Chapter 36: Comparing Vertebrates
advertisement

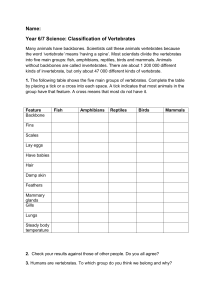
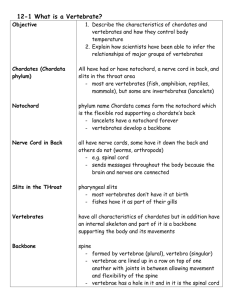
Chapter 36: Comparing Vertebrates Section 2: Form and Function in Vertebrates Form and Function in Vertebrates Vertebrates perform the essential functions of life with a variety of body structures Evolutionary processes have modified certain basic structures over time As you move through the vertebrate classes from fishes to mammals, _________________________________________ tend to become increasingly _________________________ Movement All vertebrates except jawless fishes have a vertebral column _______________________________ made of numerous individual bones called _______________________________ o Connected to one another by tough ligaments that allow the vertebral column to bend to a certain extent o ______________________________________________ are attached to this basic supporting structure by sets of bones called _________________________________________ o Most of the bones in the body can be made to move through the __________________________________________________ that are attached to the bones Fish and snakes o Main body muscles are arranged into blocks that are positioned on either side of the vertebral column o Contract in _______________________, one after another o Make the body bend rapidly ____________________________________ Amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals o The position of the limbs relative to the body shifts toward the __________________________ o The movement of the vertebral column when the animal runs changes from a side-to-side motion to an up-and-down motion Feeding The ________________ of vertebrates show many adaptations for feeding The organs of the digestive systems of vertebrates are equally well adapted for different feeding habits o _________________________________ Short digestive tracts with special enzymes that break down meat o _________________________________ Long intestines and stomachs with bacteria that break down cellulose Respiration _______________________________________________ o Use ___________________ for respiration As water passes over the gill filaments, oxygen diffuses into the blood in the capillaries and carbon dioxide diffuses from the blood into the water _______________________________________________ o Use ____________________ to breathe When the animals inhale, oxygen-rich air enters the lungs When the animals exhale, carbon dioxide-rich air is expelled Internal Transport Fishes and larval amphibians o ________________________________________________________ Blood travels from the heart to the gills to the body and back to the heart o _______________________________________________ Vertebrates with lungs o _______________________________________________________ Heart and lungs Heart and body Excretion Excretory systems eliminate nitrogenous wastes and regulate the amount of water in the body Most vertebrates rely on ______________________ for excretion Nitrogenous wastes are first produced in the form of _______________________ o Aquatic amphibians and fish Ammonia diffuses __________________________________ into the surrounding water o Mammals, terrestrial amphibians, and cartilaginous fishes Ammonia is changed into _________________ o Reptiles and birds Ammonia is changed into ____________________________ Response All vertebrates display a high degree of _________________________________ The size and complexity of the cerebrum and cerebellum increase as you move through the vertebrate classes from fish to mammals Reproduction Almost all vertebrates reproduce _____________________________ In some vertebrates fertilization is external In other fertilization occurs inside the body of the female Vertebrates show three different modes of development o _______________________________ Eggs develop outside the mother’s body o _______________________________ Eggs develop inside the mother’s body but the embryos receive the nutrients they need from the yolk that surrounds them, not from the mother directly o _______________________________ Developing embryos obtain nutrients directly from the mother’s body