zone ocean
advertisement

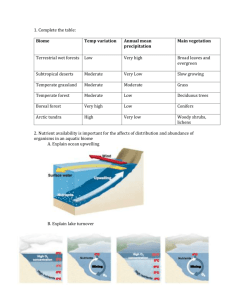
11.1 Worksheet Start-up: Complete 11.1 Section Review Questions 1. What is detritus made of, and why is it important to deep-sea organisms? 2. Why does the deep oceanic zone have no plants? 3. What are the producers of the open ocean? 4. Compare the map in Figure 11.3 to the one in Figure 1.8 on page 10. What type of winds drive the Gulf Stream current? The World Ocean and the Oceanic Zone 1. All of the oceans of the world are connected. 2. The 3 vertical zones apply to the depth of the zone. Define the following 3 zones using either the glossary or Chapter 10. a. photic--The top layer of the water in which light reaches through. b. aphotic—The layer below the photic zone where no light reaches. c. benthic—The very bottom layer of a body of water 3-5. Label the photic, aphotic, and benthic zones on the below diagram. 6-8. Color the photic zone yellow, the aphotic zone blue, and the benthic zone brown on the left diagram. 7-10. Using Figure 11.1 Label the neritic zone, the continental shelf, the oceanic zone, and the intertidal zone. 11-13. On the right diagram, color the intertidal zone brown, the continental shelf yellow, the neritic zone light green, and the oceanic zone light blue 14. Complete the color keys for each diagram. 7. intertidal 8. neritic 3. 9 oceanic photic 10. continental shelf 4. benthic 5. aphotic http://www.bio.miami.edu/ecosummer/lectures/lec_biomes.html photic zone intertidal zone aphotic zone continental shelf benthic zone neritic zone oceanic zone 15. Which zone is the largest? oceanic 16. What organisms are the only producers of the open ocean? phytoplankton 17. Define the following terms using the glossary a. plankton—a general term for microorganisms that float near the surface of the water b. phytoplankton—plankton that carry out photosynthesis and are the main producers in aquatic biomes. 18. Sketch a food chain of phytoplankton, zooplankton, and small fish. The arrow points in the direction of energy transfer. For example, if you were to sketch a shark eating a seal, the arrow would point from the seal to the shark. Phytoplankton zooplankton small fish 19. Which aquatic zone is the equivalent of the terrestrial desert? The oceanic zone 20. Define detritus. Tiny pieces of dead organic material that are food for organisms at the base of an aquatic food web 21. Based on what you know about the ocean zones, where do you think benthic organisms live? The bottom of the body of water (on the substrate—the sediment or dirt) 22. Where do oceans receive more radiation from the sun? What effects does this have on the properties of the water? The equator. The water is warmer and more saline (saltier due to higher evaporation) 23. Due to the influx of melted water from glaciers and polar ice in the polar regions, the water is colder and less saline than elsewhere. Low temperatures make the water more dense. 24. Define or describe ocean currents Water flow in the ocean in a characteristic pattern 25. Ocean currents are driven by wind and a result of these currents is that one mass of water can be very different from an adjacent mass of water. Fish and other organisms follow the patterns of the currents. 26. For years, people have been dumping waste into the oceans, believing that they would become diluted to safe levels. However, these pollutants do have very harmful effects. Name the act that banned the disposal of industrial wastes at sea. The Ocean Dumping Act (1988)