Plate Tectonics: Continental Drift & Seafloor Spreading
advertisement

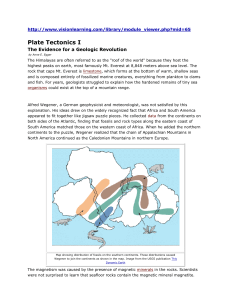
Chapter 13 – Plate Tectonics 13.1 Continental Drift Evidence - Pangaea o Means “all land” o Alfred Wegener theorized no coincidence for continents fitting together o Suggested they were together at one point in the past o One large landmass o Proposed “continental drift” theory Continents have moved slowly to their current locations - fossil clues to support Pangaea o reptile Mesosaurus fossil found on Africa and S. America o fern Glossopteris fossil found in Africa, Australia, India, S. America, and Antarctica\ o Also suggested different locations on Earth with different climates - climate clues o Glacial deposits in grooves in S. America, Africa, India, and Australia indicates glaciers covered these continents o Indicates possibly connected and located near poles at one time - rock clues o similar rock structures are found on different continents o parts of Appalachian mtns are similar to those found in Greenland and Europe 13.2 Seafloor Spreading Clues on ocean floor - discovery of mid-ocean ridges sparked investigations for new sea floor formation - Seafloor spreading o Hot, less-dense material below Earth’s crust is forced upward toward surface o Turns once it reaches the surface and flows sideways o As it spreads, magma moves upward and flows through cracks o Solidifies, cools and forms new seafloor o Becomes more dense than the material around it and therefore begins to sink o Age of rocks No rocks at ridge older than 180 my Continental rocks as old as 4 by Youngest rocks are located right at the ridge Further out from ridge, older the rocks get o Magnetic clues Iron composed minerals (ex. Magnetite) are attracted to Earth’s magnetic field Magnetic reversals Normal pattern is from south pole to north Reversal sends pattern from north to south Iron composed minerals show shift Creates parallel strips on ocean floor Reversals occur thousands or millions of years 13.3 Plate Tectonics Plate tectonics – Earth’s crust and upper mantle are broken into sections - move on the asthenosphere o plasticlike layer below lithosphere Plates - Lithosphere o composed of the crust and part of upper mantle - interact 3 ways: o converge plates colliding 3 types: 1 - Both plates forced up creating mountain ranges Subduction zone o When one plate is forced under another 2 - Deep sea trenches are formed 3 - Volcanic mountains o diverge moving apart _ opposite directions seafloor spreading mid-ocean ridges o transform sliding past each other earthquakes occur Causes - convections currents o the cycle of heating, rising, cooling, sinking o different densities get hot from Earths interior, becomes less dense, rises, cools as it moves further away from heat source, becomes more dense, then sinks again o affects the asthenosphere therefore affecting the lithosphere Effects - faults - rift valleys - mountains, arcs, volcanoes - ridges - earthquakes