Name - Cloudfront.net
advertisement

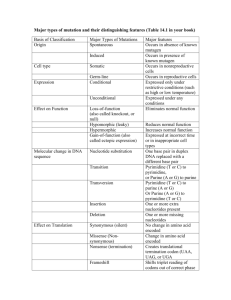
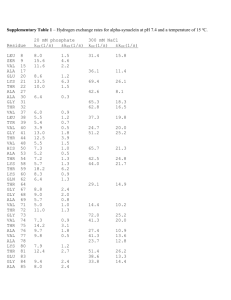
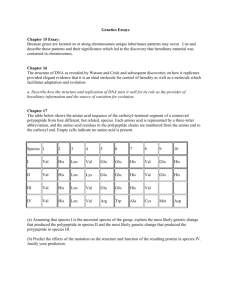
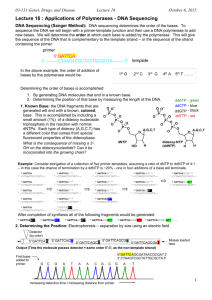
Name: _______________________________________________ Date: ________________ Period: ______ Biology: Biochemical Evidence for Evolution Background Information: If two organisms have similar DNA molecules, they must have similar amino acids and thus similar proteins. Therefore, DNA comparisons can be made by examining the sequences of amino acids within a protein. Scientists have long believed that similar DNA sequences indicate a common origin and ancestor. The more similar the DNA of two living organisms, the more closely related they may be to one another. Hemoglobin, a protein in red blood cells, has been studied. Scientists know the specific amino acids and their arrangements in hemoglobin molecules of humans, gorilla, and horses. In this investigation, you will a. count and record the molecules of each amino acid present in similar portions of humans, gorilla, and horse hemoglobin. b. Count and record differences in the sequence of amino acids in similar portions of human, gorilla, and horse hemoglobin. c. Use this data to show how biochemical evidence can be used to support evolution. Procedure Part A: Amino Acid Sequence 1) Read the amino acid sequences from left to right beginning at the upper left hand corner of figure 391. Compare the sequences of humans to the sequences of gorillas and horses. An example of a sequence difference between humans and horses is shown in figure 39-1. 2) Record in Table 39-1 the total number of differences in the sequences of gorilla and human amino acids. Then repeat this for horse and human, and for gorilla and horse. Table 39-1. Number of Amino Acid Sequence Differences Organisms Number of Differences Gorilla and Human Horse and Human Gorilla and Horse Using the information you collected, graph the differences between the three organisms below. Be sure to title your graph and label both axes. Part B: Numbers of Amino Acids 1) Figure 39-1 represents the amino acid sequence of corresponding portions of the hemoglobin molecules or horses, gorillas, and humans. 2) Count the molecules of each kind of amino acid in human’s hemoglobin. Record the totals in the proper column of table 39-2. Figure 39-1 Human: VAL Gorilla: VAL Horse: VAL HIS HIS GLU LEU LEU LEU THR THR SER Human: GLY Gorilla: GLY Horse: ASP LYS VAL ASP VAL ASP GLU VAL GLY GLY GLU ALA LEU GLY ARG LYS VAL ASP VAL ASP GLU VAL GLY GLY GLU ALA LEU GLY ARG LYS VAL ASP GLU GLU GLU VAL GLY GLY GLU ALA LEU GLY ARG TYR TYR TYR GLU GLU GLU Human: LYS Gorilla: LYS Horse: LYS ALA ALA ALA HIS HIS HIS GLY GLY GLY LYS LYS LYS LYS LYS LYS VAL VAL VAL LEU LEU LEU GLY GLY HIS ALA ALA SER Human: ALA Gorilla: ALA Horse: HIS HIS HIS HIS LEU LEU LEU ASP ASP ASP ASP ASP ASP LEU LEU LEU LYS LYS LYS GLY GLY GLY THR THR THR PHE PHE PHE Human: LEU Gorilla: LEU Horse: LEU HIS HIS HIS CYS CYS CYS ASP ASP ASP LYS LYS LYS LEU LEU LEU HIS HIS HIS Human: LEU Gorilla: LEU Horse: LEU GLY GLY GLY ASP ASP ASP VAL VAL VAL LEU LEU LEU VAL VAL ALA CYS CYS LEU VAL VAL VAL LEU LEU VAL ALA ALA ALA Human: GLU Gorilla: GLU Horse: ASP PHE PHE PHE THR THR THR PRO PRO PRO PRO PRO GLU VAL VAL LEU GLU GLU GLU ALA ALA ALA ALA ALA SER TYR TYR TYR ASP ASP ASP ALA ALA ALA LEU LEU LEU ALA ALA ALA VAL VAL VAL ALA ALA ALA GLU GLU GLU VAL VAL VAL LEU LEU LEU THR PRO ASP THR PRO ASP ASP PRO GLY THR THR THR ALA ALA ALA ASP ASP ASP ALA ALA ALA TRY TRY TRY SER SER ALA Human: GLY Gorilla: GLY Horse: GLY SER SER SER PRO PRO PRO LYS LYS LYS LEU LEU LEU VAL VAL VAL VAL VAL VAL GLU GLU GLU Human: LEU Gorilla: LEU Horse: LEU Human: GLY Gorilla: GLY Horse: GLY VAL VAL VAL PRO PRO GLY VAL VAL VAL ASP ASP ASP HIS HIS HIS ARG ARG ARG MET MET MET PRO PRO PRO LYS LYS LYS THR THR LEU PHE PHE PHE PHE PHE PHE GLY GLY GLY ASP ASP ASP PHE PHE PHE SER SER GLY ALA ALA ALA GLU GLU GLU THR THR ALA ASP ASP ASP HIS HIS ARG ALA ALA ALA GLU GLU ASP PRO PRO PRO GLU GLU GLU LYS LYS LYS TYR TYR TYR HIS HIS HIS SER SER SER LYS LYS LYS TRY TRY TRY PHE PHE PHE VAL VAL VAL ASP ASP GLU GLY GLY GLY LEU LEU VAL LEU LEU LEU SER SER SER GLU GLU GLU PHE PHE PHE HIS HIS HIS LEU LEU LEU ARG LEU ARG LEU LEU LEU PHE PHE PHE GLY GLY GLY LYS LYS LYS VAL VAL VAL VAL VAL VAL ALA ALA ALA Table 39-2. Number of Each Amino Acid Amino Acid Abbreviation Alanine Ala Arginine Arg Aspartic acid Asp Cysteine Cys Glutamic acid Glu Glycine Gly Histidine His Leucine Leu Lysine Lys Methionine Met Phenylalanine Phe Proline Pro Serine Ser Threonine Thr Tryptophan Try Tyrosine Tyr Valine Val Human Gorilla Horse Data Analysis: 1) Of the 17 different types of amino acids found in hemoglobin, a. How many are present in the same number in humans and gorillas? ________________________ b. In humans and horse? ____________________________________________________________ c. In gorillas and horses? ____________________________________________________________ 2) Neatly, list all the possible DNA codes for the amino acid Leucine. _______________________________________________________________________________________ 3) Which amino acid would be created from the DNA segment TTA? ___________________________ Be sure to answer the following questions using your best writing skills. 4) Which two animals seem to have more similar hemoglobin? Explain your reasoning. _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ 5) What if the DNA had a mutation and the code was changed to TTG (instead of TTA). How would this affect the overall amino acid and protein? _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ 6) The sequence of amino acids is determined by the sequence of nitrogen bases in DNA. What can we conclude about the DNA sequence of these three animals? _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ 7) In your own words, describe what it means when different organisms such as a gorilla and human have similar amino acids in the protein hemoglobin. _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________