Chapter 8 Test Review Sheet
advertisement

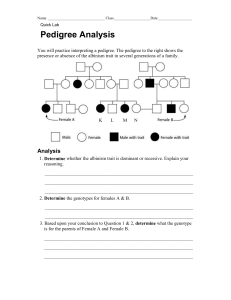
Chapter 8 Test Review General information 1. What is the study of heredity? 2. The passing of traits from parents to offspring is called…? 3. What is a phenotype? 4. What is a genotype? 5. What genotype is it when there are two identical alleles for a trait? 6. What genotype is it when there are different alleles for a trait? 7. What type of cross involves one pair of contrasting traits? 8. What are alleles? 9. In a heterozygous organism, what allele is expressed? 10. What is a carrier? Gregor Mendel 1. Why was Gregor Mendel considered the father of genetics? 2. Why were peas a good choice for Mendel? 3. In a Mendel’s cross what were the generations? 4. What were the phenotypes in those generations? 5. What trait (allele) reappeared in the F2 generation? 6. What is fertilization within a single plant called? 7. What is transferring pollen between plants called? 8. What is the law of segregation? 9. What is the law of independent assortment? Punnett Squares 1. heterozygous x heterozygous 2. heterozygous x homozygous recessive 3. homozygous dominant x heterozygous 4. homozygous dominant x homozygous recessive 5. heterozygous x hemizygous dominant 6. homozygous dominant x hemizygous dominant Test Cross 1. If the offspring of a test cross all have the dominant phenotype, what was genotype of the individual tested? 2. If the offspring of a test cross have half dominant and half recessive phenotypes, what was the genotype of the individual tested? 3. What is a test cross? Sex-linked Traits 1. Are sex-linked traits caused by hormones? 2. What gender are affected most by sex-linked traits? 3. What chromosome can most sex-linked traits be found? 4. What is a sex-linked trait that affects blood clotting? Pedigree 1. What trait shows up in every generation of a pedigree? 2. What are three things that would be found in a recessive, sex-linked pedigree 3. What is a pedigree? 4. From pedigree below: father’s genotype, # 3’s genotype, sex-linked? Codominance/Incomplete dominance/Multiple alleles 1. What is codominance? 2. What is incomplete dominance? 3. Do all genes have two alleles for a trait? 4. How many phenotypes can be found for codominance? 5. What is an example of multiple alleles 6. If a person inherited an A allele and and O allele, what would their blood type be? 7. What antigens and antibodies do a person with blood type A have? Autosomal Traits 1. What autosomal disorder was caused by a dominant allele? 2. What amino acid should a person with PKU avoid? 3. What is albinism? 4. Cross two cystic fibrosis carriers. Miscellaneous 1. What do sickle cell anemia and hemophilia have in common? 2. What is genetic counseling? Problems 1. Dihybrid cross: parents, F1 Punnett square, F1 phenotypes, F1 phenotypic data extrapolation 2. Mendel’s ratios – flower position 3. Sex-linked crosses – hemophilia, colorblindness General information 1. What is the study of heredity? - Genetics 2. The passing of traits from parents to offspring is called…? - Heredity 3. What is a phenotype? – The physical appearance of a trait 4. What is a genotype? – The set of alleles an organism inherited 5. What genotype is it when there are two identical alleles for a trait? - homozygous 6. What genotype is it when there are different alleles for a trait? - heterozygous 7. What type of cross involves one pair of contrasting traits? - monohybrid 8. What are alleles? – different forms of a particular gene 9. In a heterozygous organism, what allele is expressed? - dominant 10. What is a carrier? – a heterozygous organism (usually associated with a disorder) Gregor Mendel 1. Who was considered the father of genetics? – Gregor Mendel 2. Why were peas a good choice for Mendel? – mature quickly, produce many offspring, self-fertilize 3. In a Mendel’s cross what were the generations? – P, F1, F2 4. What were the phenotypes in those generations? – P – each was purebreeding of opposite trait, F1 was all similar to one parent, F2 – ¾ similar to F1 and ¼ similar to hidden trait 5. What trait (allele) reappeared in the F2 generation? - recessive 6. What is fertilization within a single plant called? - self- pollination 7. What is transferring pollen between plants called? – cross-pollination 8. What is the law of segregation? The members of each pair of alleles separate when gametes are formed 9. What is the law of independent assortment? – different genes separate independently of one another during gamete formation Punnett Squares – you should be able to determine phenotypes, genotypes, phenotypic ratios, genotypic ratios for each 7. heterozygous x heterozygous 8. heterozygous x homozygous recessive 1. homozygous dominant x heterozygous 2. homozygous dominant x homozygous recessive 3. heterozygous x hemizygous dominant 4. homozygous dominant x hemizygous dominant Test Cross 1. If the offspring of a test cross all have the dominant phenotype, what was genotype of the individual tested? – homozygous dominant 2. If the offspring of a test cross have half dominant and half recessive phenotypes, what was the genotype of the individual tested? - heterozygous 3. What is a test cross? Determining the unknown genotype of an individual with a dominant phenotype Sex-linked Traits 1. Are sex-linked traits caused by hormones? - no 2. What gender are affected most by sex-linked traits? - males 3. What chromosome can most sex-linked traits be found? – X chromosome 4. What is a sex-linked trait that affects blood clotting? - hemophilia Pedigree 1. What trait shows up in every generation of a pedigree? dominant 2. What are three things that would be found in a recessive, sex-linked pedigree – 1. found mostly in males, only females are carriers, skips generations 3. What is a pedigree? A diagram in which several generations of a family and the occurrence of certain genetic characteristics are shown 4. On your own Codominance/Incomplete dominance/Multiple alleles 1. What is codominance? – two dominant alleles are expressed at the same time 2. What is incomplete dominance? – a phenomenon in which a heterozygous organism has a phenotype that is intermediate between the phenotypes of its two homozygous parents 3. Do all genes have two alleles for a trait? – no, multiple allelic genes have mole than two 4. How many phenotypes can be found for codominance? - 3 5. What is an example of multiple alleles – human blood types 6. If a person inherited an A allele and and O allele, what would their blood type be? - A 7. What antigens and antibodies do a person with blood type A have? – A antigen and anti-B antibodies Autosomal Traits 1. What autosomal disorder was caused by a dominant allele? – Huntingtons 2. What amino acid should a person with PKU avoid? - phenylalanine 3. What is albinism? – lacking pigment 4. Cross two cystic fibrosis carriers. – ¾ normal, ¼ cystic fibrosis, ¼ homozygous dominant, ½ heterozygous, ¼ homozygous recessive Miscellaneous 1. What do sickle cell anemia and hemophilia have in common? – defective proteins within red blood cells 2. What is genetic counseling? – Identifies parents at risk for genetic defects, uses pedigrees, assists parents in deciding whether or not to have children Problems 1. Dihybrid cross: parents, F1 Punnett square, F1 phenotypes, F1 phenotypic data extrapolation – on your own 2. Mendel’s ratios – flower position - on your own 3. Sex-linked crosses – hemophilia, colorblindness - on your own