ____________________ discs – ____________________________________ while ________________________________________. o _________ person – discs = _________________________ – ______________ _________________________________. o As you _________ – ________________________________ – _____________ _______________________________________ Can ______________________________________________________. Can __________________ from ________________________________ ____________________________ on ___________________________ _____________= ____________________ & excruciating ___________ _____________ & _________________________________ of spine _______________ ________________ to head when we walk or run. o o _________________________ curvatures __________________________________ regions __________________________________ __________________________ curvatures ________________ curvature appears ___________________________ _____________________________________ ________________ curvature when baby _________________________ _______________________ spinal curvatures o __________________ - abnormal __________________________ of the spine. o __________________ - Abnormal __________________________ of the spine, resulting in ______________________. o ___________________ - Abnormal _________________________ of the spine in the _______________ region. Vertebrae All vertebrae have a similar structural pattern. o _______________: disclike, _________________________ part facing anteriorly. o ____________________________: formed from the joining of all posterior extensions, the laminae & pedicles. o ____________________________: _____________ through which the spinal cord passes. o ____________________________: 2 lateral projections from the vertebral arch. o _____________________________: single projection arising from the posterior aspect of the vertebral arch (fused laminae). o ________________________________________ __________________: ______________ projections lateral to the vertebral foramen allowing a __________ ___________________________________________ ___________________________________________. Cervical Vertebrae 7 (___________) – form the ___________ region. First 2 – __________________________ – are different because they perform functions not shared by any other cervical vertebrae. ____________ (C1) has _________________; the superior surfaces of its transverse processes contain large depressions that ________________ ___________________________________; allows you to nod “_________.” _____________ (C2) has a _________________ __________________ (_________ or _____________________________), which acts as a _________________________________; allows you to indicate “_______.” C3 through C7 are the smallest, lightest vertebrae All transverse processes ___________________ _______________________________________________through which ___________ _______________ pass to the brain. Thoracic Vertebrae ____ with body somewhat __________________ ______________ w/ ______________________ __________, which receive the heads of the ribs. _____________________________ is long & ______________________________________ (from the side looks like a __________________ head). Lumbar Vertebrae ___ w/ massive __________________________ & ________________________________________ ____________ (looks like ______________ head from side). ________________ vertebrae – ______________ ________________. Sacrum Formed by the ____________________________________________. Winglike ________________________________ laterally ________________________ forming the ___________________________________. Forms the __________________________________________________________. ________________________________________ roughens the posterior midline & are flanked by ____________________________________. Vertebral canal continues inside the sacrum as the _______________________ – terminates in large inferior opening called the ______________________________. Coccyx Formed by ____________________________________, irregularly shaped vertebrae This is the human “____________________” – a remnant of the tail other vertebrate animals have. Bony Thorax Made-up of three parts o ______________________ o ______________________ o ____________________________________ Often called the “_______________________________” b/c it forms a ______________ ______________________ of slender bones to protect the major organs of the thoracic cavity. ____________________– “breastbone” o Flat bone that is a result of the ________________________________ – the ________________________________________________________________ o __________________ to the __________________________________ o Three important bony landmarks: 1. _____________________________ (concave ______________ border of the ____________________) – can be felt easily – generally at __________ 2. ____________________________ - where manubrium & body meet formed at level of ______________ (reference to locate ________________ _______________ for ___________________________________________) 3. ____________________________ – body and xiphoid process fuse (level of _______) o ________________________________ used to get bone marrow tissue to __________________________________________________________ Ribs – _______________ – form walls of bony thorax o Articulate w/ vertebral column posteriorly & curve downward toward anterior body surface. o ___________________ = __________________ – _______________________ to sternum by _______________________________________ o ___________________ = __________________ – _______________________ ___________________________________ (______________________ are called “_____________________” b/c they are the ones not attached at all) o Contrary to popular myth – men & women have the same number of ribs!!