W7_SP_medium term
advertisement

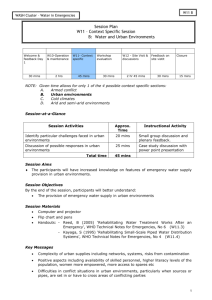
WASH Cluster – Water in Emergencies W7 Session Plan W7 – Medium Term Water Supply Solutions Timetable Opening & Introduction W1-Water W2-Water supply linkages needs pt1 1 hr 30 mins W6-Meeting immediate water needs W7-Medium term water responses 30 mins 45 mins 30 mins W8-Case study exercise W2-Water needs pt2 W3-Local regulations cultural norms & good practice 45 mins 45 mins W9 - Water facilities & good practice 45 mins 1 hr W10 – Operation, Maintenance and Sustainability 2 hours 30 mins W4-Water sources, treatment & implications 45 mins W11 –Water Context 1 hour 15 mins W5Assessments, prioritisation, monitoring 1 hr W12 – Site Visit 2 hours 45 mins Session-at-a-Glance Session Activities Approx. Time Introduction of medium term water response solutions 10 mins Power point presentation Comparison of advantages and disadvantages of different water supply and treatment options. 35 mins Group discussion, use of VIPP cards and plenary feedback. Total time Instructional Activity 45 mins Session Aims To enable participants to be able to select appropriate water responses for the medium term and to reinforce the possible impacts of their development Session Objectives By the end of the session participants will have improved knowledge of: The range of medium term solutions for water supply in emergencies The advantages and disadvantages of a number of short and medium term solutions Session Materials Computer and projector Flip chart and pens VIPP cards Key Messages Understand the differences in possible responses for immediate and medium term Understand some of the advantages and disadvantages of the different options – particular emphasis on the O&M and ongoing costs and possible impacts of development 1 WASH Cluster – Water in Emergencies W7 Recognise the importance of ensuring agreements reached with government, landowner and existing and new users before finalising and implementing any water solution. Facilitator Guidance Background reading for facilitator: Action Contre la Faim (2005) ‘Water, Sanitation and Hygiene for Populations at Risk’, Hermann Davis, J & Lambert, R (2002, 2nd edition) ‘Engineering in Emergencies, A Practical Guide for Relief Workers’, IT Publications MSF (1994) ‘Public Health Engineering in Emergency Situation, A Handbook for implementing health programmes in deprived environments, in particular in camps of displaced persons’ Wisner, B & Adams, J (2002) ‘Environmental Health in Emergencies and Disasters, A practical guide’, WHO Session plan Introduction to medium term responses: (10 min) PP slides 2-7 2. Discuss the point a response would start moving from immediate response to medium term. Identify the key benefits of the change. 3-7. Use the PowerPoint slides to introduce the features of medium term water responses and a few examples. 3&4. Use the examples in the slides, highlight that particular care should be taken to investigate, discuss and agree with local communities the following: Determine if there are any existing conflicts over the use of the water source Permission and rights for use for the affected populations & the local populations Is there sufficient supply for the affected population & the local population Who owns the water source (and who will own it if after displaced populations leave if a new one) Who will be responsible for O&M and paying for O&M – now and in the future? Session Plan – W7 2 WASH Cluster – Water in Emergencies - W7 5&6. Mechanical pumping schemes: Require a high level of on-going operation and maintenance – systems for O&M and for on-going costs should be agreed before the water source is developed & a formal agreement written and signed Permission is usually needed from the government to drill boreholes Care needed to assess the potential impacts of boreholes: change of cattle migration patterns possible conflicts over access and use environmental damage lowering of the water table 7. Private supplies where the owner has a financial benefit can be more sustainable than community supplies in some circumstances – scattered communities, urban environments, pastoral areas NB. Do not spend too much time on the examples, as the main part of this session is the exercise with feedback and discussion Comparing advantages and disadvantages of different water supply and treatment options, group exercise: (35 min) PP slides 8 8. Split the group into 3 smaller groups (max 5 per group) and allocate two of the given water supply options to each group. Ask the groups to identify the advantages & disadvantages for their two water supply options. Ask the participants to consider both the immediate and medium term responses and write the advantages and disadvantages for both on flip charts / or VIPP cards (15 min) Put the flip charts and / or the VIPP cards on the wall A spokesperson from each group briefly feedbacks on their two options to the plenary and comments asked from the rest of the group Session Plan – W7 3 WASH Cluster – Water in Emergencies W7 (15 min) In plenary ask the participants what solutions they would choose in their particular emergency scenario, then which would they prioritise as the best response for immediate & medium term (5 min) The conclusion to this exercise, is the need to be aware of the advantages and disadvantages of each option, as these will have implications on the appropriateness of the options for different stages of an emergency Mention session W10 on O&M and sustainability will provide more information. Session Plan – W7 4