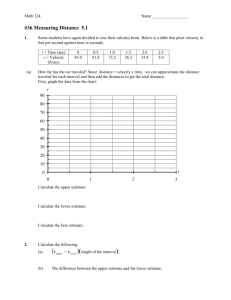
Sample Paper Physics - Department of Science & Technology
advertisement

Sample Paper Science Quiz (Physics) Q 1. Units of magnetic flux are : (a) (c) weber/metre joule x coulomb/meter Q 2. Magnetic intensity is measured in : (a) (c) A m ¯1 gauss (b) (d) newton metre/ampere tesla (b) (d) tesla weber Q 3. Earth has a mass of 5.98 x 1024 kg. The average mass of atoms that make up the earth is 40 u. Number of atoms in earth is : (a) (c) 9.0 x 1049 9.0 x 1052 Q 4. Which of the following is a dimensional constant ? (a) (c) refractive index relative density (b) (d) (b) (d) 9.0 x 1046 1.49 x 1024 dielectric constant gravitational constant Q 5. If units of two systems of measurement are in the ratio 2 : 3, then the ratio of units of angular momentum in those two system is : (a) (c) 2:3 4:9 (b) (d) 9:4 1:1 Q 6. If speed of light (c), acceleration due to gravity (g) and pressure (p) are taken as fundamental units, the dimensions of gravitational constant (G) are : (a) (c) c g p¯3 c0 g2 p¯1 (b) (d) c2 g3 p¯2 c2 g2 p¯2 Q 7. The length of a cylinder is measures with a metre rod having least count 0.1 cm. Its diameter is measured with vernier callipers having least count 0.01 cm. Given the length is 5·0 cm and radius is 2.00 cm. The percentage error in the calculated value of volume will be : (a) (c) 2% 3% (b) (d) Q 8. How many seconds are there in a light fermi ? (a) (c) 10¯15 3.33 x 10¯24 (b) (d) 1% 4% 3.0 x 108 3.3 x 10¯7 Q 9. The unit of thermal conductance is ? (a) (c) WK¯1 WK (b) (d) JK¯1 JK Q 10. A student measured the length of a pendulum as 1.35 m and time for 30 vibrations as 2 min. 20 sec. using a wrist watch. Find the percentage error in g. (a) (c) 1.72% 1.63% (b) (d) 2.16 % 1.81% Q 11. A particle has two equal accelerations in two given directions. If one of the accelerations is halved, then the angle which the resultant makes with the other is also halved. The angle between the accelerations is : (a) (c) 1200 600 (b) (d) 900 450 Q 12. Out of the following pairs of forces, the resultant of which can not be 4 N ? (a) (c) 2N and 2N 2N and 6N (b) (d) 2N and 4N 2N and 8N Q 13. The resultant of which of the following sets of forces can not be zero : (a) (c) 10, 20 and 40 10, 20 and 20 (b) (d) 10, 10 and 20 10, 10 and 10 Q 14. The sum of the magnitude of two forces acting at a point is 18 and the magnitude of their resultant is 12. If the resultant is at 900 with the force of the smaller magnitude, then their magnitudes are : (a) (c) 3, 15 5, 13 (b) (d) 4, 14 6, 12 Q 15. The square of resultant of two equal forces is three times their product. Angle between the forces is : (a) (c) π π/4 (b) (d) π/2 π/3 Q 16. The line of action of the resultant of two like parallel forces shifts by one-fourth of the distance between the forces when the two forces are interchanged. The ratio of the two forces is: (a) (c) 1:2 3:4 (b) (d) 2:3 3:5 Q 17. The sum of two forces acting at a point is 16 N. If the resultant force is 8 N and its direction is perpendicular to minimum force then the forces are : (a) (c) 6 N and 10 N 4 N and 12 N (b) (d) 8 N and 8 N 2 N and 14 N Q 18. Two boats are moving in same direction in a river. What is the best condition so that they move parallel in the same direction? (a) (b) (c) (d) Both move away from each other They are slightly bent to each other They are parallel to each other It is not possible Q 19. An aeroplane moves 400 m towards north, 300 m towards west and then 1200 m vertically upwards. Then its displacement from the initial position is : (a) (c) 1300 m 1500 m (b) (d) 1400 m 1600 m Q 20. A bus travelling the first one third distance at a speed of 10km/h, the next one fourth at 20 km/h and the remaining at 40 km/h. The average speed of the bus is nearly (a) (c) 9 km/h 18 km/h (b) (d) 16 km/h 48 km/h Q 21. A stone is dropped from the top of a tower and travels 24.5 m in last second of its journey. The height of the tower is : (a) (c) 44.1 m 78.4 m (b) (d) 49 m 72 m Q 22. A body freely falling from rest has a velocity ν after its falls through a height h. The distance it has to fall down further for its velocity to become double is : (a) (c) h 3h (b) (d) 2h 4h Q 23. Drops of water fall from the roof of a building 9 m high at regular intervals of time, the first drop reaching the ground at the same instant fourth drop starts its fall. What are the distances of the second and third drops from the roof ? (a) (c) 6m and 2m 4m and 1m (b) (d) 6m and 3m 4m and 2m Q 24 A particle accelerates from rest at a constant rate for some time and attains a velocity of 8 m/s. Afterwards it decelerates with the constant rate and comes to rest. If the total time taken is 4 second, the distance travelled is : (a) (c) 4m 32 m (b) (d) 16 m none of the above Q 25 A car is moving on a road and rain falling vertically. Select the correct answer: (a) (b) (c) (d) The rain will strike the hind screen only The rain will strike the front screen only The rain will strike both the screens The rain will not strike any of the screens Q 26. A sprinter accelerates to his maximum speed in 4s. If such a sprinter finishes a 140 m race in 9s, what is the runner’s acceleration during the first four seconds? Assume acceleration to be constant (a) (c) 3.5 ms ¯2 5.0 ms ¯2 (b) (d) 4.2 ms ¯2 5.5 ms ¯2 Q 27 A steamer takes 12 days to reach from port x to port y. Every day only one steamer sets out from both the ports. How many steamers does each steamer meet in the open sea? (a) (c) 23 27 (b) (d) 25 21 Q 28 In a race for 100 m dash, the first and the second runners have a gap of one metre at the mid way stage. Assuming the first runner goes steady, by what percentage should the second runner increases his speed just to win the race. (a) (c) 2% more than 4% (b) (d) 4% less than 4 % Q 29 A motor boat covers a given distance in 6 hours moving down stream of a river. It covers the same distance in 10 hours moving upstream. The time (in hours) it takes to cover the same distance in still water is : (a) (c) 6 10 (b) (d) 7.5 15 Q 30 A point initially at rest moves along x-axis. Its acceleration varies with time a = (6 t + 5) in ms¯2. If it starts from origin, the distance covered in 1 second is : (a) (c) 3m 4m (b) (d) as 3.5 m 4.5 m Q 31 A ball rolls off the top of stairway with a horizontal velocity of magnitude 1 · 8 m/s. The steps are 0 · 20 m high and 0 · 20 m wide. Which step will the ball hit first? (a) (c) first third (b) (d) second fourth Q 32 When air resistance is taken into account while dealing with the motion of the projectile which of the following properties of the projectile, shows an increase, (a) (c) (d) range (b) maximum height speed at which it strikes the ground the angle at which the projectile strikes the ground Q 33 The range of a projectile fired at an angle of 150 is 50 m. If it is fired with the same speed at an angle of 450, its range will be : (a) (c) 25 m 100 m (b) (d) 50 m 77.6 m Q 34 In case of a projectile, what is the angle between the instantaneous velocity and acceleration at the highest point? (a) (c) 450 900 (b) (d) 1800 00 Q 35 A man can throw a stone to a max distance of 80 metres. The maximum height to which it will rise in metres is : (a) (c) 10 m 30 m (b) (d) Q 36 The equation of projectile is y = px - qx2. Its horizontal range is : (a) (c) pq p (b) (d) 20 m 40 m p/q q Q 37 A grass hopper finds that he can jump a maximum horizontal distance of 1 m. With what speed can he travel along the path if he spends a negligible time on the ground : (a) (c) 9.8 m/s 2.21 m/s (b) (d) 4.42 m/s 3.16 m/s Q 38 The speed of projection of a projectile is increased by 10%, without changing the angle of projection. The percentage increase in the range will be : (a) (c) 10% 15% (b) (d) 20% 5% Q 39 Two paper screens A and B are separated by a distance of 200 m. A bullet pierces A and then B. The hole in B is 40 cm below the hole in A. If the bullet is travelling horizontally at the time of hitting A, then the velocity of the bullet at A is : (a) (c) 200 m/s 600 m/s (b) (d) 400 m/s 700 m/s Q 40 With what minimum speed a particle be projected from the origin so that it is ablve to pass through a given point (30m, 40 m) : (a) (c) 30 ms ¯ 1 50 ms ¯ 1 Q 41 A car accelerates on a horizontal road due to the force exerted by : (a) (c) road on the car driver of car (b) (d) (b) (d) 40 ms ¯ 1 60 ms ¯ 1 engine of car car on earth Q 42 A ball of mass 0 · 4 kg thrown up in air with velocity of 30 ms ¯ 1 reaches the highest point in 2 · 5 sec. The air resistance encountered by the ball during upward motion is : (a) (c) 0.88 N 300 N (b) (d) 8800 N 300 dyne Q 43 A fat hose pipe is held horizontal by a fireman. It delivers water through a nozzle at one litre/sec. If by increasing the pressure, the water is delivered of 2 litre/sec, the fireman now has to : (a) (b) (c) (d) Push forward twice as hard Push forward four times as hard Push forward eight times as hard Pull backward four times as hard Q 44 A dish of mass 10 g is kept horizontally in air by firing bullets of mass 5 gm each at the rate of 10 per sec. If the bullets rebound with the same speed, what is the velocity with which the bullets are fired? (a) (c) 49 cm/sec 147 cm/sec (b) (d) 98 cm/sec 196 cm/sec Q 45 A player caught a cricket ball of mass 150 gram, which was moving with a velocity of 20 m/s. If the catching process is completed in 0·1 second, the blow exerted by the ball on the hands of the player is : (a) (c) 100 N 20 N (b) (d) 30 N 15 N Q 46 A cricket ball of mass 250 g collides with a bat with velocity 10 m/s and returns with same velocity within 0·01 sec. The force acting on bat is : (a) (c) 25 N 250 N (b) (d) 50 N 500 N Q 47 A machine gun has a mass 5 kg. It fires 50 gram bullets at the rate of 30 bullets per minute at a speed of 400 ms ¯ 1. What force is required to keep the gun in position? (a) (c) 10 N 15 N (b) (d) 5N 30 N Q 48 A uniform chain of length 8 m and mass 4 kg is hanging vertically from a pulley. The work done is winding the chain on to the pulley is (g = 10 m/s2) : (a) (c) 16 J 32 J (b) (d) 160 J 320 J Q 49 A 60 kg woman pushes a 20 kg suitcase on wheels, a distance of 10 m by exerting a constant force of 2 N on it in the direction of motion, starting from rest. The work done by the woman is : (a) (c) 20 joule 200 joule (b) (d) 2 joule 400 joule Q 50 A car covers a distance of 10 km along an inclined plane under the action of a horizontal force of 5 N. The work done on car is 25 kJ. The inclination of the plane to horizontal is : (a) (c) Q 51 (a) (c) 0o 60o (b) (d) 30o 90o Work done in holding a 15 kg suitcase while waiting for a bus for 15 minutes is : 1 kg.m 15 x 15 x 60 J (b) (d) 225 J Zero Q 52 A body is projected vertically up. At certain height h above the ground, its PE and KE are in the ratio 1 : 4. At what height above the ground PE and KE will be in the ratio 4 : 1 ? (a) (c) 4h 5h (b) (d) h/4 h/5 Q 53 Once a choice is made regarding zero potential energy references state, the changes in potential energy : (a) (c) (d) are same (b) are different depend strictly on the choice of the zero of potential become indeterminate Q 54 A ball of mass 0·01 kg moves with a velocity of 100 m/sec. How much uniform force will stop it in 10 seconds ? (a) (c) 0·2 newton 0·01 newton (b) (d) 1·0 newton 0·1 newton Q 55 A rail way truck of mass 2 x 104 kg travelling at 0.5 m/s collides with another truck of half its mass moving in opposite direction with velocity 0.4 m/s. If two trucks couple, their common velocity would be: (a) (c) 0·2 m/s 0·4 m/s (b) (d) 0·3 m/s 0·5 m/s Q 56 When a body is projected vertically up from the ground, its PE and KE at a point P are in the ratio 2 : 3. If same body is projected with double the previous velocity, then at the same point P ratio of its P.E. and KE would be: (a) (c) 9:1 1:1 (b) (d) 1:9 4:9 Q 57 In an ice rink, a skator moving at 3 m/s encounters a rough patch that reduces her speed by 45%. Find the length of the rough patch if frictional force is 25 % of her weight : (a) (c) 1·28 m 1·66 m (b) (d) 1·46 m 1·96 m Q 58 An aeroplane flies in a horizontal circle of radius 3·06 km at a speed of 150 m/s. The direction of the resultant force on air craft is : (a) (c) 37o with the vertical 30o with the vertical (b) (d) 53o with the vertical 45o with the vertical Q 59 A coin is placed on a gramophone record rotating at a speed of 45 rpm. It flies away when the rotational speed is 50 rpm. It two such coins are placed one over the other on the same record, both of them will fly away when rotational speed is : (a) (c) 100 rpm 12.5 rpm (b) (d) Q 60 The ratio of the angular speed of minutes hand and hour hand of a watch is : (a) (c) 6:1 1:6 Q 61 What is the ratio of the angular speeds of the minute hand and second hand of a clock? (a) (c) 1 : 12 1 : 60 (b) (d) (b) (d) 25 rpm 50 rpm 12 : 1 1 : 12 12 : 1 60 : 1 Q 62 A string can withstand a tension of 25 N. What is the greatest speed at which a body of mass 1 kg can be whirled in a horizontal circle using 1m length of the string? (a) (c) 2.5 ms¯1 7.5 ms¯1 (b) (d) 5 ms¯1 10 ms¯1 Q 63 A body of mass 5 kg is whirled in a vertical circle by a string 1 m long. Calculate velocity at the top of the circle for just looping the vertical loop (a) (c) 3·1 m/s 9 m/s (b) (d) 7 m/s 7.3 m/s Q 64 A curved road of 50 m radius is banked at correct angle for a given speed. If the speed is to be doubled keeping the same banking angle, the radius of curvature of the road should be changed to : (a) (c) 25 m 150 m (b) (d) 100 m 200 m Q 65 The bob of a simple pendulum of length 1 · 2 m has a velocity of 7 m/s when it is at the lowest point. The bob would leave the circular path above the centre at a height : (a) (c) 1·0m 0 · 652 m (b) (d) 0 · 867 m 0 · 512 m Q 66 When a shell travelling along a parabolic path is the gravitational field explodes in the mid air, the centre of mass of fragments will continue to move : (a) (c) (d) vertically down (b) vertically up and then vertically down horizontally followed by parabolic path Q 67 If the resultant of all external forces is zero, then velocity of centre of mass will be : (a) (c) zero either (a) or (b) (b) (d) along the original parabolic path constant neither (a) nor (b) Q 68 Two bodies of masses 2 kg and 4 kg are moving with velocities 2 m/s and 10 m/s towards eachother due to mutual gravitational attraction. What is the velocity of their centre of mass? (a) (c) 5 · 3 m/s zero (b) (d) Q 69 The ratio of angular momentum of earth for its orbital motion and its daily rotation is : (a) (c) much greater than 1 equal to 1 (b) (d) 6 · 4 m/s 8 · 1 m/s smaller than 1 slightly greater than 1 Q 70 A circular disc is rolling on a horizontal plane. Its total K.E. is 150 J. What is its translational K.E. ? (a) (c) 200 J 125 J (b) (d) 100 J none of these Q 71 In a circular motion the angle between a particle’s linear momentum and its angular moment is : (a) (c) 0o 90o (b) (d) 45o 180o Q 72 A solid sphere rolls down two different inclined planes of same height, but of different inclinations. In both cases : (a) (b) (c) (d) speed and time of descent will be same speed will be same, but time of descent will be different speed will be different, but time of descent will be same speed and time of descent both are different Q 73 A cylinder of height h is placed on an inclined plane, the angle of inclination of which is slowly increased. It begins to slip when angle of inclination is 45o. What is the radius of the cylinder? (a) (c) h h/2 (b) (d) h/4 3 h/4 Q 74 A small ball describes a horizontal circle on the smooth inner surface of a conical funnel. If the height of the plane of the circle above the vertex by 10 cm, what is the speed of the particle: (a) (c) 2 m/s 16 m/s (b) (d) 4 m/s 1 m/s Q 75 A circular ring of wire of mass 0.5 kg and radius 2.5 m is rotating in its own plane about a perpendicular axis passing through its centre with a constant angular speed of 10 rps. The tension produced in the ring will be : (a) (c) 5 x 103 N 785 N (b) (d) 104 N none of these Q 76 If the distance between the sun and the earth is increased by three times then attraction between two will : (a) (c) remains constant decrease by 83% (b) (d) decrease by 63% decrease by 89% Q 77 The radius of the Earth is about 6400 km and that of the Mars is 3200 km. The mass of the Earth is about 10 times the mass of the Mars. An object weighs 200 N on the surface of Earth, its weight on the surface of Mars will be : (a) (c) 8N 40 N (b) (d) 20 N 80 N Q 78 Two spherical planets A and B have same mass but densities in the ratio 8 : 1. For these planets, the ratio of acceleration due to gravity at the surface of A to its value at the surface of B is : (a) (c) 1:4 4:1 (b) (d) 1:2 8:1 Q 79 At a distance 320 km above the surface of earth, the value of acceleration due to gravity will be lower than its value on the surface of the earth by nearly (radius of earth = 6400 km) : (a) (c) 2% 10% (b) (d) 6% 14% Q 80 A mass m is placed at a point B in the gravitational field of mass M. When the mass m is brought from B to near point A, its gravitational potential energy will : (a) (c) remains unchanged decrease (b) (d) Q 81 Weightlessness experienced while orbiting the earth, in space ships, is the result of : (a) (c) Inertia Zero gravity (b) (d) increase become zero Acceleration Centre of gravity Q 82 By what minimum percentage should orbital velocity of moon be increased so that it departs forever? (a) (c) 100% 41.4% (b) (d) 50% none of the above Q 83 By what percent the energy of a satellite has to be increased to shift it from an orbit of radius r to 3 r : (a) (c) 22.3% 66.7% (b) (d) 33.3% 100% Q 84 Two pieces of wire A and B of the same material have their lengths in the ratio 1 : 2, and their diameters are in the ratio 2 : 1. If they are stretched by the same force, their elongations will be in the ratio : (a) (c) 2:1 1:8 (b) (d) Q 85 The Young’s modulus of a perfectly rigid body is : (a) (c) unity infinity (b) (d) 1:4 8:1 zero some finite non-zero constant Q 86 A cube is subjected to a uniform volume compression. If the side of the cube decreases by 2%, the bulk strain is : (a) (c) 0.02 0.04 (b) (d) 0.03 0.06 Q 87 In case of rubber band the workdone by it in returning to its original shape : (a) (b) (c) (d) is less than the work required to deform it is greater than the work required to deform it is equal to the work required to deform it all the above Q 88 A wire can be broken by applying a load of 20 kg wt. The force required to break the wire of twice the diameter (same length and same material) is : (a) (c) 5 kg wt. 80 kg. wt. (b) (d) Q 89 Solids which break or rupture above the elastic limit are classified as : (a) (c) brittle ductile (b) (d) 160 kg. wt. 20 kg. wt. elastic malleable Q 90 A material has Poisson’s ratio 0·5. If a uniform rod of it suffers a longitudinal strain of 2 x 10¯3 , what percentage increase in volume takes place? (a) (c) 2% 5% (b) (d) 2.5% 0% Q 91 An air-tight cage with a parrot sitting in it is suspended from the spring balance. The parrot start flying. The reading of the spring balance will : (a) (c) increase not change (b) (d) decrease be zero Q 92 An ice block floats in a liquid whose density is less than water. A part of block is outside the liquid. When whole of ice has melted, the liquid level will : (a) (c) rise remain same Q 93 Surface tension of a liquid is due to : (a) (b) (c) (d) gravitation force between molecules electrical force between molecules adhesive force between molecules cohesive force between molecules (b) (d) go down first rise than go down Q 94 A drop of liquid of diameter 2.8 mm breaks up into 125 identical drops. The change in energy is nearly (S = 75 dynes/cm): (a) (c) zero 46 erg. (b) (d) 19 erg. 74 erg. Q 95 A liquid will NOT wet the surface of a solid if its angle of contact is: (a) (c) zero more than 900 (b) (d) less than 900 900 Q 96 At which of the following temperatures, the value of surface tension of water is minimum? (a) (c) 40C 500C (b) (d) 250C 750C Q 97 Two hail stones with radii in the ratio of 1 : 2 fall from a great height through the atmosphere. Then the ratio of their momenta after they have attained terminal velocity is : (a) (c) 1:1 1 : 16 (b) (d) Q 98 For flow of a fluid to be turbulent : (a) (b) (c) (d) Fluid should have high density Critical velocity should be large Reynold number should be less than 2000 all the above 1:4 1 : 32 Q 99 A cylindrical vessel is filled with equal amounts by weights of mercury and water. The total height of the two layers is 29·2 cm. The pressure of the liquid at the bottom of the vessel is (specific gravity of mercury is 13·6) : (a) (c) 8 cm of Hg 4 cm of Hg (b) (d) 6 cm of Hg 2 cm of Hg Q100. In what type of fluid is there the maximum probability of stream-line flow ? (a) (c) Low density, low viscosity High density, low viscosity (b) (d) Low density, high viscosity High density, high viscosity Q101. At what temperature, volume of an ideal gas at 00C become triple? (a) (c) 5460C 8190C (b) (d) 1820C 6460C Q102. One gram of ice is mixed with one gram of steam. At thermal equilibrium the temperature of the mixture is: (a) (c) 00C 550C (b) (d) 1000C 800C (b) (d) 00 Q103. Specific heat of melting ice is : (a) (c) 0·5 0 1 Q104. Coefficient of cubical expansion of water is minimum at : (a) (c) 00C 15.50C (b) (d) 40C 1000C Q105. Two rods A and B of the same length and radius are joined together. The thermal conductivity of A and B are 2 K and K, if the temperature difference between the open ends of A and B is 360C, the temperature across A is : (a) (c) 120C 240C (b) (d) 180C 90C Q106. The ratio of thermal conductivity of two rods of different materials is 5 : 4. The two rods of same area of cross section and same thermal resistance will have the lengths in the ratio : (a) (c) 5:4 9:1 (b) (d) 1:9 4:5 Q107. The temperature of a black body is increased by 50%, then the percentage of increase of radiation is approximately : (a) (c) 100% 400% (b) (d) 25% 500% Q108. If temperature of a black body increases from 70C to 2870C, then the rate of energy radiation increases by : (a) (c) (287/7)4 4 (b) (d) 16 2 Q109. Four spheres A, B, C and D of different metals but of same radius are kept at same temperature. The ratio of their densities is 2 : 3 : 5 : 1. If specific heats of their materials are in the ratio 3 : 6 : 2 : 4, which sphere will show initially the fastest rate of cooling? : (a) (c) D B (b) (d) C A Q110. The temperature of a room heated by a heater is 200C, when outside temperature is - 200C, and it is 100C, when the outside temperature is -400C, . The temperature of heater is : (a) (c) 600C 800C (b) (d) 400C 1000C Q111. For a gram-molecule of a gas, the value of the constant R in the equation PV = RT is nearly : (a) (c) 2 cal/K 0.2 cal/K (b) (d) 10 cal/K 200 cal/K Q112. When a gas filled in a closed vessel is heated through 10C, its pressure increased by 0.4%. The initial temperature of the gas was : (a) (c) 250 K 2500C (b) (d) 2500 K 250C Q113. The r.m.s. velocity of gas molecules is 300m/sec. The r.m.s. velocity of molecules of gas with twice the molecular weight and half the absolute temperature is : (a) (c) 300 m/sec 75 m/sec (b) (d) 600 m/sec 150 m/sec Q114. If the pressure in a closed vessel is reduced by drawing out some gas, the mean-free path of the molecules : (a) (c) (d) is decreased (b) is increased remains unchanged increases or decreases according to the nature of the gas. Q115. At a certain temperature, the ratio of the rms velocity of H2 molecules to O2 molecule is : (a) (c) 1:1 4:1 (b) (d) 1:4 16 : 1 Q116. What is the degree of freedom in case of a monoatomic gas? (a) (c) 1 4 (b) (d) 3 5 (b) (d) vibrational motion all of these Q117. The molecules of monoatomic gas do only : (a) (c) translational motion rotational motion Q118. Equal masses of N2 and O2 gases are filled in vessels A and B. The volume of vessel B is double of A. The ratio of pressure in vessel A and B will be : (a) (c) 16 : 14 16 : 7 (b) (d) 32 : 7 none of the above Q119. 22 g of carbondioxide at 270C is mixed in a closed container with 16 g of oxygen at 370C. If both gases are considered as ideal gases, then the temperature of the mixture is : (a) (c) 24·20C 31·50C (b) (d) 28·50C 33·50C Q120. Two moles of monoatomic gas is mixed with three moles of a diatomic gas. The molar specific heat of the mixture of constant volume is : (a) (c) 1·55 R 1·63 R (d) (b) 2·10 R 2·20 R Q121. A monoatomic ideal gas at 270C is suddenly compressed to one tenth of its original volume. After compression, its temperature is : (a) (c) 12650K 20090K (b) (d) 13920K 72100K Q122. When the amount of work done is 333 cal and increase in internal energy is 167 cal, then the heat supplied is : (a) (c) 500 cal 400 cal (b) (d) 166 cal 333 cal Q123. If R is universal gas constant, the amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of 2 moles of an ideal monoatomic gas from 273 to 373 K when no work is done is : (a) (c) 100 R 300 R (b) (d) 150 R 500 R Q124. The efficiency of a Carnot engine working between 800 K and 500 K is : (a) (c) 0.4 0.375 (b) (d) 0.625 0.5 Q125. What is the temp. of source in Carnot cycle of 10% efficiency when heat exhausts at 270 K? (a) (c) 400 K 300 K (b) (d) 500 K 600 K Q126. A Carnot engine whose course is at 400 K takes 200 cals of heat and rejects 150 cals to the sink. What is the temp. of the sink? (a) (c) 800 K 300 K (b) (d) 400 K cannot say Q127. A refrigerator absorbs 2000 cals of heat from ice trays. If the coefficient of performance is 4, then work done by the motor is : (a) (c) 2100 J 8400 J (b) (d) 4200 J 500 J Q128. If for a gas, R/Cv = 0.67, this gas is made up of molecules which are: (a) (c) diatomic triatomic (b) (d) monoatomic cannot say Q129. For a monoatomic gas, work done at constant pressure is W. The heat supplied at constant volume for the same rise in temperature of the gas is : (a) (c) W/2 5W/2 (b) (d) 3W/2 W Q130. If pressure and temperature of an ideal gas are doubled and volume is halved, the number of molecules of the gas: (a) (c) become half become 4 times (b) (d) become two times remain constant Q131. Two gram of helium is enclosed in a vessel at NTP. How much heat should be given to it to double the pressure. Specific heat of He is 3 joule/g K. (a) (c) 1638 J 800 J (b) (d) 1600 J 819 J. Q132. Two simple pendulums of length 100 cm and 1600 cm are in phase at the mean position at a certain instant of time. If T is the time period of first pendulum, then the minimum time after which they will be in phase again is : (a) (c) 3T/4 3T/2 (b) (d) 4T/3 4T Q133. A particle executes S.H.M. Then the graph of velocity as a function of displacement is : (a) (c) a straight line an ellipse (b) (d) a circle a hyperbola Q134. A particle executes S.H.M. along a straight line so that its period is 12 sec. The time it takes in traversing a distance equal to half its amplitude from its extreme position is : (a) (c) 6 sec 2 sec (b) (d) 4 sec 1 sec Q135. A particle of mass 10 grams is executing simple harmonic motion with an amplitude of 0·5 m and periodic time of (π / 5) seconds. The maximum value of the force acting on the particle is : (a) (c) 25 N 2·5 N (b) (d) 5N 0·5 N Q136. The composition of two simple harmonic motions of equal periods at right angle to each other and with a phase difference of π results in the displacement of the particle along : (a) (c) circle straight line (b) (d) figure of eight ellipse Q137. The work done by the string of a simple pendulum during one complete oscillation is equal to : (a) (c) total energy of the pendulum potential energy of the pendulum (b) (d) kinetic energy of the pendulum zero Q138. When a mass is attached to a spring, its length is increased by 20cm. It is now further lowered and released. The time period is : (a) (c) 2 π /7 sec 2 π sec (b) (d) 7 sec enough data not available Q139. A hollow sphere is filled with water through a small hole in it. It is hung by a long thread and made to oscillate. As the water slowly flows out of the hole at the bottom, the period of oscillation will : (a) (c) first increase and then decrease continuously increase (b) (d) first decrease and then increase continuously decrease Q140. In a spring block system length of the spring is reduced by 2%, the time period will : (a) (c) increase by 2% decrease by 2% (b) (d) increase by 1% decrease by 1 % Q141. When a sound wave goes from one medium to another, the quantity that remains unchanged is : (a) (c) frequency wavelength (b) (d) amplitude speed Q142. The wavelength of infrasonics in air is of the order of : (a) (c) 100 m 10¯1 m (b) (d) 101 m 10¯2 m Q143. A bomb explosion on the moon. How long will it take for the sound to reach the earth? (a) (c) 1000 sec 10 sec` (b) (d) 1 day None of these Q144. Two wires made up of same material are of equal lengths but their radii are in the ratio 1 : 2. On stretching each of these two strings by the same tension, the ratio between the fundamental frequencies is : (a) (c) 1:2 1:4 (b) (d) 2:1 4:1 Q145. In two similar wires of tensions 16 N and T, 3 beats are heard: then T = (a) (c) 49 N 64 N (b) (d) 25 N None of these Q146. A fork of frequency 256 hz resonates with a closed organ pipe of length 25.4 cm. If the length of pipe be increased by 2 mm, the number of heats/sec. will be : (a) (c) 4 2 (b) (d) 1 3 Q147. A whistle giving out 450 Hz approaches a stationary observer at a speed of 33 m / s. The frequency heard by the observer in Hz is [velocity of sound in air = 333 ms¯1 ] : (a) 409 (b) 429 (c) 517 (d) 500 Q148. Two uniform strings A and B made of steel are made to vibrate under the same tension. If the first overtone of A is equal to the second overtone of B and if the radius of A is twice that of B, the ratio of the length of the strings is : (a) (c) 2:1 3:2 (b) (d) 3:4 1:3 Q149. A closed organ pipe and an open organ pipe of same length produce 2 beats/sec when they are out into vibrations together in fundamental mode. The length of open pipe is now halved and that of closed pipe is doubled. The number of beats produced will be : (a) (c) 7 8 (b) (d) 4 2 Q150. A jet plane is flying at a speed more than that of sound wave. If the sound of the jet appears to be vertically downwards, the edge of sight of aeroplane with the vertical can be : (a) (c) 300 400 (b) (d) 150 600 Q151. Light year is : (a) (b) (c) (d) Light emitted by the sun in one year. Time taken by light to travel from sun to earth The distance travelled by light in free space in one year Time taken by earth to go once around the sun. Q152. If T denotes the surface tension and R, the radius of a capillary tube, then the dimensions of T/R are the same as that of : (a) (c) pressure force (b) (d) energy none of these Q153. The dimensional formula for force per unit linear density of wire is same as that for : (a) (c) velocity specific heat (b) (d) acceleration latent heat Q154. Two soap cakes A and B are such that dimensions of B are 50% more than each dimension of A. Soap content of B as compared to that of A is : (a) (c) 1.5 3.0 (b) (d) 2.25 3.375 Q155. Which of the following numerical value have three significant figures ? (a) (c) 3.033 30.30 (b) (d) 0.030 0.300 Q156. The correct order in which the dimensions of time decreases in the following physical quantities is 1 Stefan’s constant 2 Coefficient of volume expansion 3 Work done 4 Velocity gradient (a) (c) 2, 4, 3, 1 4, 3, 2, 1 (b) (d) 1, 2, 3, 4 1, 2, 4, 3 Q157. A motor boat covers the distance between the two localities on a river in 6 hours downstream and 8 hours upstream. The speed of the boat is how many times that of the river ? (a) (c) 5 times 7 times (b) (d) 8 times 6 times Q158. A garden roller of 100 kg weight is pulled with a force of 200 N acting at an angle of 45 0 with ground. What is the effective pulling weight of roller ? (a) (c) 100 kg f 838.6 N (b) (d) 300 N 1221.4 N Q159. A force is inclined at 600 to the horizontal. If its rectangular component in the horizontal direction is 50 N, then magnitude of the force in the vertical direction is : (a) (c) 25 N 87 N (b) (d) 75 N 100 N Q160. A boy is hanging from a horizontal branch of a tree. The tension in the arms will be maximum when the angle between the arms is : (a) (c) 00 900 (b) (d) 600 1200 Q161. Two persons are holding a rope of negligible weight tightly at its ends, so that it is horizontal. A 15 kg weight is attached to the rope at the mid point, which is now no longer horizontal. The minimum tension required to completely straighten the rope is : (a) (c) 15 kg 30 kg (b) (d) 75 kg infinitely large Q162. A pendulum is suspended from the roof of a car. The car is moving with acceleration 49 cm / s2 . By what angle to the vertical will its string be inclined? (a) (c) 30 nearly 100 nearly (b) (d) 00 400 nearly Q163. A body released from the top of a tower falls through half the height of the tower in 3 seconds. It will reach the ground after nearly (a) (c) 3.5 sec 4.71 sec (b) (d) 4.24 sec 6 sec Q164. A man throws balls into the air one after the other, throwing one when other is at the highest point. How high the balls rise if he throws twice a second: (a) (c) 2.45 m 19.6 m (b) (d) 1.25 m 4.9 m Q165. A body moving with uniform acceleration describes 12 metre in the third second of the motion and 20 metre in the fifth second. Find the velocity after 10th sec (a) (c) 40 m/s 52 m/s (b) (d) 42 m/s 4 m/s Q166. Acceleration due to gravity on moon is 1.6 m/sec2. An inflated balloon is released on moon. It will : (a) move down with acceleration 1.6 m/s2 (b) move up with acceleration 1.6 m/s2 (c) move up with acceleration 9.8 m/s2 (d) move down with acceleration 9.8 m/s2 Q167. A particle moving with a uniform acceleration travels 24 m and 64 m in the first two consecutive intervals of 4 sec each. Its initial velocity is : (a) (c) 1 m/sec 5 m/sec (b) (d) 10 m/sec 2 m/sec Q168. Two particles A and B get 4m closer each second while travelling in opposite direction. They get 0.4m closer every second while travelling in same direction. The speeds of A and B are respectively: (a) (b) (c) (d) 2.2 m/sec and 0.4 m/sec 2.2 m/sec and 1.8 m/sec 4 m/sec and 0.4 m/sec none of these Q169. Wind is blowing west to east along two parallel tracks. Two trains moving with same speed in opposite directions have the stream track of one double than other. The speed of each train is : (a) (b) (c) (d) equal to that of wind double that of wind three times that of wind half that of wind Q170. A 120 m long train is moving in a direction with speed 20 m/s. A train B moving with 30 m/s in the opposite direction and 130 m long crosses the first train in a time : (a) (c) 6s 38 s (b) (d) 36 s none of these Q171. A body is projected horizontally with speed 20 m/s from top of a tower. What will be its speed nearly after 5 sec ? Take g = 10 m / s2 (a) (c) 54 m/s 50 m/s (b) (d) 20 m/s 70 m/s Q172. An aeroplane in a level flight at 144 km/h is at an altitude of 1000 m. How far from a given target should a body be released to hit the target? (a) (c) 571.43 m 371.43 m (b) (d) 671.43 m 471.43 m Q173. In a projectile motion, the velocity : (a) (b) (c) (d) is never perpendicular to the acceleration is always perpendicular to the acceleration is perpendicular to acceleration at one instant only is perpendicular to acceleration at two instants Q174. The maximum height attained by a projectile is found to be equal to 0.433 of horizontal range. The angle of projection of this projectile is : (a) (c) 300 600 (b) (d) 450 750 Q175. The range of projectile fired at an angle of 150 is 50m. If it is fired with the same speed at an angle of 600, its range will be : (a) (c) 35 m 87 m (b) (d) 65 m 100 m Q176. Ratio of minimum kinetic energies of two projectiles of same mass is 4 : 1. The ratio of the maximum height attained by them is also 4 : 1. The ratio of their ranges would be : (a) (c) 2:1 8:1 (b) (d) 4:1 16 : 1 Q177. A kite of mass m is skillfully held stationary in the sky. The net force on the kite is : (a) (c) zero ¯mg (b) (d) mg none of the above Q178. An impulse is applied to a moving object at an angle of 1200 with respect to the velocity vector. The angle between impulse vector and change in momentum vector is : (a) (c) 00 1200 (b) (d) 600 900 Q179. The average force necessary to stop a hammer with 25N-s momentum in 0.05 s is : (a) (c) 500 N 50 N (b) (d) 125 N 25 N Q180. A stretching force of 10 N is applied at one end of a spring balance and an equal stretching force is applied at the other end at the same time. What will be the reading of the balance? (a) (c) 5N 20 N (b) (d) 10 N 0 Q181. A bullet of mass 10 g is fired from a gun of mass 1 kg with recoil velocity of gun = 5 m/s. The muzzle velocity will be : (a) (c) 30 km/min 30 m/s (b) (d) 60 km/min 500 m/s Q182. In a tug of war, two opposite teams are pulling the rope with an equal and opposite force of 10 KN at each end of the rope, so that condition of equilibrium exists. What is the tension in the rope? (a) (c) Zero 10 KN (b) (d) 5 KN 20 KN Q183. Sand falls on to a conveyor belt at a constant rate of 2 kg/s. If the belt is moving at 0.1 m/s, then the extra force required to maintain speed of the belt is : (a) (c) 2N 0.2 N (b) (d) 20 N 10 N Q184. In a rocket, fuel burns at the rate if 1 kg/s. This fuel is ejected from the rocket with a velocity of 60 km/s. It exerts a force on the rocket equal to : (a) (c) 60 N 6000 N (b) (d) 600 N 60000 N Q185. A body is under the action of two equal and opposite forces, each of 3 N. The body is displaced by 2 m. The work done is : (a) (c) +6J 0 (b) (d) -6J none of the above Q186. A box is dragged across a floor by a rope which makes an angle of 450 with the horizontal. The tension in the rope is 100 N while the box is dragged 10 m. The work done is : (a) (c) 607.1 J 1414.2 J (b) (d) 707.1 J 900 J Q187. The P.E. and KE of a helicopter flying horizontally at a height 400 m are in the ratio 5 : 2. The velocity of helicopter is : (a) (c) 28 m/s 56 m/s (b) (d) 14 m/s 30 m/s Q188. A coconut of mass 1.0 kg falls to earth from a height of 10 m. The kinetic energy of the coconut, when it is 4 m above the ground is : (a) (c) 0.588 joule 5.88 joule (b) (d) 58.8 joule 588 joule Q189. If the linear momentum is increased by 5%, the kinetic energy will increase by : (a) (c) 50% 125% (b) (d) 100% 10% (b) (d) 931 eV 931 MeV Q190. 1 amu of mass is equal to : (a) (c) 1J 931 MeV Q191. The same retarding force is applied to stop a train. The train stops after 80 m. If the speed is doubled, then the distance will be : (a) (c) the same halved (b) (d) doubled four times Q192. A block is moved from rest through a distance of 4 m along a st. line path. The mass of the block is 5 kg and the force acting on it is 20 N. If K.E. acquired by the block be 40 J, at what angle to the path is the force acting? (a) (c) 300 450 (b) (d) 600 00 Q193. A boy blowing a whistle sends out air at one gram per second with a speed of 200 m/s. His lungs power is : (a) (c) 60 W 10 W (b) (d) 20 W 40 W Q194. If the radius of the circular path of particle going around the circle is doubled without changing its frequency of rotation, then centripetal force on it is : (a) (c) unchanged halved (b) (d) doubled quadrupled Q195. The speed of revolution of a particle going around a circle is doubled and its angular speed is halved. What happens to the centripetal acceleration ? (a) (c) Becomes four times Halved (b) (d) Doubled Remains unchanged Q196. A particle is moving along a circular path with a uniform speed. How does its angular velocity change when it completes half of the circular path ? (a) (c) No change decreases (b) (d) increases cannot say Q197. A particle performing uniform circular motion has : (a) (b) (c) (d) a radial velocity and radial acceleration a radial velocity and transverse acceleration transverse velocity and radial acceleration transverse velocity and transverse acceleration Q198. When a body moves with a constant speed along a circle : (a) (b) (c) (d) its velocity remains constant no force acts on it no work is done on it no acceleration is produced in it Q199. An object of mass 5 kg is whirled round in a vertical circle of radius 2 m with a constant speed of 6 m/s. The maximum tension in the string is : (a) (c) 152 N 121 N (b) (d) 139 N 103 N Q200. A body crosses the topmost point of a vertical circle with critical speed. What will be its acceleration when the string is horizontal? (a) (c) g 3g (b) (d) 2g 6g Q201. A body falling vertically downwards under gravity breaks in two parts of unequal masses. The centre of mass of both parts taken together : (a) (b) (c) (d) shifts towards lighter piece shifts towards heavier piece shifts horizontally lies on the same vertical line Q202. The diameter of a flywheel is increased by 1%. Increase in its moment of inertia about the central axis is : (a) (c) 1% 2% (b) (d) 0.5% 4% Q203. The moment of inertia of a cube will be minimum about an axis which : (a) (c) is an edge of the cube joins mid points of opposite faces (b) (d) in a face diagonal is a body diagonal Q204. Of the two eggs which have identical sizes, shapes and weights, one is raw, and other is half boiled. The ratio between the moment of inertia of the raw to the half boiled egg about central axis is : (a) (c) one less than one (b) (d) greater than one not comparable Q205. If a sphere is rolling, the ratio of the translational energy to total kinetic energy is given by : (a) (c) 7 : 10 10 : 7 (b) (d) 2:5 5:7 Q206. An engine developes 100 kW, when rotating at 1800 rpm. Torque required to deliver the power is : (a) (c) 531 N-m 520 N-m (b) (d) 570 N-m 551 N-m Q207. A solid sphere rolls down without slipping on an inclined plane at angle 600 over a distance of 10 m. The acceleration (in m/s2) is : (a) (c) 4 6 (b) (d) 5 7 Q208. A body rolls down an inclined plane. If its K.E. of rotational motion is 40% of its K.E. of translation, then the body is : (a) (c) cylinder solid disc (b) (d) ring solid sphere Q209. If the universal gravitational constant was time dependent, then which of the following quantities would be conserved? (a) (c) potential energy linear momentum (b) (d) kinetic energy angular momentum Q210. The tidal wave in the sea are primarily due to gravitational effect of : (a) (c) earth on the sea earth on the moon (b) (d) sun on the earth moon on the earth Q211. The unit of G/g is : (a) (c) kg/m m2/kg (b) (d) kg/m2 m/kg Q212. If both the masses and radius of the earth, each decrease by 50%, the acceleration due to gravity would : (a) (c) remain same decrease by 100% (b) (d) decrease by 50% increase by 100% Q213. If the radius of the earth were to shrink by 1% its mass remaining same, the acceleration due to gravity on the earth’s surface would : (a) (c) decrease by 2% increase by 2% (b) (d) remain unchanged become zero Q214. At what height in km over the earth’s pole the free fall acceleration decreases by one percent? (Assume the radius of the earth to be 6400 km). (a) (c) 32 80 (b) (d) 64 1·253 Q215. What will be the effect on the weight of a body placed on the surface of earth suddenly starts rotating with half of its angular velocity of rotation: (a) no effect (b) weight will increase (c) weight will decrease (d) weight will become zero Q216. The Radii of the circular orbits of two satellites around the earth are in the ratio 1 : 4 then the ratio of their respective periods of revolution is : (a) (c) 1:4 1:8 (b) (d) 4:1 8:1 Q217. A cube is subjected to a uniform volume compression. If the side of the cube decreases by 1%, the bulk strain is : (a) (c) 0.01 0.03 (b) (d) 0.02 0.06 Q218. Four wires, identical in all respect are subjected to the same longitudinal stress. Their elongation is given in order below. Guess which one has the highest Young’s modulus of elasticity. (a) (c) 0.105 cm 0.168 cm (b) (d) 0.152 cm 0.177 cm Q219. Two wires of the same material and length but diameter in the ratio 1 : 2 are stretched by the same force. The ratio of potential energy per unit volume for the two wires when stretched will be : (a) (c) 1:1 4:1 (b) (d) 2:1 16 : 1 Q220. The substance which shows practically no elastic after effect is : (a) (c) Copper Quartz (b) (d) Rubber All of these Q221. A parrot sitting on the floor of a wire cage which is being carried by a boy, starts flying. The boy will feel that the box is now: (a) (c) (d) heavier shows no change in weight lighter in the beginning and heavier later. (b) lighter Q222. The height of a barometer filled with a liquid of density 3.4 g/cc, under normal condition is approximately : (a) (c) 8m 3m (b) (d) 5m 1m Q223. A boat having a length of 3 metres and breadth 2 metres is floating on a lake. The boat sinks by one cm when a man gets on its. The mass of the man is : (a) (c) 60 kg 72 kg (b) (d) 62 kg 128 kg Q224. A vessel containing water is in equilibrium on a beam balance. When a man puts his finger into the water without touching the bottom or the sides of the vessel, the scale pan on which the vessel stands : : (a) (c) will sink will rise (b) (d) will first rise then sink will neither rise nor sink Q225. A number of small drops of mercury adiabatically coalesce to form a single drop. The temperature of the drop will : (a) (c) increase decrease (b) (d) remain same depend on size Q226. What is the ratio of surface energy of 1 small drop and 1 large drop if 1000 drops combined to form 1 large drop? (a) (c) 100 : 1 10 : 1 (b) (d) 1000 : 1 1 : 100 Q227. Which one of the following would raise the temperature of 20 gram of water at 300C most when mixed with: (a) (c) 20 gram of water at 400C 10 gram of water at 500C (b) (d) 40 gram of water at 350C 4 gram of water at 800C Q228. The amount of mechanical work to be done to completely melt one gram of ice at 00C is: (a) (c) 4·2 joule 42 joule (b) (d) 80 joule 336 joule Q229. Two metal role A and B are having their initial length in the ratio 2 : 3 and the coefficients of linear expansion in the ratio 3 : 4. When they are heated through the same temperature differences, the ratio of their linear expansion is : (a) (c) 3:4 2:3 (b) (d) 1:2 4:3 Q230. In a pressure cooker, cooking is faster because the increase of vapour pressure: (a) (c) increases sp. heat decreases the boiling point (b) (d) decreases sp. heat increases the boiling point Q231. A real gas behaves as an ideal gas : (a) (b) (c) (d) at very low pressure and high temperature high pressure and low temperature high pressure and high temperature low pressure and low temperature Q232. The molar gas constant is the same for all gases because at the same temperature and pressure equal volumes of gases have the same : (a) (c) number of molecules ratio of specific heats (b) (d) average kinetic energy density Q233. How much should be pressure be increased in order to decrease the volume of a gas by 5% at a constant temperature? (a) (c) 5% 10% (b) (d) 5.26% 4.26% Q234. When the temperature of a gas filled in a closed vessel is increased by 10C, its pressure increases by 0.4%. The initial temperature of the gas was : (a) (c) 2500C 250 K (b) (d) 250C 25 K Q235. An electric fan is switched on in a closed room. The air in the room is : (a) cooled (b) heated (c) maintains its temperature (d) heated or cooled depending on the atmospheric pressure. Q236. An ideal gas A and a real gas B have their volumes increased from V to 2 V under isothermal conditions. The increase in internal energy : (a) (c) of A will be more than B will be same in both cases (b) (d) of A will be less than B will be zero in both cases Q237. Air in a cylinder is suddenly compressed by a piston, which is then maintained at the same position. With the passage of time : (a) (b) (c) (d) the pressure increases the pressure may increase or decrease the pressure remain the same the pressure decreases Q238. A Carnot engine has the same efficiency between 800 K to 500 K and x K to 600 K. The value of x is : (a) (c) 100 K 846 K (b) (d) 960 K 754 K (b) (d) 40 K, 20 K 120 K, 100 K Q239. Four engines are working between : (a) 100 K, 80 K (c) 60 K, 40 K which one has maximum efficiency? Q240. The coefficient of performance of a refrigerator working between 100C and 200C is : (a) (c) 28·3 2 (b) (d) 29·3 cannot be calculated Q241. Two pendulums of lengths 121 cm and 100 cm start vibrating. At same instant the two are in the mean position in the same phase. After how many vibrations of the shorter pendulum, the two will be in phase in the mean position: (a) (c) 10 20 (b) (d) 11 21 Q242. A particle executes S.H.M. having time period T. Then the time period with which the potential energy changes is : (a) (c) T T/2 (b) (d) 2T ∞ Q243. When the displacement is half of the amplitude, then wheat fraction of the total energy of a simple harmonic oscillator is kinetic? (a) (c) 2/7th 2/9th (b) (d) 3/4th 5/7th Q244. When a force of 0·1 N is applied, the spring is stretched by 1·5 cm. The spring is cut into three parts and one part is stretched by 3 cm., the force required for doing so is : (a) (c) 0·2 N 0·6 N (b) (d) 0·4 N 0·3 N Q245. If a simple pendulum is taken to a place where g decreases by 2%, then the time period : (a) (c) increases by 0·5% increases by2·0% (b) (d) increases by 1% decreases by 0·5% Q246. In a longitudinal wave, pressure variation and displacement variation are : (a) (c) in phase 450 out of phase (b) (d) 900 out of phase 1800 out of phase (b) (d) Pettiro’s effect Coulomb’s law Q247. Ultrasonic waves are produced by : (a) (c) Piezoelectric effect Doppler’s effect Q248. A tuning fork of frequency 512 hz is used to produce vibrations in a sonometer wire of natural frequency 256 hz. The wire will vibrate in : (a) (c) one segment four segments (b) (d) two segments three segments Q249. The tension in a wire is decreased by 19%. The percentage decrease in frequency will be (a) (c) 19% 0.19% (b) (d) 10% none of these Q250. A source of frequency 10 kHz when vibrated over the mouth of a closed organ pipe is in unison at 300 K. The beats produced/sec, when temperature rises by 1 K is : (a) (c) 30 40 (b) (d) 13·33 16·67 251. If a cube of site 5 cm has a charge of 6 microcoulombs, then the surface charge density is (a) 4x102 µ C/m2 (b) 4x102 C/m2 (c ) 4x103 µ C/m2 (d) 4x103 C/m2 252. A polythene piece, rubbed with wool , is found to have negative charge of 4x10-7 C. The number of elections transferred from wool to polythene is (a) 1.5x1012 (b) 2.5x1012 (c ) 2.5x1013 (d) 3.5x1013 253. Two conducting sphere of radii r1 and r2 are at the same potential. The ratio of their charges is (a) r2/1/ r2/2 (b) r2/2/ r2/1 (b) r1/ r2 (d) r2/ r1 254. Two insulated metal sphers of radii 10 cm and 15 cm charged to a potential of 150 V and 100 V respectively are connected by means of a metallic wire. What is the charge on the first sphere? (a) 2 e.s.u. (b) 4 e.s.u (b) 6 e.s.u. (d) 8 e.s.u. 255. n small drops of same are charged to V volt each. If they coalesce to form a single large drop, then it potential will be (a) Vn (b) Vn-1 ( c) Vn1/3 (d) Vn2/3 256. The electric potential at the surface of an atomic nucleus (Z =50) of radius of 9x10-15 m is (a) 80 V (b) 8X106 V ( c) 9 V (d) 9x105 V 257. The S.I. unit of the line integral of electrical field is (a) NC-1 (b) N m2 C1 ( c) JC-1 (d) V m-1 258. The electric potential V is given as a function of distance x (meter) by V =(5x2+10x-4) volt. Value of electric field at x = 1 m is (a) -23V/m (b) 11V/m ( c) 6 V/m (d) -20V/m 259. Two free protons are separated by a distance of 1 Ǻ. If they are released, the kinetic energy of each proton when at infinite separation is (a) 11.5 x 10-19 J (b) 23x10-19 J ( c) 46x10-19 J (d) 5.6x10-12 J 260. A uniform electric field having a magnitude Eo and direction along the positive X-axis exists. If the potential V is zero at X=0, then its value at x = + x will be (a) V (x) = + x E0 (b) V (x) = - x E0 2 ( c) V (x) = + x E0 (d) V (x) = - x2 E0 261. A ball of mass 1g carrying charge 10-8 C moves from a point A at potential 600 V to a point B at zero potential. The change in its K.E. is (a) -6x10-6 erg (b) -6x10-6 J ( c) 6x10-6 J (d) 6x10-6 erg. 262. Potential energy of two equal negative point charges 2 µ C each held 1 m apart in air is (a) 2 J (b) 2 eV ( c) 4 J (d) 0.036 J. 263. A sphere of radius 1 m encloses a charge of 5 µ C. Another charge of -5 µ C is placed inside the sphere. The net electric flux would be (a) double (b) four times ( c) zero (d) none of the above 264. The S.I. unit of surface integral of electric field is (a) V –m (b) V -1 ( c) NC m (d) Cm-3 265. There is an air-filled 1 pF parallel plate capacitor. When the plate separation is doubled and the space is filled with wax, the capacitance increase to 2pF. The dielectric constant of wax is (a) 2 (b) 8 ( c) 4 (d) 6 266. A capacitor is charged to store an energy U. The charging battery is disconnected. An identical capacitor is now connected to the first capacitor in parallel. The energy in each of the capacitor isφ (a) 3 U/2 (b) U ( c) U/4 (d) U/2 267. A parallel plate air capacitor has a capacitance 18 µF. If the distance between the plates is trebled and a dielectric medium is introduced the capacitance becomes 72 µF. The dielectric constant of the medium is ( a) 4 (b) 9 (c) 12 (d) 2 268. Two metal plates being 3 cm apart from each other, are at a p.d. of 900 volt. A charged particle of mass 1.96 X10-15 kg is kept in equilibrium between the plates, than the electric field is (a) 2700 Vm-1 (b) 30000 V m-1 ( c) 300 V m-1 (d) 3 V m-1 269. A capacitor connected to a 10 V battery collects a charge of 40 µ C with air as dielectric and 100 µ C with a given oil as dielectric. The dielectric constant of the oil is (b) 1.5 (b) 2.0 ( c) 2.5 (d) 3.0 270. A parallel plate capacitor is charged and then isolated. What is the effect of increasing the plate separation on charge, potential, capacitance, respectively? (a) constant, decreases, decreases (b) Increases, decreases, decreases (c) constant, decreases, increases (d) constant, increases, decreases 271. The capacitance of a spherical condenser is 1 µF. If the spacing between two spheres is 1mm, the radius of the outer sphere is (a) 3 m (b) 7 m ( c) 8 m (d) 9 m 272. If a slab of insulating material 4x10-5 m thick is introduced between the plates of a parallel plate capacitor, the distance between the plates has to be increased by 3.5 x 10-5 m to restore the capacity to original value. Then the dielectric constant of the material of slab is (b) 8 (b) 6 ( c) 12 (d) 10 273. A parallel plate capacitor is made by stocking n equally spaced plates connected alternately. if the capacitance between any two plates is x, then the total capacitance is (a) nx (b) n/x 2 ( c) n x (d) (n-1)x 274. Three capacitors each of capacitance 1 µ F are connected in parallel. To this combination, a forth capacitor of capacitance 1 µ F is connected in series. The resultant capacitance of the system is (a) 4µF (b) (4/3) µ F (c ) 2µF (d) (3/4) µ F 275. Two capacitors of equal capacities when connected in series have some resultant capacity. Then they are connected in parallel. Their resultant capacity is (a) same as previous value (b) two times of previous value (c) three times of previous value (d) four times of previous value 276. Two capacitors of 3 µ F and 6 µ F are connected in series across a potential difference of 120 V. Then the potential difference across 3 µ F capacitor is (a) 50 V (b) 60 V (c ) 70 V (d) 80 V 277. How many capacitors each of 8 µ F and 250 V are required to form a composite capacitor of 16 µ F & 1 kV? (b) 16 (b) 64 (c ) 8 (d) 32 278. Two capacitors of 2 µ F and 4 µ F are connected in parallel. A third capacitor of 6 µ F is connected in series. The combination is connected across a 12 V battery. The voltage across 2 µ F capacitor is (a) 2 V (b) 8 V (c ) 6 V (d) 1 V 279. A 10 µ F capacitor is charged to 500 V and then its plates are joined together through a resistance of 10 ohm. The heat produced in the resistance is (a) 500 J (b) 125 J (b) 250 J (d) 1.25 J 280. 1000 similar electrified rain drops merge together into one drop so that their total charge remains unchanged. How is the Electric energy affected? (a) 100 times (b) 102 times (c ) 200 times (d) 400 times 281. The plates of a parallel plate capacitor have an area of 100 cm2 each and are separated by 2.5 mm. The capacitor is charged to 200 V. Calculate the energy stored in the capacitor (a) 70.8 x 10-11 J (b) 70x10-7 J (c ) 7.02 x 10-7 J (d) 7.08 x 10-7 J 282. A 2 µ F capacitor is charged to 100 V and then its plates are connected by a wire. How much heat will be produced? (a) IJ (b) 0.1 J (c ) 0.01 J (d) 0.001 J 283. Two spherical conductors each of capacity C are charged to potential V and –V. These are then connected by means of a fine wire. The loss of energy is (a) Zero (b) ½ CV2 (c ) CV2 (d) 2 CV2 284. The electric potential at a point (x,y) in the xy-plane is given by V= - K xy The electric field intensity at a distance r from the origin varies as (a) r2 (b) r (c ) 2r (d) 2r2 285. A parallel plate capacitor is connected to a battery. The plates are pulled apart with a uniform speed V. If X is the separation between the plates, then the time rate of change of the electrostatic energy of the condenser is proportional to (a) x2 (b) x 2 (c ) 1/x (d) 1/x 286. A small electric dipole is placed at origin with its dipole moment directed along positive x-axis. The direction of electric field at point (2, 2√2,0) is (a) along negative z-axis (b) along z-axis (c) along negative y-axis (d) along positive y-axis 287. A capacitor is connected to a battery. The force of attraction between the plates when the separation between them is halved (a) becomes four times (b) becomes two times (c) becomes eight times (d) remains the same. 288. A charged particle of mass m and charge q is released from rest in an electric field of constant magnitude E. The kinetic energy of the particle after a time t is (a) 2 E2 t2/ m q (b) E q2 m/2 t2 (c ) E2 q2 t2/2 m (d) E q m/2 t. 289. A 4 µ F capacitor is charged by a 200 v supply. It is then disconnected from the supply and is connected to another uncharged 2 µ F capacitor. The energy lost in the process is (a) 3 x 10-2 J (b) 3x102 J ( c) 2.67x10-2 J (d) 2.8x102 J. 290. A free α particle and a free proton, which are separated by a distance of 1010 m are released. The K.E. of α particle when at infinite separation is (a) 46 x 10-19 J (b) 23 x 10-19 J (c ) 36.8 x 10-19 J (d) 9.2 x 10-19 J. 291. When there is an electric current through a conducting wire along its length, then an electric field must exist (a) Outside the wire but parallel to it (b) Outside the wire but perpendicular to it (c) Inside the wire but parallel to it (d) Inside the wire but perpendicular to it 292. Which of the following characteristics of electron determines the current in a conductor? (a) Thermal velocity alone (b) Drift velocity alone (c) Both thermal velocity and drift velocity (d) None of the above 293. A potential difference V is applied to a copper wire of length L and thickness d. If V is doubled the drift velocity (a) is doubled (b) is halved (c ) remains same (d) becomes zero 294. When a motor car is started its light becomes slightly dim because of (a) Induced current in the coil (b) Large potential drop due to internal resistance of cell (c) Starter draws high current (d) Battery e.m.f. fails. 295. A capacitor of 10 µ F has a pot. diff. of 40 volts across it. If it is discharged in 0.2 second, the average current during discharge is (a) 2 m A (b) 4mA ( c) 1 m A (d) 0.5 m A 296. A charge of 2 x 10-2 C moves at 30 revolutions per second in a circle of diameter 80 cm. The current linked with the circuit is (a) 0.02 A (b) 20 A (c ) 0.60 A (d) 60 A 297. Current flows through a metallic conductor whose area of cross section increases in the direction of the current. If we move in this direction, (a) the carrier density will change (b) the current will change (c) the drift velocity will decrease (d) the drift velocity will increase 298. The amount of charge Q passed in time t through a cross section of a wire is Q=5 t 2+3 t +1. The value of current at time t = 5 s is (a) 9A (c ) 53 A 299. (b) (d) 49 A none of the above The length of a conductor is doubled. Its conductance will be (a) Unchanged (b) halved (c ) doubled (d) quadrupled 300. A pot diff. of 20 V is applied across a conductance of 8S. The current in the conductor is (a) 2.5 A (b) 28 A (c) 160 A (d) None of the above. 301. If an increase in length of copper wire is 0.5% due to stretching, the percentage increase in its resistance will be (a) 0.1% (b) 0.2% (c ) 1% (d) 2% 302. 1 kg piece of copper is drawn into a wire 1 mm thick and another piece into a wire 2 mm thick. Compare the resistance of these wires (a) 2:1 (b) 4:1 (c ) 8:1 (d) 16:1 303. A resistor of 20 cm length and resistance 5 ohm is stretched to a uniform wire of 40 cm length. The resistance now is (a) 10 ohm (b) 5 ohm (c ) 20 ohm (d) 200 ohm 304. Conductivity of a conductor depends upon (a) length (b) area of cross section (c ) volume (d) temperature 305. The temperature coefficient of resistance for a wire is 0.00125ºC -1. At 300 K its resistance is 1 ohm. The temperature at which the resistance becomes 1.5 ohm is (a) 450 K (b) 727 K (b) 454 K (d) 900 K 306. The equivalent resistance of network of three 2 Ω resistors can not be (a) 0.67 Ω (b) 2Ω (b) 3Ω (d) 6Ω 307. The least number of cells each of e.m.f. 2.1 volt and internal resistance 0.525 ohm to produce a current of 6 ampere in an external resistance 0.7 ohm will be (a) 3 (b) 6 (b) 8 (d) 12 308. The length of a potentiometer wire is 5 meters. An electron in this wire experience a force of 4.8 x 10-19 newton, e.m.f. of the main cell used in potentiometer is (a) 3 volt (b) 15 volt (b) 1.5 volt (d) 5 volt 309. A cell of e.m.f. E and internal resistance r is connected in series with an external resistance nr. Then the ratio of the terminal potential difference to e.m.f. of cell is (a) (1/n) (b) 1/(n+1) (b) n/(n+1) (d) (n+1)/n 310. The length of a potentiometer wire is ℓ. A cell of emf E is balanced at a length ℓ /5 from the positive end of the wire. If length of the wire is increased by ℓ /2. At what distance will the same cell give a balance point. (a) 2/15 ℓ (b) 3/15 ℓ (b) 3/10 ℓ (d) 4/10 ℓ 311. All the edges with parallel faces are unequal. Its longest edge is thrice its shortage edge. The ratio of the maximum to minimum resistance between parallel faces is (a) 8 (b) 9 (b) 3 (d) none of the above 312. An electric current of 5 A is passing through a circuit containing three wires arranged in parallel. If the length and radius of the wires are in the ratio 2:3:4 and 3:4:5, then the ratio of current passing through wires would be (a) 3:6:10 (b) 4:9:16 (b) 9:16:25 (d) 54:64:75 313. A 100 V voltmeter having an internal resistance of 20 k Ω. When connected in series with a large resistance R across a 110 V line reads 5 V. The magnitude of resistance R is (a) 210 k Ω (b) 310 k Ω (b) 420 k Ω (d) 440 k Ω 314. An electric lamp is marked 60 W, 240 V. If it operates at 200 V, the current through it will be (a) 0.18 A (b) 0.21 A (c ) 0.25 A (d) 0.30 A 315. What will be the wattage of a 50 W, 200 V lamp when used on 160 V power supply? (a) 32 W (b) 64 W (c ) 96 W (d) 128 W 316. The two head lamps of a car are in parallel. They together consume 48 watts with the help of 6 V battery. The resistance of each bulb is (a) 0.67 ohms (b) 3.0 ohms (c ) 4.0 ohms (d) 1.5 ohms 317. If the strength of the current decreases by 4% then the power of the bulb will decrease nearly by (a) 4% (b) 8% (c ) 0.08% (d) 0.04% 318. by If the voltage across a lamp decreases by 5% then the power output decreases (a) 2.5% (c ) 10% (b) (d) 5% 20% 319. A resistor R1 dissipates the power P when connected to a certain generator. If a resistor R2 is put in series with R1, the power dissipated by R1. (a) decreases (b) increases (c ) remains the same (d) any of the above depending upon the relative values of R1 and R2 320. Two heating wires of equal length are first connected in series and then in parallel to a constant voltage sources. The ratio of heat produced in two cases is (a) 1: 4 (b) 4: 1 (c ) 1: 2 (d) 2: 1 321. Two bulls when connected in parallel to a source take 60 W each. The total power consumed when they are connected in series with the same source is (a) 15 W (b) 30 W (c ) 60 W (d) 120 W 322. Two head lamps of a car are in parallel. They together consume 48 W with the help of a 6 V battery. The resistance of each bulb is (a) 3.0 Ω (b) 4.0 Ω (c ) 1.5 Ω (d) 0.75 Ω 323. A heater of 220 V heats a volume of water is 5 minutes time. A heater of 110 V heats the same volume of water in (a) 5 minutes (b) 8 minutes (c ) 10 minutes (d) 20 minutes 324. The e.m.f. of the battery in a thermocouple is doubled. The rate of heat generated at one of the two junctions will (a) remain unchanged (b) become half (c ) be doubled (d) be four times. 325. The temperature of hot junction of a thermocouple changes from 80⁰ C to 100⁰ C, the percentage change in thermoelectric power is (a) 25% (b) 20% (c ) 10% (d) 8% 326. To liberate two litre of hydrogen at 22.4 atmosphere from acidulated water the quantity of electricity that must pass through is (a) 44.8 C (b) 96500 C (c ) 193000 C (d) 386000 C 327. A cell of resistance R is connected between the terminals of a battery. The quantity of heat produced in 5 minutes is H1. Now that coil is cut into three equal parts and are connected between same two terminals in parallel. This time heat produced in 5 minutes is H2. Then the ratio of H1 : H2 is (a) 1: 3 (b) 1: 6 (c ) 1: 9 (d) 3: 1 328. A moving charge will produce (a) no field (b) (c ) a magnetic field (d) an electric field both ‘b’ and `c’ 329. Ratio of magnetic field induction at the centre of a current carrying coil of radius r and at a distance 3 r on its axis is (a) √10 (b) 2 √10 (c ) 10 √10 (d) 20 √10 330. If a current is passed in a spring, it (a) gets compressed (b) gets expended (c) oscillates (d) remains unchanged 331. A uniform electric field and a uniform magnetic field are pointed in the same direction. If an electron is projected in the same direction, the electron (a) velocity will increase in magnitude (b) velocity will decrease in magnitude (c) will turn to its left (d) will turn to its right 332. Imagine that you are seated in a room and there is a uniform magnetic field pointing vertically downwards in its. At the centre of the room, an electron is projected horizontally with a certain speed. Discuss the speed and the path of the electron in this field. (a) electron moves in anticlockwise path (b) electron moves in clockwise path (c) electron moves left wards (d) electron moves right wards. 333. An electron having a charge e moves with a velocity v in X-direction. An electric field acts on it in Y-direction. The force on the electron acts in (a) positive direction Y-axis (b) negative direction of Y-axis (c) positive direction of Z-axis (d) negative direction of Z-axis 334. A cyclotron is accelerating proton, where the applied magnetic field is 2 T, the potential gap is 100 KV, then how much turn the proton has to more between the dees to acquire a kinetic energy 20 MeV (a) 200 (b) 300 (b) 150 (d) 100. 335. The current in wire is directed towards east and the wire is placed in magnetic field directed towards north. The force on the wire is (a) vertically upwards (b) vertically downwards (c ) due south (d) due east. 336. A wire of length ℓ in formed into a circular loop of one turn only and is suspended in a magnetic field B. When a current I is passed through the loop, the torque experienced by it is (a) (1/4 π ) B Iℓ (b) (1/4 π) ℓ 2IB (c ) (1/4π) B2 Iℓ (d) (1/4 π ) BI2 ℓ . 337. Voltmeters V1 and V2 are connected in series across a d.c. line. V1 reads 80 volt and has a per volt resistance of 200 Ω and V2 has a total resistance of 32k Ω. The line voltage is (a) 120 V (b) 180 V (c ) 240 V (d) 300 V 338. An ammeter is obtained by shunting a 30 Ω galvanometer with a 30 Ω resistance. What additional shunt should be connected across it to double the range? (a) 5 Ω (b) 10 Ω (c ) 15 Ω (d) none of the above. 339. A thin bar magnet of length 2L and magnetic moment M is bent at the midpoint so that the angle between them is 60⁰. The new magnetic moment is (a) M (b) M/2 (b) 2 M (d) M √3 340. Can a system have magnetic moment even through its net charge is zero? (a) Yes (b) No (c ) Sometimes yes sometimes no (d ) cannot say. 341. The hysteresis cycle for the matrial of a transformer core is (a) Short and wide (b) Tall and narrow (c) Tall and wide (d) Short and narrow. 342. Metals getting magnetized by orientation of atomic magnetic moments in external magnetic field are called. (a) diamagnetics (b) paramagnetics (c ) ferromagnetics (d) antimagnetics. 343. Reduction factor of a tangent galvnmeter is related to number of turns as proportional to (a) n (b) n2 (c ) n-1/2 (d) n-1 344. The arms of a deflection magnetometer in the tangent B position are placed along (a) the east west direction (b) the north south direction (c) the north east-south west direction (d) the north west-south east direction 345. A vibration magnetometer is placed at South pole, then the time period will be (a) zero (b) infinity (c) same as at magnetic equator (d) same at any other place on earth 346. The unit of magnetic permeability is (a) A m-1 (b) A m-2 (b) H (d) H m-1 347. The period of oscillations of a magnet is 2 sec. When it is magnetized so that the pole strength is 4 times, its period will be (a) 4 sec (b) 1 sec (b) 2 sec (d) 1/2 sec 348. The mass of a specimen of a ferromagnetic material is 0.6 kg and its density is 7.8 x 103 kg/m3. If the area of hystersis loop of alternating magnetising field of frequency 50 Hz is 0.772 MKS units, then the hysteresis loss second will be (a) 277.7 x 10-5 joule (b) 277.7 x 10-6 joule (c) 277.7 x 10-4 joule (d) 277.7 x 10-4 joule 349. The correct measure of magnetic hardness of a material is (a) Remanant magnetism (b) Hystersis loss (c) Coercivity (d) Curie temperature 350. Force between two identical short bar magnets whose centers are r metre apart is 8.1 N, when their axes are along the same line. If separation is increased to 3 r and the axis are rearranged perpendicularly, the force between them would become (a) 2.4 N (b) 1.2 N (b) 0.1 N (d) 0.15 N 351. The magnetic potential at a point distant 10 cm from the middle point of a magnetic dipole on a line inclined at 60⁰ with the axis is 3 CGS units (e.m.u). Then the magnetic moment of the magnet is (a) 300 ab-amp cm2 (b) 30 ab-amp cm2 (b) 600 ab-amp cm2 (d) 60 ab-amp cm2 352. The susceptibility of a paramagnetic material is K at 27 ⁰C. At what temperature will its susceptibility be K/2? (a) 600 ⁰C (b) 287 ⁰C (c ) 54 ⁰C (d) 327 ⁰C 353. A magnet makes 5 oscillations per minute in B = 0.3 x 10 -4 T. By what amount should the field be increased so that number of oscillations is 10 in the same time? (a) 0.3 x 10-4 T (b) 0.6 x 10-4 T (c ) 0.9 x 10-4 T (d) 1.2 x 10-4 T 354. The wing span of an aeroplane is 36 m. If the plane is flying at 400 km/h, the e.m.f. induced between the wings tips is (assume V = 4X10-5 T) (a) 16V (b) 1.6 V (c) 0.16 V (d) 0.016 V. 355. A two meter wire is moving with a velocity of 1 m/s perpendicular to a magnetic field of 0.5 Wh/m2. The e.m.f. enduced in it will be (a) 0.5V (b) 0.1 V (c) 1 V (d) 2 V. 356. One tesla is equal to (a) 107 gauss (c ) 104 gauss (b) 10-4 gauss (d) 10-8 gauss 357. The e.m.f produced in a wire by its motion across a magnetic field does not depend upon (a) The length of the wire (b) The composition of the wire (c) The diameter of the wire (d) The orientation of the wire 358. Which of the following phenomena is utilized in the construction of the mouth piece of a telephone now a days? (a) Thermo electric effect (b) Photo electric effect (c) Change of resistance with pressure (d) Electromagnetic induction. 359. When the rate of change of current is unity, induced e.m.f. is equal to (a) thickness of coil (b) no. of turns in coil (c) co-efficient of self-induction (d) total flux linked with coil. 360. If N is number of turns in a coil, the value of self inductance varies as (a) N (b) N0 (c) N2 (d) N-2 361. A 5 cm long solenoid having 10 ohm resistance and 5 mH inductance is joined to a 10 V battery. At steady state, current through solenoid is (a) 5 A (c) 1 A (b) 2 A (d) Zero 362. The induced e.m.f. of a generator when the flux of poles is doubled and speed is doubled (a) becomes half (b) remains same (c) becomes double (d) becomes 4 times 363. A transformer has an efficiency of 80%. It works at 4kW and 100 V. If secondary voltage is 240 V, the current in primary coil is (a) 0.4 A (b) 4 A (c) 10 A (d) 40 A 364. A magnet is suspended lengthwise from a spring and while it oscillates, the magnet moves in and out of the coil C connected to a galvanometer G, Then as the magnet oscillates. (a) G shows no deflection (b) G shows deflection on one side (c) Deflection of G to the left and right has constant amplitude (d) Deflection of G to the left and right has decreasing amplitude 365. A closed loop lying in the xy carries a current. If a uniform magnetic field B is present in the region, the force acting on the loop will be zero, if B is in (a) the y-direction (b) the z-direction (c) the x-direction (d) any of the above directions 366. The instantaneous current in a circuit is given by I = 2 cos (ωt +φ) ampere. The r.m.s. value of the current is (a) zero (b) √2 A (c ) 2 A (d) 2 √2 A. 367. Alternating voltage V = 400 sin (500 π t) is applied across a resistance of 0.2 k Ω. The r.m.s. value of current will be equal to (a) 14.14 A (b) 1.414 A (c) 0.1414 A (d) 2.0 A 368. An a.c. source is of 120 volt, 60 Hz. The value of the voltage after 1/360 sec. from the start will be (a) 146.4 volt (c) 106.8 volt (b) 42.4 volt (d) 20.2 volt 369. The effective value of an alternating current is 5A. The current passes through 24 Ω resister. The maximum potential difference across the resistor is (a) 10 V (b) 17 V (c) 170 V (d) 1700 V 370. In an A.C. circuit, maximum value of voltage is 423 volt. Its effective voltage is (a) 323 V (b) 340 V (c) 400 V (d) 300 V 371. In the non resonant circuit, what will be the nature of the circuit for frequencies higher than the resonant frequently? (a) Resistive (b) Capacitative (c) Inductive (d) None of the above. 372. The message signal is usually of (a) audio frequency range (b) radio frequency range (c) audio and radio frequency range (d) mixture of both. 373. Current in a circuit is wattles, if (a) current is alternating (a) resistance in circuit is zero (b) inductance in circuit is zero (c) resistance and inductance both are zero 374. If a power of 100 W is being supplied across a potential difference of 200 V, current flowing is (a) 2 A (b) 0.5 A (c) 1 A (d) 20 A 375. In an ac circuit, with voltage V and current I the power dissipated is (a) VI (b) ½ VI (c ) 1/√2 VI (d) depends on the phase angle between V and I. 376. The energy stored in a 50 m H inductor carrying a current of 4A will be (a) 0.4 J (b) 4.0 J (c ) 0.8 J (d) 0.04 J 377. An AC ammeter is used to measure current in a circuit. When a given direct current passes through the circuit. AC ammeter rends 3 ampere. When another alternating current passes through the circuit, the AC ammeter reads 4 ampere. Then the reading of this ammeter if DC and AC flows through the circuit simultaneously is (a) 3 ampere (b) 4 ampere (c ) 7 ampere (d) 5 ampere 378. A current of 2 A is increasing at a rate of 4 A/s through a coil of inductance 2 H. The energy stored in the inductor per unit time is (a) 16 J/s (b) 4 J/s (c) 2 J/s (d) 1 J/s 379. Conduction current flows (a) only through resistance (b) through wires and resistance (c) only through capacitor (d) through wires resistance and capacitance. 380. The conduction current is same as displacement current when source is (a) a. c. only (b) d. c. only (c ) both a. c. and d. c. (d) neither for d. c. nor for a. c. 381. According to Maxwell’s hypothesis, a changing electric field gives rise to (a) an e.m.f. (b) electric current (c ) magnetic field (d) pressure radiant. 382. The electromagnetic waves (a) travel with the speed of sound (b) travel with the same speed in all media (c) travel in free space with the speed of light (d) do not travel through a medium 383. If a free electron is placed in the path of a plane electromagnetic wave, it will start moving along (a) center of earth (b) equator of earth (c ) magnetic field (d) electric field 384. Which of the following electromagnetic waves have the longest wavelength? (a) heat waves (b) light waves (c ) radiowaves (d) microwaves 385. X-rays are produced by jumping of (a) electrons from lower to higher energy orbit of atom (b) electrons from higher to lower energy orbit of atom (c) protons from lower to higher energy orbit of nucleus (d) proton from higher to lower energy orbit of nucleus 386. The atmosphere between the heights of 50 km and 80 km is called (a) mesosphere (b) ozonosphere (c ) Ionosphere (d) troposphere 387. Some scientists have predicted that a global nuclear war on the earth would be followed by a severe (a) rain (b) winter (c ) summer (d) radiations hilly rays 388. Long distance radio broadcasts use short wave bands became (a) they have short wavelength (b) they scatter less (c) they are reflected by ionosphere (d) they have more energy to propagate. 389. The magnetic field between the plates of radius 12 cm separated by distance of 4 mm of a parallel plate capacitor of capacitance 100 pF along the axis of plates having conduction current of 0.15 A is (a) zero (b) 1.5 T (c ) 15 T (d) 0.15 T 390. Electric fields induced by changing magnetic fields are (a) conservative (b) non-conservative (c ) may be conservative or non-conservative depending on the conditions (d)nothing can be said 391. Out of the following of which colour, sensitivity of human eye is the highest? (b) green (b) red (c ) violet (d) white 392. Light appears to travel in straight lines since (a) It is not absorbed by the atmosphere (b) It is reflected by the atmosphere (c) Its wavelength is very small (d) Its velocity is very large. 393. The device which produces highly coherent sources is (a) Fresnel biprism (b) Young’s double slit (c ) Laser (d) Lloyd’s mirror 394. A calcite crystal is placed over a dot on a piece of paper and rotated. On viewing through calcite, one will see (a) A single dot (b) two stationery dots (c ) two rotating dots (d) one dot rotating about the other 395. When light is incident at polarising angel, which is completely polarised? (a) reflected light (b) refracted light (c ) both (d) neither 396. Two Nicols are oriented with their principal planes making an angle of 60⁰. Then the percentage of incident unpolarised light which passes through the system is (a) 100 (b) 50 (c )12.5 (d) 37.5 397. When a source of light is receding away from an observer, then the spectral lines will get displaced towards (a) violet region (b) red region (c ) ultraviolet region (d) blue region 398. When the light source is moving towards an observer, (a) wavelength of light decreases (b) wavelength of light increases (c) wavelength of light remains unchanged (d) velocity of light increase 399. In the context of Doppler effect in light, the term red shift signifies (a) decrease in frequency (b) increase in frequency (c) decrease in intensity (d) increase in intensity 400. If a source of light is moving away from a stationery observer, then frequency of light wave appears to change because of (a) Doppler’s effect (b) Interference (c) Diffraction (d) None of the above. 401. The ratio of intensity at the centre of a bright fringe to the intensity at a point distant one fourth of the distance between two successive bright fringes will be (a) 4 (b) 3 (c ) 2 (d) 1. 402. The path difference between two interfering waves at a point on the screen is λ/8. The ratio of intensity at this point and that at the central fringe will be (a) 0.853 (b) 8.53 (c ) 85.3 (d) 853. 403. White light is incident on a soap film of thickness 5x 10 -5 cm and refractive index 1.33. Which wavelength is reflected max. in the visible region? (a) 26000 Å (b) 8866 Å (c ) 5320 Å (d) 3800 Å 404. Yellow light is used in a single slit diffraction experiment with a silt of width 0.6 mm. If yellow light is replaced by X-rays, then the observed pattern will reveal (a) more number of fringes (b) less number of fringes (c) no diffraction pattern (d) that the central maximum is narrower 405. The luminous intensity of 100 W unidirectional bulb is 100 candela. The total luminous flux emitted from bulb will be (a) 100 π lumen (b) 200 π lumen (c ) 300 π lumen (d) 400 π lumen 406. A point source of 100 candela is held 5 m above a sheet of blotting paper which reflects 75% of light incident upon it. The illuminance of blotting paper is (a) 4 phot (b) 4 lux (b) 3 phot (d) 3 lux 407. A lamp is hanging at a height of 40 cm from the centre of a table. If its height is increased by 10 cm the illuminance on the table will decrease by (a) 10% (b) 20% (c ) 27% (d) 36% 408. It is desired to photograph the image of an object placed at a distance of 3 m from plane mirror. The camera, which is at a distance of 4.5 m from mirror should be focused for a distance of (a) 3 m (b) 4.5 m (c ) 6 m (d) 7.5 m. 409. A lens of power +2 diopter is placed in contact with a lens of power -1 diopter. The combination will behave like (a) a convergent lens of focal length 50 cm (b) a divvergent lens of focal length 100 cm (c) a convergent lens of focal length 100 cm (d) a convergent lens of focal length 200 cm 410. Fraunhofer spectrum is a (a) line absorption spectrum (b) band absorption spectrum (c) line emission spectrum (d) band emission spectrum. 411. A ray of light is incident at an angle of 60⁰ on one face of a prism of angle 30⁰. The emergent ray of light makes angle of 30⁰ with incident ray of light makes an angle of 30⁰ with incident ray. The angle made by emergent ray with second face of prism will be (a) 0⁰ (b) 90⁰ (c ) 45⁰ (d) 30⁰ . 412. In above question, the angle of refraction (r2 ) at the other face of prism will be (b) 0⁰ (b) 90⁰ (c ) 45⁰ (d) 30⁰ . 413. In the propagation of light waves, the angle between the plane of vibration & plane of polarization is (a) 0⁰ (b) 45⁰ (c ) 90⁰ (d) 180⁰ . 414. When the length of a microscope tube increases, its magnifying power (a) decreases (b) increases (c ) does not change (d) may increase or decrease depending on the observer and the place of observation. 415. An observer looks at a tree of height 15 meters with a telescope of magnifying power 10. To him, the tree appears (a) 10 times taller (b) 15 times taller (c ) 10 times nearer (d) 15 times nearer. 416. The focal length of objective and eye piece of a microscope are 1cm and 5 cm respectively. If the magnifying power for relaxed eye is 45, then length of the tube is (a) 9 cm (b) 15 cm (c ) 12 cm (d) 6 cm. 417. A concave mirror has a focal length 20 cm. The distance between the two positions of the object for which the image size is double of the object size is (a) 30 cm (b) 20 cm (c ) 60 cm (d) 40 cm. 418. The refractive index of a prism is 2. This prism can have a maximum refracting angle of (a) 45⁰ (b) 30⁰ (c) 90⁰ (d) 60⁰ 419. An object is kept at a distance of 16 cm from a thin lens and the image formed is real. If the object is kept at a distance of 6 cm from the same lens, the image formed is virtual. If the sizes of the images formed are equal, the focal length of the lens will be (a) 21 cm (b) 11 cm (c ) 15 cm (d) 17 cm. 420. A microscope has an objective of focal length 1.5 cm and eye piece of 2.5 cm. If the distance between objective and eye piece is 25 cm, what is the approximate value of magnification produced for relaxed eye (a) 140 (b) 75 (c ) 110 (d) 25 421. Cathode rays are made to pass between the poles of a magnet perpendicular to axis, the effect of the magnetic field is: (a) to increase the velocity of rays (b) to deflect them towards the north pole (c) to deflect them towards the south pole (d) to deflect them upwards above the plane of paper. 422. The ratio of specific charge of ionic deuterium to that of proton will be (a) 4: 1 (b) 2: 1 (c ) 1: 4 (d) 1: 2. 423. The specific charge for positive rays is much less than that for cathode rays. This is because (a) masses of positive rays much larger (b) charge on positive ray is less (c ) positive rays are positively charged (d)experimental method is wrong. 424. Planck’s constant has the dimensions of (a) Energy (b) Mass (c ) Frequency (d) Angular momentum. 425. A metal surface is illuminated by the photons of energy 5 eV and 2.5eV respectively. The ratio of their wavelength is (a) 1: 3 (b) 1: 4 (c ) 2: 1 (d) 1: 2. 426. The number of photons required to give a definite energy varies (a) inversely as the wavelength (b) inversely as the frequency (c) directly as the frequency (d) independent of the frequency. 427. Photo electric effect shows (a) wave like behavior of light (b) particle like behavior of light (c) both wave like and particle like behavior of light (d) neither wave nor particle like behavior of light 428. The best metal to be used for photoemission is (a) Potassium (b) Sodium (c ) Cesium (d) Lithium. 429. The maximum energy of photoelectrons emitted in photocell is 2eV. For no photoelectrons to reach the anode, the stopping potential should be (a) 2 V (b) -2 V (c ) 4 V (d) -4 V. 430. If E and p are the energy and the momentum of a photon respectively then on increasing the wavelength of photon (a) p and E both will decrease (b) p and E both will increase (c) p will increase and E will decrease (d) p will decrease and E will increase. 431. Dual nature of radiation is shown by (a) diffraction and reflection (b) refraction and diffraction (c) Photoelectric effect alone (d) Photoelectric effect and diffraction. 432. If the uncertainty in the position of proton is 6X10 -8 m, then the minimum uncertainty in its speed will be (a) 1 cm/s (c ) 1 mm/ s (b) 1 m/s (d) 100 mm/s. 433. The wavelength of characteristic X-rays depends upon (a) temperature of target (b) size of target (c) atomic number of target (d) mass of target. 434. The frequency of the Kα line of the characteristic X-ray spectrum is proportional to (Z = atomic number) (a) Z1/2 (b) Z (c) Z3/2 (d) Z2 435. A hydrogen atom in the ground state absorbs a photon of ultraviolet radiation of wave length 50nm. Assuming that the entire photon energy is taken by electron, with what kinetic energy will be the electron be ejected? (a) 3.4 eV (b) 10.2 eV (c ) 11.24 eV (d) 13.6 eV. 436. The filament current in the electron gun of a coolidge tube is increased while the potential difference used to accelerate the electrons is decreased. As a result, in the emitted radiation (a) the intensity increases while the minimum wavelength decreases (b) the intensity decreases while the minimum wavelength increases (c) the intensity as well as the minimum wavelength increases (d) the intensity as well as the minimum wavelength decreases 437. If the velocity of the particle is increased three times, then the percentage decreases in its de-Broglie wavelength will be (a) 33.3% (b) 66.6% (c) 99.9% (d) 133.2% 438. The mean free path of the electron in a discharge tube is 15cm. The length of the tube is 10 cm only. Then the length of the Crooke’s dark space is (a) 15 cm (b) 10 cm (c ) 5 cm (d) 25 cm. 439. To explain his theory , Bhor used (a) conservation of linear momentum (b) conservation of angular momentum (c) conservation of quantum frequency (d) conservation of energy 440. Isotopes are atoms having (a) same number of protons , but different number of neutrons (b) same number of neutrons but different numbers of protons (c) same number of protons and neutrons (d) all of the above. 441. A heavy nucleus at rest breaks into two fragments which fly off with velocities 8:1. The ratio of radii of the fragments is (a) 1: 2 (b) 1: 4 (c ) 4: 1 (d) 2: 1. 442. The nuclear radius is of the order of (a) 10 -10 m (b) 10 -6 m (c ) 10 -15 m (d) 10 -14 m 443. Radioactivity is (a) Irreversible process (b) Self disintegration process (c) Spontaneous (d) all of the above 444. Plutonium decays with half life of 24000 years. If plutonium is stored for 72000 years, the fraction of it that remains is (a) 1/8 (b) 1/3 (c ) 1/4 (d) 1/2. 445. Control rods used in nuclear reactor are made of (a) stainless steel (b) graphite (c) cadmium (d) plutonium. 446.Nuclear energy is released in fission since binding energy per nucleon is (a) sometimes larger and sometimes smaller (b) larger for fission fragments than for parent nucleus (c) same for fission fragments and nucleus (d) smaller for fission fragments than for parent nucleus. 447.The functions of graphite and the control rods in a nuclear reactor are (a) to produce neutrons and to shield the reactor respectively (b) to slow down the neutrons and to absorb the excess neutron reactor respectively (c) to absorb the excess neutrons and to shield the reactor respectively (d) to absorb neutrons and to reduce the energy of the neutrons respectively . 448. During a nuclear fission reaction (a) A heavy nucleus breaks into two fragments by itself (b) A light nucleus bombarded by thermal neutrons breaks up (c) A heavy nucleus bombarded by thermal neutrons breaks up (d) two light nuclei combine to give a heavier nucleus and possibly other products. 449.The ratio of molecular mass of two radioactive substances is 3/2 and the ratio of their decay constants is 4/3. Then, the ratio of their initial activity per mole will be (a) 2 (b) 4/3 (c ) 8/9 (d) 9/8. 450.When an electron in hydrogen atom in ground state absorbs a photom of energy 12.1 eV, its angular momentum (a) decreases by 2.11 x 10-34 Js (b) increases by 1.055 x 10-34 Js (c) decreases by 1.055 x 10-34 Js (d) increases by 2.11 x 10-34 Js 451.Work function of a metal depends upon (a) Its mass (b) Its valency (c) electron density (d) None of the above 452.Which of the following is a crystalline solid? (a) graphite (b) calcite (c ) gallium (d) oxygen. 453.Diamond is very hard because (a) it is covalent solid (b) it has large cohesive energy (c) high melting point (d) insoluble in all solvents 454. Resistivity of a semiconductor depends on (a) shape of semiconductor (b) atomic nature of semiconductor (c) length of semiconductor (d) shape and atomic nature of semiconductor 455. Change in temperature (a) increase forward resistance (b) increase reverse resistance (c) affects V-I characteristics of p-n junction (d) does not affect V-I character of p-n junction. 456. Efficiency of (a) half wave rectifier is more than full wave rectifier (b) half wave rectifier is almost negligible (c) full wave rectifier is more than half wave rectifier (d) all of the above. 457. Transistor parameter (a)never change (b)are not same even for transistors of the same type (c )always change (d)are always same 458. In the binary number system 100 + 1011 is equal to (a) 1000 (b) 1011 (c ) 1110 (d) 1111. 459. Digital circuit can be made by repetitive use of (a) OR gates (b) NOT gates (c ) AND gates (d) NAND gates . 460. The binary number of decimal number (9.25)10 is (b) 1101.01 (b) 1001.01 (c ) 1001.10 (d) 1110.01. 461. The value of form factor of full wave rectifier is (a) π/2 (b) π/ √2 (c ) π/2 √2 (d) π. 462. The value of form factor of half wave rectifier is (a) π/2 (b) π/ √2 (c ) π/2 √2 (d) π. 463. In the binary number system [1101]2 + [1101]2 is equal to (a) [110110] (c ) [100110] (b) [101110] (d) [100101] 464. If the output of a logic gate is 0 when all the inputs are at logic 1, then the gat is either (a) NAND or Ex-NOR (b) NOR or OR (c ) Ex-OR or NOR (d) AND or NOR. 465. Present day communication systems are (a) electrical (b) electronic (c ) optical (d) all of the above. 466. The transmission media can be (a) guided only (b) unguided only (c ) both (a) and (b) (d) neither (a) nor (b). 467. The sky wave propagation is suitable for radiowaves of frequency (a) upto 2 MHz (b) from 2 MHz to 20 MHz (c) from 2 MHz to 30 MHz (d) none of the above. 468. Fading is the variation in the strength of a signal at a receiver due to (a) interference of waves (b) diffraction of waves (c) polarisation of waves (d) none of the above. 469. Point to point communication requires the use of (a) a guided medium only (b) unguided medium only (c ) any medium (d) neither. 470. For a twisted pair, upper limit on repeater spacing is (a) 6 km (b) 60 km (c ) 600 km (d) 6000 km. 471. Co-axial cable can carry (a) digital signals only (c ) both digital and analog signals (b) analog signals only (d) neither digital nor analog. 472. The losses in transmission lines are (a) radiation losses only (b) conductor heating only (c) dielectric heating only (d) all of the three above. 473. Which fibers are less expensive and simple to construct? (a) Single-mode step index fiber (b) Multi-mode step index fiber (c) Multi graded-index fiber (d) All are equally expensive. 474. The population inversion in helium-neon laser is produced by (a) photon excitation (b) electron excitation (c ) inelastic atomic collisions (d) chemical reaction. 475. The velocity factor of a transmission line is x. If dielectric constant of the medium is 2.6, the value of x is (a) 0.26 (b) 0.62 (c ) 2.6 (d) 6.2. 476. The modulation index of an FM signals is 0.25. If modulating frequency is 2kHz, the max. deviation in frequency would be (a) 500 Hz (b) 1000 Hz (c ) 1500 Hz (d) 500 kHz. 477. In amplitude modulation, if modulation index is more than 100%, then (a) the wave gets distorted (b) efficiency increases (c ) power decreases (d) none of the above. 478. A hollow metallic sphere of radius 10 cm is given a charge of 3.2 X 10 -9 C. The electric intensity at a point 4 cm from the centre is (a) 9x10-9 NC-1 (b) 288 NC-1 (c ) 2.88 NC-1 (d) zero. 479. An α-particle and a proton are accelerated through same potential difference from rest. Find the ratio of their final velocity (a) √2: 1 (b) 1: 1 (c ) 1: √2 (d) 1: 2 . 480. Two particles of masses m and 2 m with charges 2q and 2q are placed in a uniform electric field E and allowed to move for the same time. The ratio of their K.E. will be (a) 2: 1 (b) 8: 1 (c ) 4: 1 (d) 1: 4 . 481. Which of the following are true when the cells are connected in series? (a) current capacity decreases (b) current capacity increases (c) the e.m.f. decreases (d) the e.m.f increases 482. Voltmeter has a resistance of 20 k Ω. When it is connected inseries with a resistance R across a 230 V supply, it reads 200V. What is the value of R? (a) 2k Ω (b) 3k Ω (c) 4k Ω (d) 1k Ω 483. The same mass of copper is drawn into two wires 1 mm and 3 mm thick. These two wires are connected in series to the source of current. What is the ratio of heat produced in wires (a) 1: 9 (b) 1: 91 (c ) 9: 1 (d) 81: 1 . 484. The e.m.f of the battery in a thermocouple is doubled. The rate of heat generated at one of the two junctions will (a) Remain unchanged (b) become half (c ) be doubled (d) be four times. 485. A long solenoid is formed by winding 20 turns/cm. The current necessary to produce a magnetic field of 20 milli tesla inside the solenoid will be approximately. (a) 1.0 A (b) 2.0 A (c ) 4.0 A (d) 8.0 A 486. A beam of protons is moving parallel to a beam of electrons. Both the beams will tend to (a) Repel each other (b) come closer (c ) move more apart (d) either ‘b’ or ‘c’. 487. The resultant magnetic moment of neon atom will be (a) Infinity (b) µB (c ) µB /2 (d) zero . 488. Two identical bar magnets are suspended first with their like poles on eachother and then with unlike poles on eachother. If T1 T2 are the respective time periods of vibration in two configurations, then T1 /T2 is (a) Zero (b) >1 (c ) <1 (d) ∞ . 489. Two pure indicators each of self inductance L are connected in parallel. The total inductance is (a) L/2 (b) L (c ) 2 L (d) L/4 . 490. A choke coil is used with an arc lamp (a) to increase the voltage (b) to increase the current (c) to limit the current without much power loss (d) to limit the resistance without power loss 491. Reactance of a capacitor of 1/π farad at 50 Hz is (a) 100 Ω (b) 10 Ω (c ) 50 Ω (d) 10 -2 Ω. 492. A d.c. circuit contains 10 Ω of resistance in series with 10H coil. The impedance of the circuit is (a) 10 Ω (b) 20 Ω (c ) 1 Ω (d) Zero. 493. The wavelength of ultraviolet rays is of the order of (a) 10-3 m (b) 10-6 m (c ) 10-8 m (d) between ‘b’ and ‘c’. 494. The wavelength of ultraviolet rays is of the order of (a) 10-3 m (b) 10-6 m (c ) 10 -8 m (d) between ‘b’ and ‘c’. 495. The interference fringes formed by a thin oil film on water are seen in yellow light of sodium lamp. We find the fringes (a) coloured (b) black and white (c)yellow and black (d) coloured without yellow. 496. One of the refracting surfaces of a prism of angle 30⁰ is silvered. A ray of light incident at an angle of 60⁰ retraces its path. The refractive index of the material of prism is (a) √3 (b) 3/ 2 (c ) 2 (d) √3. 497. In a Coolidge tube, the potential difference across the tube is 20 kV, and 10mA current flows through the voltage supply. Only 5% of the energy carried by the electrons striking the target is converted into X-rays. The X-ray beam carries a power of (a) 0.1 W (b) 10 W (c ) 2 W (d) 1 W. 498. In fusion, the percentage of mass converted into energy is about (a) 0.01% (b) 0.1 % (c ) 1% (d) 10%. 499. Air becomes conducting when the pressure ranges between (a) 76 cm and 10 cm (b) 10 cm and 1 cm -3 (c ) 1 cm and 10 cm (d) 10-4 cm and 10-7 cm. 500. Plate current in a diode depends (a) only on plate potential (b) only on area of plate (c) only on temperature of cathode (d) on plate potential and temperature of cathode. ANSWER SHEET PHYSICS-1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 b a a d c c c c a b a d a c d d a a a c 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 a c c b b c a c b b d d c c b b d b d a 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 a a b b b d a b a c d a a d a b a a d b 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 c b a d b b c c a b c b c d c d d c c c 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 c c c c c d a c a d c b d d c d d a c b ANSWER SHEET PHYSICS-2 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 a b b b a a c b c a a a d b c b a c c b 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 b a c c c c a b b a a b c c d c d a a d 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 a b d b a c d d a d c a d d d a c c c d 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 d a b b b a a b c d a a c c c b a a a b 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 d c c d c b c b d c d b b b d a c c b c ANSWER SHEET PHYSICS-3 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 d c d b d a c d d d c d c a b c c a d c 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 b c a a a d d d b d a a b c b d d b b a 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256 257 258 259 260 b c b c b d a b b d 261 262 263 264 265 266 267 268 269 270 271 272 273 274 275 276 277 278 279 280 281 282 283 284 285 286 287 288 289 290 291 292 293 294 295 296 297 298 299 300 ANSWER SHEET PHYSICS-4 Q. No. 251 252 253 254 255 256 257 258 259 260 261 262 263 264 265 266 267 268 269 270 Ans. a b c b d b c d a b c d c a c c c b c d Q. No. 271 272 273 274 275 276 277 278 279 280 281 282 283 284 285 286 287 288 289 290 Ans. a a d d d d d c d a d c c b c d a c c d Q. No. 291 292 293 294 295 296 297 298 299 300 301 302 303 304 305 306 307 308 309 310 Ans. C C A B A C c c b c c d c d b b d b c c Q. No. 311 312 313 314 315 316 317 318 319 320 321 322 323 324 325 326 327 328 329 330 Ans. b d c b a d b c a b b c d b a d c d c a ANSWER SHEET PHYSICS-5 Q. No. 331 332 333 Ans. Ans. b b b Q. No. 351 352 353 334 335 336 337 338 339 340 341 342 343 344 345 346 347 348 349 350 Ans. c d c Q. No. 371 372 373 d a b c c b a b b d b b d b a c c 354 355 356 357 358 359 360 361 362 363 364 365 366 367 368 369 370 Ans. c a b Q. No. 391 392 393 c c c b c c c c d d d d b b a c d 374 375 376 377 378 379 380 381 382 383 384 385 386 387 388 389 390 b d a d a b c c c d c b a b c c b 394 395 396 397 398 399 400 401 402 403 404 405 406 407 408 409 410 d a c b a a a c a c d d b d d c a a c c ANSWER SHEET PHYSICS-6 Q. No. 411 412 413 414 415 416 417 418 419 420 Ans. Ans. b a d a c b b d b b Q. No. 431 432 433 434 435 436 437 438 439 440 421 422 423 424 425 426 427 428 429 430 Ans. d b c d c c b b b a Q. No. 451 452 453 454 455 456 457 458 459 460 d d a d d b b c b a 441 442 443 444 445 446 447 448 449 450 a d d a c b b d b d 461 462 463 464 465 466 467 468 469 470 a c c a d c c a a a d b b b c c b d b b Q. No. 471 472 473 474 475 476 477 478 479 480 Ans. 481 482 483 484 485 486 487 488 489 490 491 492 493 494 495 496 497 498 499 500 d c a c d d d a a c a a d d c b b c c d c d b b b a a d c b