Dynamic Earth Test
advertisement

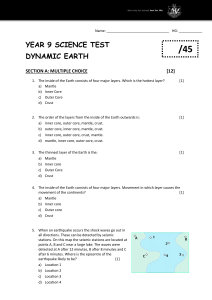
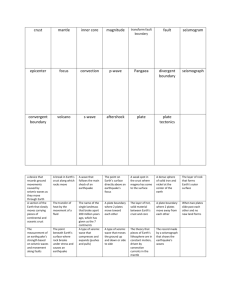
Name: ________________________________ HG: ____________ YEAR 9 SCIENCE TEST /45 DYNAMIC EARTH SECTION A: MULTIPLE CHOICE [12] 1. The inside of the Earth consists of four major layers. Which is the hottest layer? a) Mantle b) Inner Core c) Outer Core d) Crust [1] 2. The order of the layers from the inside of the Earth outwards is: a) inner core, outer core, mantle, crust. b) outer core, inner core, mantle, crust. c) inner core, outer core, crust, mantle. d) mantle, inner core, outer core, crust. [1] 3. The thinnest layer of the Earth is the: a) Mantle b) Inner core c) Outer Core d) Crust [1] 4. The inside of the Earth consists of four major layers. Movement in which layer causes the movement of the continents? [1] a) Mantle b) Inner core c) Outer core d) Crust 5. When an earthquake occurs the shock waves go out in all directions. These can be detected by seismic stations. On this map the seismic stations are located at points A, B and C near a large lake. The waves were detected at A after 12 minutes, B after 8 minutes and C after 6 minutes. Where is the epicentre of the earthquake likely to be? [1] a) Location 1 b) Location 2 c) Location 3 d) Location 4 6. An earthquake measuring 8 on the Richter scale is stronger than one measuring 6. How much stronger is it? a) 2 times b) 4 times c) 10 times d) 100 times [1] 7. At a divergent plate boundary a) Two plates move closer together b) Two plates move apart from each other c) When the plates are transformed into another organism millions of years later. d) When the plates suddenly transform into hard rock [1] 8. At a transform fault plate boundary, the plates: a) Move past each other in the same direction at different speeds. b) Move past each other in opposite directions at the same speed c) Push together d) Spread apart [1] 9. The fastest moving waves are: a) S waves b) P waves c) L waves d) All of the above, they move at the same speed [1] 10. The theory of sea-floor spreading supports ideas that a) the earth is expanding b) the earth is contracting c) new crust is being made along oceanic trenches d) new crust is being made along mid-ocean ridges [1] 11.The Himalayan mountains are thought to have been formed by the collision of a) two continental plates b) two oceanic plates c) an oceanic plate and a continental plate d) two transform faults [1] 12. The idea that the Earth’s outer core is liquid is best supported by the statement that the [1] outer core a) is the source of volcanic material b) does not transmit S waves c) is composed of metamorphic rocks d) transmits S waves faster than P waves SECTION B: SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS [33] 1. The hypothesis suggesting that continents were once joined together and have drifted apart was first proposed by Alfred Wegener in 1915 and this is now widely accepted as part of the modern “Plate Tectonic Theory”. Provide two pieces of evidence which support Wegener’s original hypothesis. [4] ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 2. This is a diagram of an active volcano. Write a single word to label each of the parts, using these choices: crater, lava and ash, crust, magma, vent. [5] 3. Why are volcanoes and earthquakes usually found along or near the plate boundaries? [2] ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ 4. What is the difference between lava and magma? [2] ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ 5. Explain the difference between a seismogram and a seismograph. [2] ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ 6. The volcanic rocks pumice and obsidian have a similar composition but are very different in appearance. Explain this difference. (Hint: use the coke and froth analogy) _______________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________ 7. Match up the following words with their definitions using lines. Focus The break between different areas of rock in which movement has occurred. Tsunamis The point on the Earth’s surface directly above the point underground where the Earthquake originated from. Fault Large, often fast moving waves which are triggered by earthquakes under the ocean or by underwater landslides. Epicentre The point underground where the Earthquake originated from. [4] 8. The diagram below displays the locations of the major earthquakes / volcanoes throughout the world. Use the theory of plate tectonics to explain why; (a) Earthquakes and volcanoes are occur in the middle of oceans [2] __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ (b) Earthquakes and volcanoes occur on the west side of South America. [2] __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ (c ) Northern India and Pakistan experience earthquakes regularly [2] __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ 9. An earthquake occurs and the time of arrival of S and P waves is detected by seismograph stations in three Australian cities. Data was recorded in columns 2 and 3 of the table below (h: hours, min: minutes, s: seconds): [6] Use this data and the graph below to calculate the distance of each city from the epicentre, which you should enter in column 5 of the table above. You will need to work out the difference in the time of arrival of the P and S waves, which you should enter in column 4 of the table above. Difference in the times of arrival of P and S waves (min) 0 1000 2000 3000 4000 5000 6000 7000 Distance from earthquake (km) 8000