Variations of the Mekong discharge over the half past century
advertisement

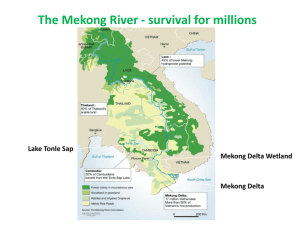
International Conference on Forest Environment in continental river basins; with a focus on the Mekong River. December 5-7, 2005, Phnom Penh, Cambodia ______________________________________________________________________________ Variations of the Mekong discharge over the half past century Katia Laval, T. Ngo-duc, J. Polcher Laboratoire de Météorologie Dynamique, University of Pierre Marie Curie, Paris, France Coresponding author: Katia Laval (laval@lmd.jussieu.fr) Keywords: Land surface scheme, soil water storage, river discharge, flood plains. 1. Introduction Detection of changes in long time series of hydrological data is important for planning of future water resource management. Up to present, these studies are principally based on the historical observed river discharge data, but often experience difficulty because of missing values and gaps in the observed data. Land Surface Models (LSMs), which simulate river discharges through a routing scheme, appear thus to be a good tool for completing such studies. 2. Land surface Model and forcing data The Land Surface Model, ORCHIDEE (Verant et al., 2004; Krinner et al., 2005) developed at the Institute Pierre Simon Laplace, France, can be integrated to compute the hydrological balance of a specific river basin if we can provide atmospheric data to force the model. ORCHIDEE represents the water and energy exchanges between land, vegetation and atmosphere. Water, which leaves the soil reservoir either through runoff or drainage, is stored in the three reservoirs of routine scheme and cascades progressively towards ocean (Figure 1). Figure 1. Principle of the river routing scheme 1 International Conference on Forest Environment in continental river basins; with a focus on the Mekong River. December 5-7, 2005, Phnom Penh, Cambodia ______________________________________________________________________________ In order to study the inter annual variability of surface conditions over a larger number of years, we have built a forcing data set, NCC, based on reanalysis data, NCEP, corrected by CRU precipitation. We were able to define 53 years of data as forcing to the ORCHIDEE Model; and compute the evolution of land water storage over the last 53 years (Ngo-duc et al., 2005a). 3. Results and Discussion The results of the hydrological budget were validated by observed river discharges of the world’s 10 largest rivers. The seasonal variations of simulated Mekong discharge are compared with the observed ones (Figure 2). We take advantage also of the recent GRACE Mission to evaluate seasonal water storage over the catchment basin (Figure 3). The evolution of continental water budget is used to analyze trends of this storage (Ngo-duc et al., 2005 b). According to the simulations, the Mekong discharge variability seems to have been changed these last 20 years. The influence of flood plains and irrigation on the water balance over the basin is investigated; we show that they have a substantial effect on water storage. Figure 2. Seasonal variations of river discharge at the Pakse station (simulated and observed) 2 International Conference on Forest Environment in continental river basins; with a focus on the Mekong River. December 5-7, 2005, Phnom Penh, Cambodia ______________________________________________________________________________ Figure 3. Water storage variations simulated by the two version of ORCHIDEE and evaluated by the GRACE mission (o) References: Verant S., K. Laval, J. Polcher and M. de Castro: (2004): Sensitivity of the continental hydrological cycle to the spatial resolution over the Iberian Peninsula, J. of Hydrometeorology., 5( 4), 265-283. Krinner G., Viovy N., de Noblet-Ducoudré N., Ogée J., Polcher J., Friedlingstein P., Ciais P., Sitch S., Prentice I. C. (2005): A dynamic global vegetation model for studies of the coupled atmosphere-biosphere system. Global Biogeochem. Cycles, 19(1), GB1015. Ngo-duc, T, J. Polcher, and K. Laval, 2005a: A 53 year forcing data set for Land Surface Models, J. Geophys Res., 110, D06116. Ngo-duc, T, K. Laval, J. Polcher, A. Lombard and A. Cazenave, 2005b: Effect of land water storage on global mean sea level over the past 50 years, Geophys Res. Letters, 32, L09704. 3